Analytical methods and controlling techniques for deformation and environmental influence of deep excavations in soft soils
-
摘要: 随着基坑规模日益增大以及邻近环境设施愈加复杂,合理评估并控制基坑变形及对周边环境影响成为软土基坑工程面临的重要挑战。基于理论分析与工程应用,对软土深基坑变形与环境影响分析方法及控制技术进行了系统研究。首先,在统筹考虑安全与经济的前提下,提出了软土深基坑环境保护等级和变形控制指标,为基坑周边不同类型环境设施的保护提供了依据。其次,系统建立了便于工程应用的基坑变形影响简化分析方法,并提出了基于土体小应变特性的基坑开挖对环境影响的计算分析方法以及确定全套小应变本构模型参数的实用方法,为复杂环境下深基坑环境影响分析提供了重要手段。同时,针对承压水降水影响难以准确量化评估的难题,提出了根据群井抽水试验反演确定关键水文地质参数并评估深层承压水降水对地层和环境变形影响的计算方法,满足了复杂地层承压水降水影响分析的工程需求。此外,还提出了包括支护结构与主体地下结构相结合、数字化微扰动搅拌桩加固、混凝土支撑主动变形控制、承压水控制超深隔渗帷幕等绿色、低碳、环境低影响的基坑变形控制新技术。成果在全国大量工程中成功应用,促进了软土深基坑工程全过程变形影响精细化分析和系统化控制技术的发展,为大规模地下空间的开发利用提供了技术支撑。Abstract: It has become a challenge to accurately estimate and reasonably control excavation-induced deformations as well as consequent influences in soft soil areas with the increasing excavation scale and complexity of adjacent facilities. The analytical methods and controlling techniques for the excavation-induced deformations and their subsequent influences have been systematically investigated. The environmental protection grade and deformation controlling standard for the excavations in soft soils are proposed considering synthetically both safety and economy aspects, which provides a basis for protection of different types of facilities close to the excavations. Furthermore, a simplified analysis method is established, helping engineers to get a quick estimation of excavation-induced influences. A sophisticated analytical method considering small strain stiffness of soils is introduced, and a practical method to determine the parameters of small strain constitutive model is proposed, making it possible to evaluate the excavation-induced deformations properly in engineering practices. To tackle the difficulty of quantifying the impact of aquifer pumping, a computational method is proposed to determine the key hydrogeological parameters and to evaluate the pumping-induced deformations based on the field group well pumping tests. Moreover, various green, low-carbon and low-environment-impact controlling techniques are proposed, including preliminary and permanent combination techniques, digital micro-disturbance soil mixing piles, automatically force-compensating concrete struts, ultra-deep soil mixing walls etc. The proposed methods and techniques have been successfully applied in many excavations, promoting further development of fine evaluation methods for the excavation-induced deformations and active protection techniques for complex facilities in urban areas and proactive providing technical support for the development and utilization of underground space.
-
0. 引言
近30 a来,中国城镇化建设进程不断深入,配套的高层建筑地下室、地下综合体、轨道交通与地下道路网等设施蓬勃发展,大规模地下空间开发利用带来了大量的深基坑工程。基坑降水和开挖过程不可避免地会打破原有土体的应力场平衡,使基坑周边地表及土体产生变形,并对邻近的既有设施产生不利影响。随着邻近地铁、隧道、市政管线及保护建筑等敏感环境设施的基坑工程越来越多,合理控制基坑变形及减小对环境设施的影响已逐渐成为基坑工程面临的首要问题。与此同时,一些具有特殊要求的建(构)筑物对于基坑工程引起的变形要求更加严苛,如上海某重大科技基础设施的超深基坑邻近磁悬浮线路,为保证磁浮的安全运营规定基坑施工引起的桥墩变形小于2 mm,对变形控制提出了更高的要求。另外,基坑工程的规模和深度也不断增大,如南京江北新区一期工程,包含24个地块,基坑总面积约30万m2;上海苏州河深隧调蓄工程设8个工作竖井,挖深达45~72 m[1],进一步增加了变形控制的难度。
软土土质松软,土体强度及刚度较小,可以提供的水平抗力及抵抗变形的能力较小,导致软土基坑的围护结构和周边土体变形往往较大,使得基坑周边环境设施面临严峻考验。而随着基坑周边环境类型日益复杂,制定合理的变形控制标准,既能为设计、施工和管理部门提供明确的控制指标,又能保证安全并减小资源浪费。另一方面,评估基坑变形和环境影响需要把基坑和周边设施作为一个整体,要能够充分考虑基坑本体、周边土体和环境设施的相互影响,分析方法既要具有理论基础也要易于工程应用。由于软土地区地下水位高,大多存在承压含水层且分布复杂,随着基坑深度不断增大,控制抽降深层承压水引起的基坑变形和环境安全成为软土深基坑工程面临的又一挑战,尤其是含水层无法隔断时抽降承压水对基坑及邻近环境设施变形的影响不容忽视[2]。基坑变形控制贯穿于围护结构施工、基坑降水和基坑开挖全过程,随着工程需要的日益多样化,研发绿色低碳、环境低影响的变形控制新技术和智能化新装备的需求也日益迫切。
针对上述挑战和工程需求,笔者和团队聚焦软土深基坑变形控制指标、分析方法与控制技术3个方面,通过二十余年的理论研究和实践探索,提出了软土深基坑环境保护等级和变形控制指标,建立了基坑变形与环境影响的简化分析方法和基于土体小应变本构模型的有限元分析方法,形成了根据群井抽水试验反演确定关键水文地质参数并评估深层承压水降水对地层和环境变形影响的计算方法,系统提出了基坑实施全过程变形控制系列新技术。成果在全国大量工程中成功应用,促进了软土深基坑工程全过程变形影响精细化分析方法和系统化控制技术的深入发展,为大规模地下空间的开发利用提供了技术支撑。
1. 软土深基坑变形控制指标
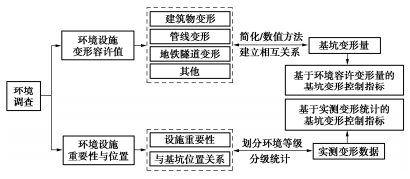
基坑工程变形控制设计应在综合考虑安全性和经济性的双重要求下,制定合理的变形控制指标。工程上确定基坑变形控制指标通常采用两种技术路线(图 1):一种是通过环境设施的容许变形量来确定变形控制指标;另一种则是基于大量工程实测数据通过统计分析得到变形控制指标。
1.1 基于环境设施容许变形量的基坑变形控制指标
基坑周边常见的环境设施一般包括建筑物、地铁隧道、地下管线等,对不同类型的环境设施的容许变形量进行分析,然后根据设施可以承受的容许变形量提出基坑变形控制值。
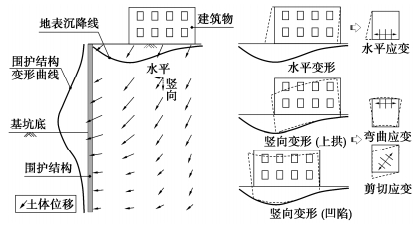
(1)建筑物容许变形
如图 2所示,当建筑物位于基坑变形影响范围内时,建筑物上不同位置处受土体变形而产生的位移也各不相同,将在建筑物内部产生附加应力,当附加应力达到一定程度时,建筑物将发生开裂。理论上砌体及混凝土墙的裂缝一般与拉应变有关,拉应变大小是决定其是否开裂和裂缝大小的关键参数。对于砖砌体而言,裂缝发生时的临界拉应变在0.05%~0.1%的范围;对于钢筋混凝土结构而言,裂缝发生时的临界拉应变在0.03%~0.05%的范围;且上述临界拉应变在数值上较受拉构件发生拉伸破坏时对应的拉应变要大得多[3]。
由于影响因素繁多,使得建筑物因变形而受损的机理非常复杂,目前关于建筑物容许变形量的有关标准都是建立在已有建筑物实测变形及损坏现象观测的基础上。建筑物在自重作用下主要产生沉降,而其水平向位移很小可以忽略,因此这种情况下建筑物的损坏主要与角变量及挠度比相关联。Bjerrum等[4]总结了根据观测资料得出的建筑物损坏与角变量之间的关系。除了用角变量外,还可以用差异沉降量和总沉降量来表示建筑物的容许沉降量,且差异沉降量和总沉降量更加直观,更易为工程师接受[5-6]。笔者和团队收集分析了上海地区基坑周边不同类型建筑物受基坑影响的实测数据[7],发现对于钢筋混凝土框架结构建筑,当建筑物总沉降量超过60 mm时,建筑物出现了不同程度的损坏;而对于砖混结构建筑,当建筑物总沉降量为40 mm以上时,绝大部分建筑物出现了不同程度的损坏。这也可以作为软土地区由开挖引起的建筑物容许沉降量的一个参考。对于历史保护建筑等重要建筑物,也可通过房屋质量检测评估其抵抗变形的能力,在此基础上提出容许变形量。
(2)地下管线容许变形
城市区域市政道路下管线分布密集,数量和类别众多,管线年代和状况也是千差万别。管线一般由管节和接头两部分组成。管节在内外荷载的作用下,内部产生环向应力、纵向应力以及径向应力。其中,径向应力主要由管内外的压力差引起,小于环向及纵向应力。在基坑施工影响范围内的管线由于周围土体的变形会产生不均匀的沉降、发生弯曲变形,在管道内产生纵向应力,而当应力达到相应材料的安全标准时管线将发生破坏。管节破坏模式大致可分为管壁破坏、管壁压屈、扰曲、纵向应力屈服以及构造破坏等。接头是管节连接的关键节点,对变形相比管身更为敏感,其力学特性则主要由接头的拔出及转动特性决定,即接头允许发生的相对错动和相对转角。
基坑开挖引起的土体差异沉降是导致管线破坏的主要原因,多表现为纵向弯矩过大引起的管节断裂,而对于非刚性连接的管线差异沉降导致的管线接头张开也普遍存在。对于基坑影响范围内的市政管线的变形容许值,国内尚无统一的指标要求,实际工程中可以根据管线类型从管身受弯应力、管线累计沉降、沉降速率、差异沉降、接头张开允许值指定相应的控制指标。工程实践表明压力管(如燃气管)和大直径管(如给水主管)对附加变形最为敏感,损坏后造成的后果最为严重,因此需要对此类管线予以特别的关注。部分规范标准给出了一些类型管线的沉降及差异沉降以及接口转角的控制值[8-9],可作为确定管线容许变形的参考。
(3)地铁隧道容许变形
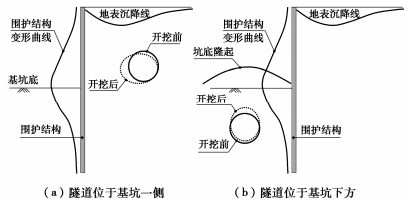
基坑周边不同位置处隧道的变形机理与模式也存在显著差异,图 3为位于基坑一侧和下方的地铁隧道受基坑开挖影响示意图。对于侧卧隧道(位于坑底标高以上),基坑开挖后,隧道整体向基坑开挖方向移动,随着坑外土体变形产生竖向沉降,同时隧道结构在竖向发生了压缩而水平方向被拉伸,表现出横鸭蛋形状的收敛特性。而对于下卧隧道,由于基坑底部土体在卸载作用下发生竖向隆起,导致隧道产生上抬,隧道结构在竖向被拉伸,在水平向被压缩,呈现出竖鸭蛋形状的收敛特性。
软土盾构隧道通常是由钢筋混凝土管片在环向和纵向通过螺栓连接而成的非连续体。在基坑开挖变形影响下,隧道沿纵向发生不均匀沉降,隧道结构内部产生附加弯矩和剪力引起纵向的变形。纵向变形主要表现为管片开裂和错台,通常情况下两者同时发生。错台和环间张角的不断增大将使相邻管片的密封垫之间发生相对错动,最终导致环间密封垫脱开,结构防水失效,引起隧道内发生漏水,严重时甚至发生漏泥、漏砂。同时沿着纵向较大的差异沉降,也将影响列车行驶的安全与舒适性。
随着中国轨道交通的蓬勃发展,各地区相继出台了相关隧道变形的控制标准[10-12],通过规定施工引起的隧道绝对沉降量、水平位移量、隧道变形曲线的曲率半径、相对弯曲、隧道收敛、裂缝宽度、道床脱空量等指标来保证基坑实施期间隧道结构的安全。
(4)基于环境设施容许变形量确定基坑变形控制指标
在确定了基坑周边环境设施的容许变形量后,需评估基坑开挖引起周边环境设施的附加变形,建立基坑变形与其周围环境设施附加变形的相互关系,并根据基坑周边建(构)筑物、管线和地铁隧道等不同环境设施的容许变形量反过来控制基坑本身的变形量。
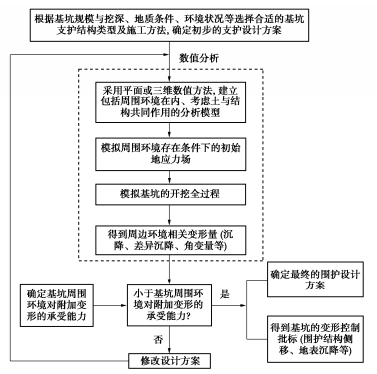
图 4为基于环境设施容许变形量确定基坑变形控制指标的具体流程。从目前的分析手段来看,数值方法能够考虑基坑开挖与基坑周围环境设施的相互作用,是工程中较为常用的分析方法。以采用数值分析方法为例,一般首先需考虑是采用平面分析方法还是三维分析方法,然后根据初步的基坑设计方案建立包括基坑本身及基坑周围环境在内的整体分析模型,采用合适的本构模型及计算参数(参考本文2.2节),采用符合实际情况的边界条件,在模拟基坑周围环境存在条件下的初始地应力场后,对基坑开挖进行全过程的模拟,得到基坑周围环境的有关变形量。然后将这个计算变形量与基坑周边不同环境设施容许变形值进行比较,如果计算得到的变形量小于容许限值,则基坑的设计方案能满足环境保护要求,否则需调整设计方案(例如采用刚度更大的围护结构,增加支撑道数或刚度,进行地基加固等),直到所得到的基坑周边环境设施的计算变形量小于其容许的变形值。通过这样的调整,得到了基坑本身的变形如围护结构的侧移、墙后地表沉降等,即可作为基坑变形的控制指标。
1.2 基于实测统计的基坑变形控制指标
基于环境设施容许变形量确定的基坑变形控制指标针对的是某一特定的基坑工程,由于不同基坑工程周边环境设施类型和其变形承受力大相径庭,由此得出的变形控制指标并不具普遍性,导致不同的基坑项目都需要单独确定变形控制指标,实际使用并不便利。
目前软土地区已有大量基坑工程得以成功实施,这些基坑包括了各种复杂环境条件,这些工程的成功实施说明其变形控制基本能保证基坑周边环境条件的安全。因此,根据大量已成功实施的基坑工程的统计资料来确定基坑的变形控制指标不失为一种有效的方法。这里以上海软土地区基坑工程实践为例,介绍根据大量已成功实施的基坑案例的统计分析来确定基坑变形控制指标的实用方法。基坑的变形控制与基坑周边环境条件密切相关,因此这里首先定义基坑的环境保护等级,然后根据统计资料来确定变形控制指标。
(1)基坑环境保护等级
基坑工程环境保护等级的划分需要考虑的要素是环境保护对象的重要性程度及其与基坑之间的距离。环境保护对象的重要性程度主要考虑两类:一类是重要性程度非常高,如优秀历史建筑、有精密仪器与设备的厂房、采用天然地基或短桩基础的医院、学校和住宅等重要建筑物、轨道交通设施、隧道、防汛墙、原水管、自来水总管、煤气总管、共同沟等重要建(构)筑物或设施,其损坏往往会对社会生活产生巨大的影响和经济损失;另一类是重要性程度较高,如较重要的自来水管、煤气管、污水管等市政管线、采用天然地基或短桩基础的建筑物等,其损坏往往会对人们的生活产生一定程度的影响和经济损失。
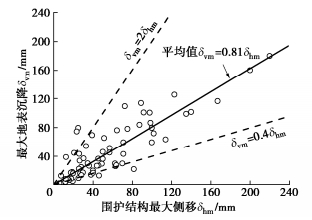
环境保护对象的变形量和它与基坑之间的距离以及坑外地表沉降的性状密切相关。Clough等[13]根据大量基坑统计资料得到的软到中等硬黏土基坑地表沉降包络线表明,在(0~0.75)H(H为基坑开挖深度)的范围内,地表沉降最大;在(0.75~2.0)H的范围内地表沉降逐渐衰减。Hsieh等[14]根据若干基坑的实测资料建议的基坑墙后地表沉降曲线表明,最大地表沉降发生于墙后0.5H处;在(0~1.0)H的范围内,地表沉降较大;在(1.0~2.0)H的范围内地表沉降逐渐减小;而在(2.0~4.0)H的范围内地表沉降由较小值衰减到可忽略的程度。图 5为笔者和团队统计的上海地区若干基坑的墙后地表沉降情况,其近似的地表沉降分布曲线与Hsieh等[14]建议的地表沉降曲线相似,即最大地表沉降发生于(0~1.0)H的区域;在(1.0~2.0)H的范围内地表沉降逐渐减小;而在(2.0~4.0)H的范围内地表沉降由较小值衰减到可忽略的程度。综合上述有关研究,将1.0H、2.0H和4.0H作为划分基坑环境保护等级时建(构)筑物所处位置的分界点。
根据上述周边环境的重要性程度分类和周边环境与基坑距离的分界点的不同组合,给出了如表 1所示的3种环境保护等级的定义。
表 1 基坑环境保护等级的定义Table 1. Definition of environment protection grade环境保护对象 保护对象与基坑的距离 环境保护等级 优秀历史建筑、有精密仪器与设备的厂房、采用天然地基或短桩基础的医院、学校和住宅等重要建筑物、轨道交通设施、隧道、防汛墙、原水管、自来水总管、煤气总管、共同沟等重要建(构)筑物或设施 s≤H 一级 H < s≤2H 二级 2H < s≤4H 三级 较重要的自来水管、煤气管、污水管等市政管线、采用天然地基或短桩基础的建筑物等 s≤H 二级 H < s≤2H 三级 注:H为基坑开挖深度,s为保护对象与基坑开挖边线的净距。 (2)基于实测统计的基坑变形控制指标
收集了上海地区若干个已成功实施的基坑工程的数据,根据表 1的分类标准对所收集的基坑进行分级,其中环境保护等级为一级的基坑有37个,环境保护等级为二级的基坑有46个。
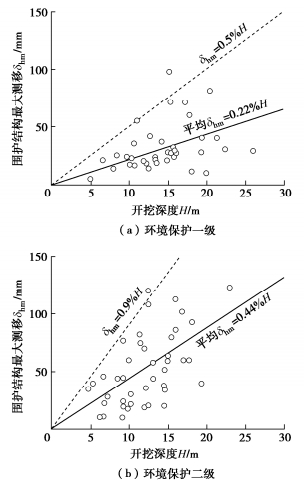
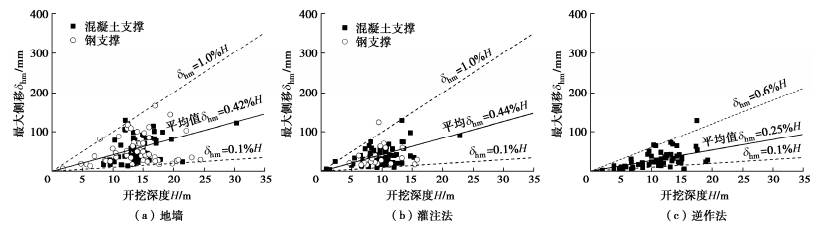
图 6为环境保护等级为一、二级基坑围护结构最大侧移与基坑挖深H之间的关系。从图 6中可以看出,围护结构的最大侧移随着开挖深度的增大呈不断增加的趋势。一级基坑围护结构的最大测移值一般小于0.5%H,平均值为0.22%H;二级基坑围护结构的最大侧移一般小于0.9%H,平均值为0.44%H。实测数据还表明,在上述变形条件下基坑周围的建(构)筑物均处于正常使用状态,因此将围护结构实测侧移平均值0.22%H和0.44%H分别定义为环境保护等级为一、二级基坑围护结构实测变形控制指标。
工程师在制定基坑方案时通常根据计算值进行设计,为方便工程设计之用,统计了基坑实测围护结构最大侧移与计算值之间的关系。结果表明,实测的围护结构最大侧移往往大于计算值,环境保护等级为一级的基坑,实测值约为计算值的1.2倍;二级基坑实测值约为设计值的1.5倍[7]。基于实测值统计得出的一级、二级环境保护等级围护结构变形控制值分别为0.22%H和0.44%H,考虑实测值与计算值的倍数关系,对应一级和二级基坑设计变形控制指标分别定义为0.18%和0.3%。而三级基坑的变形控制指标则参考了上海地区地铁基坑工程关于基坑变形控制小于0.7%H的规定。据此,将环境保护等级为一级的基坑围护结构设计变形控制指标确定为0.18%H,二级基坑取为0.3%H,三级基坑取为0.7%H。
根据收集的多个具有地表沉降的基坑工程案例,建立墙后最大地表沉降δvm与围护结构的最大侧移δhm的关系,根据围护结构的最大侧移估算墙后地表的最大沉降。图 7为实测最大地表沉降δvm与围护结构最大侧移δhm之间的关系,可以看出最大地表沉降δvm基本介于0.4δhm~2.0δhm范围内,最大地表沉降平均值约为的围护结构最大侧移的80%[15]。据此,根据上述围护结构设计变形控制指标,对应于环境保护等级为一、二和三级基坑的墙后地表最大沉降设计控制指标分别为0.15%H,0.25%H,0.55%H。
表 2为根据上海地区大量基坑案例实测数据按上述步骤统计分析得出的不同保护等级下基坑变形设计控制指标。表 2中的变形控制指标使用简单,无需确定基坑周围环境对附加变形的承受能力及基坑开挖对周围环境的影响程度,具有较广泛的适用性。参与统计的这些基坑都已成功实施,周围建(构)筑物均处于正常工作状态,因此表中的变形控制指标基本上能够保证基坑周边环境安全。这一成果现已纳入上海市《基坑工程技术标准》[16]和国家标准《建筑地基基础设计规范》[6]。
表 2 基坑变形设计控制指标Table 2. Deformation control criterion for deep excavation design基坑环境保护等级 围护结构最大侧移 坑外地表最大沉降 一级 0.18%H 0.15%H 二级 0.3%H 0.25%H 三级 0.7%H 0.55%H 针对环境保护等级为一级的基坑工程中的特殊情况,即邻近地铁隧道的基坑,笔者和团队还进一步收集了基坑开挖深度大于12 m且与邻近地铁距离小于10 m的基坑实测变形数据,统计分析表明其围护结构的平均最大侧移约为0.14%H,此值可作为邻近地铁的基坑工程围护结构变形控制标准;考虑最大地表沉降平均值约为围护结构最大侧移的80%,则最大地表沉降的控制标准约为0.1%H。这里的围护结构最大侧移和地表沉降控制标准与上海地区的《城市轨道交通结构安全保护技术标准》[10]中关于特级环境保护等级(即基坑开挖深度大于12 m且与邻近地铁的距离小于10 m的基坑)的变形控制标准一致,可作为邻近地铁隧道基坑工程的变形控制指标。
2. 软土深基坑开挖环境影响分析
基坑开挖对周边环境影响的分析方法主要有两种:简化分析方法和数值分析方法。简化分析方法以实际工程案例的统计规律为基础,使用简单,易于被工程师掌握,但需要大量的实际工程案例及实测数据作为支撑。数值分析方法(以有限元方法为例)可以综合考虑地质条件、支撑布置、降水、开挖过程以及环境设施分布等诸多因素,是模拟基坑开挖、预测基坑变形及对周边环境设施影响的重要手段。
2.1 简化分析方法
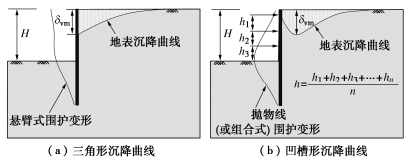
开挖引起的地表沉降差是造成基坑周边环境设施变形或损坏的主要原因,简化分析方法不考虑基坑与周边建(构)筑物的相互作用,近似认为基坑周边的建(构)筑物所在位置的地表沉降值即为该位置建(构)筑物的沉降值,以此来间接评估基坑开挖对基坑周边环境设施的影响。简化分析一般可分为3个步骤,即先确定基坑开挖引起的地表沉降,然后分析得到由基坑变形引起的环境设施的附加变形,最后根据不同类别设施的损坏准则判别其损坏程度。因此,确定基坑开挖引起的地表沉降曲线是简化分析方法的关键。
软土地区基坑工程多采用多道支撑的桩墙式支护结构,在浅部土体开挖时围护结构变形较小,后续施工也一般是先支撑后开挖,围护结构变形逐渐向深层发展,因此软土桩墙式支护基坑的地表沉降形态主要表现为凹槽形,如图 8所示。以上海地区基坑工程为例,笔者和团队在大量实测变形数据的统计分析的基础上,对凹槽形沉降曲线进行了修正[14],提出了适用上海软黏土地层的地表沉降曲线(如图 5所示的折线ABCD)。
得到沉降曲线后还需要进一步确定最大地表沉降δvm,其值可以通过数值方法计算或是基于统计分析得到经验关系进行估算。采用经验关系估算需要将收集的实测数据进行分类,按照围护结构类型、施工方法及基坑形状等分别进行了统计分析,建立不同围护结构最大侧移δhm与开挖深度H的经验关系,如图 9所示。这样根据最大地表沉降δvm与最大侧移δhm间的比例关系(图 7)就能得到最大地表沉降值及完整的地表沉降曲线。
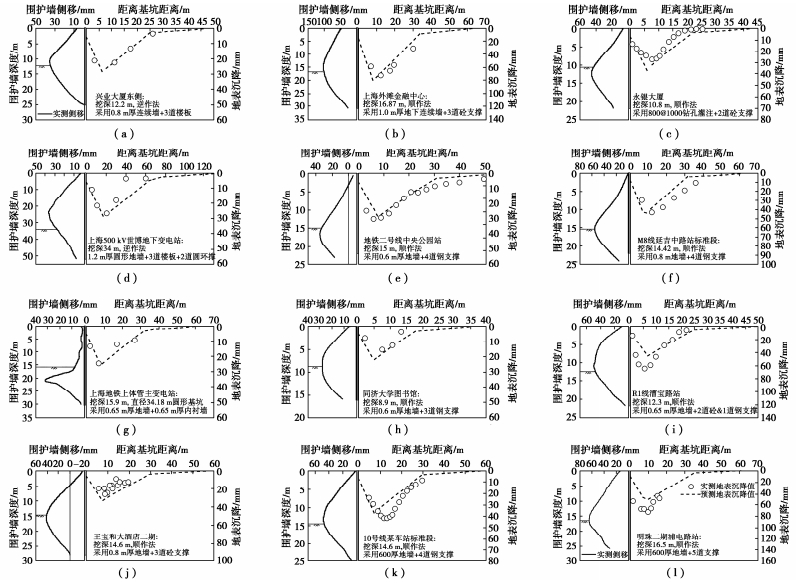
将上述简化分析方法中建立的围护墙与地表沉降的关系在实际工程项目中进行应用,通过实测的围护墙变形将预估墙后地表沉降并与实测的结果进行了对比,如图 10所示。可以看出,预估地表沉降曲线与实测值吻合较好,说明在上海地区采用上述所示经验关系能够较好地评估基坑开挖引起的地表沉降。
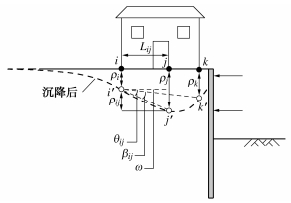
获得完整地表沉降曲线后,还需要进一步评估环境设施的变形。以建筑物为例,如图 11所示,建筑物发生刚体转动时并不会引起建筑物构件的扭曲变形,相关构件不会发生开裂破坏。而与建筑物构件扭曲或开裂直接相关的参数为角变量β,因此预估基坑开挖引起的建筑物的附加变形主要是确定建筑物的角变量β,可采用下式计算:
βij=θij−ω=δij/Lij−ω=(δi−δj)/Lij−ω。 (1) 式中:δi和δj分别为相邻基础处的附加总沉降,可以根据地表沉降曲线直接确定;Lij为相邻基础的距离;ω为建筑的刚体转动量。
上海兴业银行大厦基坑位于市中心区域,邻近多栋历史保护建筑。基坑开挖深度12.2~14.2 m,采用全逆作法施工,紧邻保护建筑侧采用1 m厚两墙合一的地下连续墙。设计时采用简化分析方法预估基坑开挖对邻近华东院大楼的影响,计算出建筑物不同位置(间隔1~4)的角变量β分别为1/2100,1/1100,1/1100和1/10600。考虑华东院大楼为上海市优秀保护建筑,其容许的角变量可按β≈1/500进行控制,可以看出简化方法预估的不同位置建筑物最大角变量均小于其容许值,说明该设计方案能够控制基坑开挖阶段建筑物的安全。施工过程中对该建筑物沉降进行了监测,实测的该建筑物在基坑开挖阶段产生的最大角变量为1/1200,与简化方法预估结果较为接近。
2.2 基于小应变本构模型的有限元分析方法
相较简化分析方法,有限元分析方法在分析复杂环境条件下基坑变形以及对周边环境影响方面具有明显优势,而选择合适的土体本构模型和计算参数是有限元分析的关键因素。
笔者和团队系统比较了不同类型本构模型在基坑开挖分析中的适用性[17],发现硬化类小应变本构模型具有能考虑软黏土应变硬化、其刚度依赖于应力历史和应力路径等特点,同时还能考虑剪切模量在小应变范围内随应变衰减的行为。相较于传统的弹性、理想弹-塑性等本构模型能给出更为合理的围护墙侧移及墙后土体变形,适用于复杂环境条件下基坑周边环境变形影响分析。
(1)HS-Small本构模型及参数
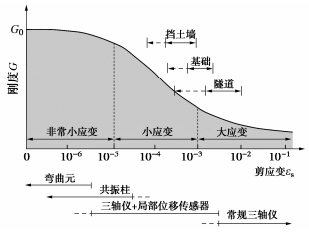
不同类型的岩土工程中土体剪应变大致可以分为3个范围:非常小应变(小于10-5)、小应变(10-5~10-3)和大应变(大于10-3)[18]。如图 13所示,基坑工程周边的土体大都位于小应变范围内,表现出初始剪切刚度较大、刚度随着应变增加而急剧减小的非线性特征。
近年来小应变本构模型的研究取得了长足的发展,但其中大部分模型理论复杂、参数众多,能够在工程中应用的较少。而HS-Small小应变硬化模型[19]物理意义明确、参数容易确定,逐渐受到学术和工程界的广泛关注并在工程设计得到大量应用。HS-Small本构模型参数包含了11个HS硬化模型参数和2个小应变参数,如表 3所示。参数大致分为强度指标、刚度指标、经验参数和小应变参数四类[20],由于篇幅所限,各参数获取方法本文不再赘述。
表 3 HS-Small本构模型参数及获取方法Table 3. Determination of parameters of HS-Small model参数类型 参数名称 获取方法 HS模型参数 强度参数 有效内聚力c′ 三轴固结试验有效应力莫尔圆 有效内摩擦角φ′ 剪胀角ψ 三轴试验或经验公式 破坏比Rf 三轴试验 刚度参数 参考切线模量Erefoed 标准固结试验 参考割线模量Eref50 三轴排水试验 参考卸载再加载模量Erefur 三轴排水试验 经验参数 静止侧压力系数K0 现场实测或经验公式 幂指数m 经验公式 泊松比νur 经验值,νur=0.2 参考应力pref 经验值,pref=100 kPa 小应变参数 刚度参数 参考初始剪切模量Gref0 共振柱试验或配有弯曲元及局部位移传感的三轴试验 参考剪应变γ0.7 (2)HS-Small本构模型全套参数确定方法
尽管通过试验可以获得该模型的全套参数,但相关试验周期较长并需要具有相当理论和试验基础的专业技术人员进行试验数据分析,因此对于一般工程项目来说,完全采用试验方法获得HS-Small模型的全套参数显然不现实,如能和常规岩土工程勘察报告中的基本参数建立联系,可以提高使用小应变本构模型进行数值分析的便利性。
以上海软黏土为例,笔者和团队在4个不同项目场地采集了上海地区典型的②~⑥层黏土层土样,进行了标准固结、三轴固结排水(不排水)试验以及室内共振柱试验,并进行了现场波速测试。对4个场地的试验结果进行了统计分析,建立了HS-Small全套参数与常规勘察报告中基本参数的经验关系。
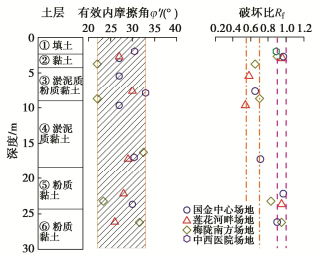
a)强度参数c′、φ′、Rf
有效内摩擦角φ′和破坏比Rf沿深度变化如图 14所示。内摩擦角φ′大都分布在22°~33°的范围内。按照临界状态理论,p′ - q平面内破坏线应通过原点,即有效黏聚力c′=0,在进行有限元计算时,为了方便计算可输入一个大于零的较小的数值作为计算参数。
从图 14中还可以看出第②、⑤、⑥层土的Rf值明显大于较软的第③、④层土。从数值上看,第②、⑤、⑥层土的Rf大都分布在0.9~0.97。而含水率及孔隙比较大的第③、④层土体的Rf约为0.54~0.71。其原因可能与土样破坏模式相关,第②、⑤、⑥层土样在三轴排水试验中产生了明显的破坏面,土体破坏后偏应力不随轴向应变的增大而增大,偏应力的破坏值与渐进值十分接近,因此得出的破坏比较大。而③、④层土样在试验中产生鼓胀,没有明显破坏面,即使轴向应变超过了15%,偏应力仍随应变的增大而增大,偏应力破坏值远小于其渐进值,因此得出的破坏比较小。根据上述试验结果,第②、⑤、⑥层黏土层的Rf统一取为0.9,第③、④层土体的Rf统一取为0.6。
b)刚度参数Erefoed、Eref50、Erefur
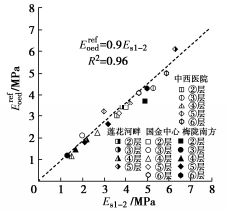
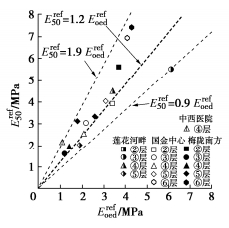
一般岩土工程勘察报告中对于土体刚度参数往往只提供压缩模量Es1-2,基于4个场地土样的室内试验结果建立了HS模型中刚度参数Erefoed、Eref50、Erefur与Es1-2的经验关系。由标准固结试验得到的参考切线模量Erefoed与压缩模量Es1-2如图 15所示。对试验数据进行拟合分析,得出Erefoed=0.9Es1−2(拟合优度R2=0.96)。这说明不同土层两模量之间的比例关系基本相同,可统一取Erefoed为0.9 Es1-2。
图 16为Eref50与Erefoed的关系曲线,Eref50/Erefoed的比值分布在0.9~1.9,这与天津软土、奥地利Lacustrine黏土等典型软黏土的比例关系相近,但明显小于较硬的台北粉质黏土的2.8倍和英国Gault黏土的3.5倍[21]。仅对第③和④层土的试验数据进行拟合时,Eref50≈1.2Erefoed(R2=0.91),加入较硬的第②、⑤、⑥层试验数据后,Eref50仍为1.2倍的Erefoed。综上所述,②~⑥层土统一取Eref50=1.2Erefoed。
图 17为Erefur与Eref50的关系曲线,试验得到的Erefur/Eref50比值分布在3.6~9.3。总体上,较为软弱的③层、④层土的Erefur/Eref50比值较小,约为5.6~9.3,该数值大于图中所示的Lacustrine黏土[22]和台北粉质黏土[23]。而较硬的第②、⑤、⑥层土样Erefur/Eref50比值较小,约为3.6~6.5。由于试验数据相对有限,对于土质较软弱的③、④层土近似取平均值Erefur=7Eref50;而对于较硬的第②、⑤、⑥层土,可近似取Erefur=5Eref50。
c)小应变参数Gref0、γ0.7
笔者和团队基于某基坑工程案例对HS-Small模型参数的敏感性进行了研究,发现围护墙最大侧移和墙后地表最大沉降对小应变参数Gref0、γ0.7最为敏感。因此,合理获取小应变参数对基坑工程周边环境变形分析至关重要。
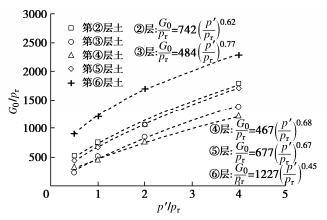
对各层土进行原位波速测试及室内共振柱试验。在室内共振柱试验中通过安装在仪器顶部和底座上的弯曲元测量土样内剪切波速,得到不同应力水平下的土层初始剪切模量G0,根据剪切模量G0与应力水平的关系得到参考压力下Gref0;并通过共振柱试验得到剪切模量随剪应变递减曲线得到参考剪应变值γ0.7。将弯曲元测量得出的剪切波速根据公式G0=ρv2s转化为土体的剪切刚度(其中ρ为土体密度,vs为剪切波速),得出如图 18所示的初始剪切刚度G0和平均有效应力p′的关系曲线。从图 18中的关系曲线可以看出各土层G0均随着p′的增加而增大。相同压力下⑥层的刚度最大,②、⑤层土刚度接近,②层土略大于⑤层土,而③、④层刚度远小于其他土层,尤其以④层土最为明显。
采用归一化公式G0pr=Sf(e)(p′pr)n对试验结果进行拟合,其中,f(e)为关于孔隙比e的经验关系,p′为土的平均有效应力,pr为参考应力,通常取1 kPa,S和n为无量纲经验参数[24]。可以看出上述归一化公式能够较好地描述初始剪切模量和固结压力的关系。第⑥层土的n值较其他土层小,约为0.45;其他土层的n值约为0.62~0.77。HS-Small模型中小应变参数Gref0为围压100 kPa时土体的初始剪切模量,从拟合公式可计算得出②、③、④、⑤、⑥层土的Gref0值分别为76,51,45,66,120 MPa,而该场地Erefur值分别为21.4,15.6,16.8,26.1,24.6 MPa,因此对应的Gref0/Erefur比值分别为3.6,3.3,2.7,2.5和4.9。
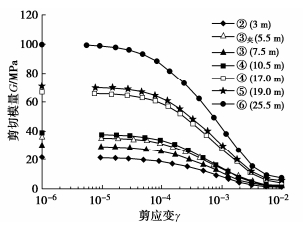
图 19为各层试样在原位应力下剪切刚度G随剪切应变γ的递减关系曲线,曲线由初始剪切刚度G0和剪切刚度随剪应变递减曲线两部分组成。初始剪切刚度G0由弯曲元试验获得,弯曲元试验引起的最大剪应变约为10-6~10-5,本文采用γ =10-6作为弯曲元试验产生的剪应变。
从图 19中可以看出,共振柱试验测得最小剪应变约为10-5,对应的最大剪切刚度与弯曲元试验结果接近。γ =10-6~10-5范围内,G0基本保持不变,因此,γ =10-6~10-5可认为是该递减曲线的平台段的终点。这与对Chalk黏土、伦敦黏土以及Bothkennar黏土三种不同类型的土体进行的小应变试验结果一致,虽然3种土体刚度大小不同,但当竖向应变εa增大至(2~3)×10-5时,G0开始迅速减小[25]。本文试验结果显示,当剪应变在γ =10-4~10-3的范围内,G0迅速减小,而当应变继续增大至10-3,各土层刚度差异逐渐变小。由此看见,土体刚度即使在小应变范围内仍表现出明显的非线性,刚度大小不仅与土的应力状态有关,还与应变大小密不可分。
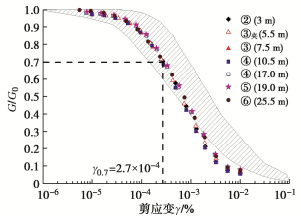
将不同土层的剪切刚度G除以初始剪切刚度G0进行归一化处理,如图 20所示。虽然不同土层的剪切刚度大小不同,但归一化后不同土层G/G0随剪应变变化曲线却基本相同。由图 20可知,当γ=10-5时,G≈0.97G0,当γ=10-4时,G≈0.87G0,当γ=10-3时,G≈0.41G0,而当γ增大至0.01时,剪切刚度G不及初始刚度G0的十分之一。常规三轴试验能够测量的最小应变值大于0.001,并且受到诸多测量误差的影响,从上述试验结果来看,由常规试验得到的土体刚度仅为初始刚度G0的40%左右。有限元计算如采用常规试验的结果将会大大低估土体抵抗变形的能力,导致在围护设计中造成不必要的浪费。HS-Small模型中,将G=0.7G0对应的剪应变定义为γ0.7,由此可见,上海典型黏土层γ0.7≈2.7×10-4。图 21中还给出了全球21种黏性土剪切刚度随应变的变化规律,覆盖了从正常固结土到超固结土的各类土样。将试验数据归一化后发现,这些不同类型黏性土G/G0随剪应变的变化规律非常相似,如图 21中阴影区域所示,对应的参考剪应变γ0.7≈1.5×10−4~1.0×10−3,在无试验数据的情况下,也可以参照本图选取γ0.7的数值。
通过对试验数据的统计分析,提出了由常规岩土勘察报告提供的压缩模Es1-2确定刚度参数Erefoed、Eref50、Erefur及小应剪切模量Gref0的实用方法,给出了Rf,m,νur,γ0.7等经验参数的取值范围,首次提出了上海典型土层的小应变本构模型的全套参数,如表 4所示,并已经纳入上海市《基坑工程技术标准》[16],可为小应变本构模型参数的取值提供借鉴和参考。
表 4 HS-Small模型主要参数取值方法Table 4. Detemination of key parameters for HS-Small model土层 Erefoed/kPa Eref50/kPa Erefur/kPa Gref0/kPa γ0.7/10-4 νur m Rf ② 0.9Es1 - 2 1.2Erefoed 6Erefoed (2.5~4.9)Erefur 1.5~9.0 0.2 0.8 0.9 ③ 8Erefoed 0.6 ④ 0.6 ⑤ 6Erefoed 0.9 ⑥ 0.9 将基于小应变本构模型的有限元分析方法和前文所述模型参数在邻近浅基础建筑、桩基建筑、地铁隧道等不同类型环境设施的基坑工程中应用,预估的基坑围护和周边设施变形与实测数据吻合度高[26-32],为敏感环境下变形与环境影响控制的设计提供了重要的指导作用。
笔者和团队还将这一方法用于超深基坑的变形分析,图 21为上海深隧排水系统工程试验段苗圃基坑剖面图,基坑直径30 m,挖深约56.3 m,采用1.5 m厚地下连续墙围护,深度约103 m。地下连续墙采用套铣接头,地墙垂直度约为1/1000。苗圃竖井基坑采用顺作法施工,水平向设一道压顶梁、五道环梁支撑体系,基坑整体分7层开挖至基底,浇筑底板后再自下而上施工内衬墙。
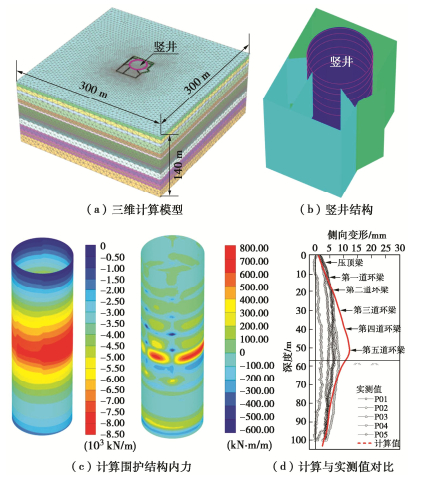
采用三维有限元对超深圆形基坑开挖性状进行分析,分析模型如图 22(a)所示,土体采用HS-Small小应变本构模型模拟。根据地勘察报告和前文所述方法确定典型黏土层的计算参数;而对于深部砂土层,采用基于工程实测数据反演分析得到的经验公式确定相关参数[30]。计算时黏土采用不排水分析,砂土采用排水分析。
图 22(b),(c)分别为开挖至基底时地墙的环向轴力和竖向弯矩分布云图。单位宽度墙体计算最大环向轴力为8389 kN、最大竖向弯矩值仅为753 kN·m/m,与通过钢筋实测应力反算结果相近。这表明圆形基坑结构受力状态以环向轴力为主竖向受弯为辅,开挖过程中分幅施工的地墙表现出很好的圆形结构的受力特性。图 22(d)将基坑周边5个测斜数据与计算值进行了对比,实测最大测斜主要发生在基底附近,最大侧向变形分布在5.2~8.5 mm,约为开挖深度的0.009%~0.015%。计算最大测斜值为12.2 mm,与实测值相比数值略大,但总体趋势基本一致,说明采用文中提出的HS-Small模型参数对于软土超深基坑分析也有较好的适用性。
3. 深基坑承压水降水环境影响分析
随着深度超过30 m、甚至达到50~60 m的基坑工程不断涌现,地下水尤其是深层承压水对基坑工程与周边环境的影响受到广泛关注。由于承压含水层水头高、分布与补给情况非常复杂,承压水处理给软土深基坑工程带来了很大的挑战。当基坑存在环境保护要求且承压含水层的厚度不大时,通常可采用截水帷幕隔断承压水层然后在坑内减压,此时坑外承压水位基本不会变化,从而对周边的环境影响基本可以忽略。对于承压含水层厚度较大而无法隔断时,可采用在基坑周边设置悬挂截水帷幕,然后进行坑内承压水减压;但坑内减压降水会引起地下水的渗流,坑外承压含水层的地下水会绕流进入坑内,从而会引起坑外承压含水层水位的降低;与此同时,由于承压水层和上部土层通常会存在一定的水力联系,导致上覆土层和下部承压含水层间产生了越流补给;坑内降水的结果是坑外承压含水层和上覆土层的孔隙水压力降低,降低的孔隙水压力将引起土骨架中有效应力增加,土体产生固结沉降,从而引起地表沉降,并引起周边的建(构)筑物等产生变形;因此长时间抽降承压水会对周边环境产生较大影响,需采用合理的方法分析降水对周边环境的影响。
3.1 承压水降水的环境影响分析流程
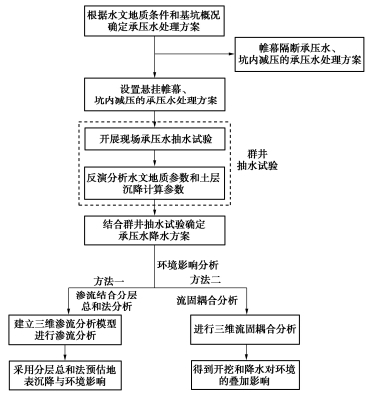
可采用如图 23所示的流程来分析承压水降水引起周边环境的变形。
(1)确定初步的承压水处理方案。通常根据土层条件和水文地质条件以及基坑的开挖深度,验算基坑的抗突涌稳定性。当抗突涌稳定性不满足要求时,根据地层条件确定是采用截水帷幕隔断承压水还是设置悬挂帷幕然后进行坑内减压的承压水处理方案。当采用悬挂帷幕方案时,需评估承压水降水对周边环境的影响。
(2)群井抽水试验、反演分析与计算参数的确定。在评估承压水降水对周边环境的影响之前,需开展现场群井抽水试验。通过在承压含水层和上部潜水含水层设置水位观测井,观测承压水层抽水试验过程中各土层的水位变化,确定承压含水层和其它土层的水力联系;通过设置地表沉降观测点,观测得到抽水过程中地表的沉降情况。结合抽水试验得到的水头下降实测数据反演分析确定相关的水文地质参数,并根据地表沉降数据反演分析得到合理的土层沉降计算参数。
(3)基坑降水引起周边环境的变形分析。根据抽水试验的结果确定承压水降水方案,在此基础上进行承压水降水的环境影响分析。可采用两种分析方法,方法一是三维渗流分析结合分层总和分析方法,即建立符合实际的基坑降水三维渗流分析模型进行渗流分析,得到基坑承压水降水产生的各土层水头变化情况,然后采用基于土体单向压缩的分层沉降总和法计算得到总的地表沉降情况,从而预估周边环境的变形。方法二是流固耦合分析方法,通常采用Biot固结理论将地下水渗流和土体固结耦合起来进行分析,既考虑基坑开挖的过程又考虑降水的过程,最终得到开挖和降水引起环境的叠加变形。
3.2 基于群井抽水试验的水文地质参数确定方法
在分析承压水降水对周边环境的影响时,需确定合理的水文地质参数,为考虑实际基坑降水过程中的降水井群相互影响的情况,可通过群井抽水试验来反演分析确定计算参数。
群井抽水试验要求一般如下:①在现场布置多口抽水试验井(一般为4~6口井),同时进行群井抽水,记录每个抽水井的抽水量,通过多个降水井的同时降水模拟降水井相互影响的工作状态;②群井抽水时间根据目标承压含水层的水文地质特征、水位降深与时间关系曲线来确定,并应确保降水达到承压水位降低的要求;③在抽水井围合区域内设置承压含水层的水位观测井,测量抽水过程中承压水位变化,检验降水是否达到承压水位降低的要求;④在抽水井围合区域内的上部土层设置水位观测井,观测抽水试验过程中上部土层的水位变化情况,确定承压含水层和上部土层的水力联系;⑤在地表按一定间距布设网状沉降观测点,观测群井抽水试验过程中的地表沉降,为分析降水对环境的影响提供依据;⑥抽水试验设备通常为深井潜水泵,泵的流量需根据基坑承压水降水需要及工程经验确定;⑦群井抽水试验结束后,进行水位恢复试验。
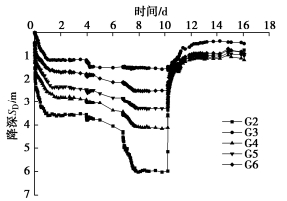
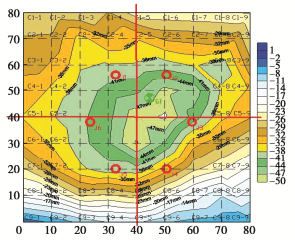
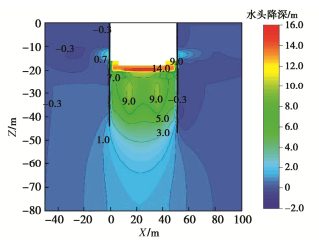
南京某工程位于南京市河西地区,属长江漫滩地貌单元。拟建场地上部以黏性土为主,中部的④1粉细砂、④2中细砂层为深厚承压含水层,下部为泥岩。群井抽水试验在承压含水层中设6口抽水井,并在承压含水层和上部黏性土层中共设6口观测井,同时在以群井试验区为中心的范围内每隔10 m设置一个地面沉降观测点。群井抽水试验时开启六口井持续抽水6 d,同时观测其它观测井内的水位变化。各观测井的水头降深时程曲线如图 24所示,随着降水的开展,各观测井水位逐步下降,降水结束后,水位快速恢复。位于群井围合区域内部的G2井水位降深明显大于位于外部区域的G4、G5、G6的降深;G3位于③淤泥质粉质黏土层中,其降深仅1.6 m。图 25为降水引起的地表沉降等值线图,群井抽水后地面均会产生一定量的沉降,大致呈盆形,且随着与群井抽水区域中心距离的增大,地面沉降有逐渐减小的趋势,抽水区域中心位置的实测最大沉降约47.7 mm。
随后建立群井抽水试验三维空间的非均质各向异性水文地质概念模型。模型考虑了各土层的分布及抽水井的分布情况,抽水井根据实际情况设置过滤器长度、出水量等参数,将抽水过程中的实测流量作为计算中的抽水井出水量。通过对观测井计算和实测地下水位的拟合,反演分析得到④1及④2层的渗透系数及贮水系数,如表 5所示。
表 5 反演分析所得的④1及④2层水文地质参数Table 5. Hydrogeological parameters of layers ④1 and ④2层号 土层名称 渗透系数平均值/(m·d-1) 贮水系数S 水平向 竖向 ④1 粉细砂 25.0 21.8 2.3×10-3 ④2 中细砂 28.0 24.3 2.4×10-3 结合三维渗流计算得到的群井抽水稳定的水位降深,采用分层总和法计算最终的地表沉降,得到④1、④2、④3层固结度达到100%时的长期沉降量值分别为71.6,131.8,16.6 mm,求和所得的地表沉降量为220 mm。实测地表最大沉降量值为47.7 mm,其与计算值的比值ξ=0.22,即得到了预估短期降水引起地表沉降的经验系数值。
3.3 承压水降水环境影响的渗流分析结合分层总和分析方法
三维渗流分析结合分层总和分析方法中地下水渗流和固结沉降是分开计算的,也即是渗流和应力不耦合的一种计算方法,它包含两个步骤。首先是进行地下水运动的三维渗流分析,需根据基坑规模和影响范围以及土层的分布情况确定计算域,在此基础上进行网格划分;根据降水方案布置抽水井,设置相应的滤管参数;根据地层分布情况设置渗透系数(根据群井抽水试验确定),并在模型中添加截水帷幕;添加适当的边界条件后进行计算分析,得到坑内降水引起的坑内、外各土层的水位降深情况。然后计算各层土体因水头变化引起的有效应力增加,在此基础上计算各层土体的沉降情况,并采用分层总和法得到总的地表沉降;假定位于地面的建(构)筑物所在位置的沉降与地表沉降相同,则就得到了降水引起的环境沉降;对于有一定的埋深的隧道等,则计算至对应埋深处的土体沉降就得到了隧道的沉降。
上海盛大中心基坑面积约7000 m2,开挖深度为17.1~22.1 m。基坑西南侧距离地铁4号线区间隧道约6 m,北侧距离地铁2号线隧道约38 m,隧道埋深均约为17 m。场地浅层为典型上海软土分布,下部第一承压含水层和其下第二承压含水层水头连通,形成厚度超过110 m的承压含水层组。基坑分为3个区先后实施,采用悬挂帷幕并在坑内设置减压井降水的承压水处理方案。基坑实施前开展了群井抽水试验,以确定水文地质参数和地表沉降计算参数。根据基坑承压水降水方案,建立整个基坑系统的三维渗流计算模型。减压井的过滤器参数根据设计方案确定,出水量根据群井抽水试验和预成井抽水情况确定。根据基坑的具体开挖工况,分阶段控制承压水水位,模拟分析即按该计划进行承压水的开启。考虑基坑开挖阶段降水时间为180 d,计算得到基坑开挖完成时承压水位降深。结果表明,坑外北侧和东侧水位降深约为1.5 m,而西南侧由于外围地下连续墙和中隔地下连续墙的双重影响,坑外承压水位降深仅约为0.6 m。
根据土层的水位降深,确定各层土体的有效应力增加,采用分层总和法计算土体沉降;地铁区间隧道埋深按17 m考虑,计算得到地铁隧道埋深标高的土体沉降等值线如图 26所示,预测北侧地铁2号线区间隧道的最大沉降约为2 mm,其穿越区域的最大地面沉降约为3 mm;预测西南侧地铁4号线区间隧道的最大沉降约为1 mm,其穿越区域的最大地面沉降约为2 mm。监测表明,基坑工程实施过程中基坑开挖和承压水降水联合影响导致的邻近4号线地铁隧道的最大沉降约为5 mm(图 27),地铁2号线的最大沉降约为0.75 mm,满足了地铁的保护要求,周边建筑物与市政道路、管线的沉降也较小。
3.4 承压水降水环境影响的流固耦合分析方法
基坑降水过程中,土体孔隙中的水排出,土体有效应力增加产生固结,宏观上表现为土体发生沉降。土体固结在微观上反映为土骨架被压密,土体的孔隙减小,引起土体渗透性降低,从而又会对渗流场产生影响。因此深基坑降水与地面沉降过程是渗流场与应力场相互影响的复杂过程,考虑渗流场与应力场的耦合作用,也就是建立地下水流连续性方程与力学平衡方程之间的耦合关系,才更符合实际情况。
流固耦合分析需采用Biot三维固结理论[33]。实际的基坑工程既要考虑开挖又要考虑降水的流固耦合,由于问题的复杂性,一般需通过大型岩土分析软件进行分析。分析前需建立整个基坑的三维模型,包括各土层及坑内每层开挖土方、围护墙、水平支撑、竖向支承等。土体可采用前述的HS-Small模型进行模拟。模拟基坑施工过程涉及土体开挖和基坑降水,其中基坑降水又包括疏干降水和减压降水。承压水减压降水,可通过在减压井滤管区域设置相应的定流量边界或定水头边界来模拟,并根据实际情况确定开启时间和降水持续时间。通过设置符合实际情况的边界条件(包括位移边界条件和地下水边界条件),并依次模拟开挖、降水、支撑等实现对基坑施工过程的模拟,求解即可得到基坑开挖和降水叠加引起周边环境的变形。
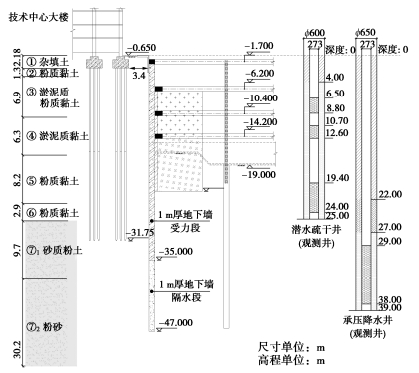
高速电梯试验塔项目基坑面积约2366 m2,挖深16.4~18.4 m。基坑东侧距离既有技术中心大楼约3.7 m,该大楼为8层钢筋混凝土框架结构,采用桩基础,桩长30 m。场地浅层为典型上海软土,下部第一承压含水层和其下第二承压含水层连通,形成厚度超过80 m的承压含水层组。基坑采用两墙合一地下连续墙结合四道水平钢筋混凝土支撑的支护方案。邻近8层技术中心大楼位置的东侧采用1000 mm厚地下连续墙,地下连续墙为悬挂帷幕,深度46.35 m(图 28)。结合群井抽水试验结果,坑内布置4口减压井,同时考虑在坑外布置6口承压水观测井兼回灌备用井,井深均为39 m。坑内设置9口潜水疏干井,并在坑外设置6口潜水观测井。
根据实际基坑支护设计方案建立考虑土与结构共同作用的三维数值分析模型。土体采用实体单元模拟,其本构模型采用HS-Small模型,其计算参数根据前述方法确定。降水涉及的主要土层即第⑦1和⑦2层的渗透系数取群井抽水试验反演得到的水平渗透系数。支护结构单元包括地下连续墙、支撑、立柱和立柱桩。地下连续墙采用板单元模拟,支撑杆件采用梁单元模拟,立柱和立柱桩采用桩单元模拟。为真实反映施工进度对基坑变形的影响,每一步降水、土方开挖和支撑施工的时间都按照实际施工进度进行模拟。每一层土方开挖之前,坑内潜水进行疏干降水。开挖至13 m后开始启动坑内减压降水,采用定水头方法来模拟减压降水。在坑内开启减压降水的同时,坑外承压水观测井兼备用井进行常压回灌。
图 29给出了计算得到的基坑东西向剖面的水头降深分布情况。可以看出,坑内在减压井深度范围内的降深较大;在深度方向,随着与减压井滤管底部距离的增大,承压水降深逐渐减小,在地下连续墙底附近的降深约为3 m;坑外主要发生沿着水平方向的渗流,随着与基坑水平距离的增加,坑外降深也逐渐减小。总体而言,计算分析得到的承压水头分布情况符合基坑工程中渗流场的认知,说明采用流固耦合的分析方法能较好地模拟地下水的运动规律。
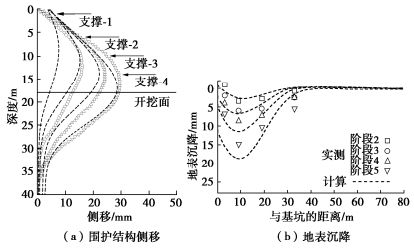
图 30(a)为基坑西侧中点附近地下连续墙测斜点在各个工况下侧移的计算值与实测值的对比情况,计算值和实测结果都表明,随着开挖的进行,地下连续墙的侧移不断增大,发生最大位移的位置也逐渐下移,并大致位于开挖面附近。开挖结束后,计算和实测最大侧移分别为30.5,28.5 mm,数值模拟结果与监测结果吻合得较好。图 30(b)为基坑西侧坑外地表沉降监测断面处测点各个工况下的地表沉降计算值与监测值的对比,可以看出,计算与实测的地表沉降形态较为吻合,计算值略大于实测值。计算与实测结果均表明,坑外地表沉降整体呈凹槽型分布,且随着开挖和降水的进行沉降不断增大,这与上海软土地区基坑地表沉降统计规律基本一致。东侧技术中心大楼和南侧钣金车间的基础沉降值也与考虑降水影响的计算值基本一致,实测最大沉降分别仅为6.2,4.7 mm,说明较好地控制了基坑开挖和降水对周边环境的影响。上述计算得到的渗流场分布、地下连续墙侧移、地表沉降、建筑物沉降及与实测的对比表明,采用流固耦合分析方法能较好地模拟基坑开挖和降水联合作用对变形的影响。
对于涉及复杂承压水处理的基坑工程,采用现场群井抽水试验可以较合理地确定水文地质参数,在此基础上确定初步的基坑承压水处理方案,并采用渗流分析结合分层总和分析方法或流固耦合分析方法预估降水对周边环境的影响,根据分析结果优化承压水控制方案,进一步根据按需减压的原则控制各个工况下承压水的抽降,必要时在坑外采取回灌措施,实现对承压水及周边环境变形影响的安全控制。
4. 软土深基坑变形与环境影响控制技术
软土深基坑实施过程中涉及的围护结构施工、抽降承压水、开挖卸载等环节会引起基坑变形并对周边环境设施造成影响。软土深基坑变形与环境影响控制是一个复杂的系统工程,应贯穿于基坑实施全过程,工程上通常从变形源头、传播路径和保护对象3个方面着手采取针对性的控制措施。变形源头控制是通过增大支护结构的刚度、制定合理分区、对坑内外土体进行加固等方法以减小围护结构以及周边土体的变形。传播路径阻隔是指在围护结构与既有设施之间设置隔离屏障,以减小开挖、降水等引起的附加应力场的影响范围,从而减缓基坑变形对周边既有设施的影响。针对基坑周边承受变形能力弱的建构筑物,可以预先对其基础或上部结构进行加固以增强其抵抗变形的能力,从而保证这些建构筑物在基坑开挖过程中的安全和正常运营,常用的基础加固方法包括托换加固和注浆加固等。近年来,笔者和团队开展了一系列绿色、低碳、环境低影响的变形控制技术的研究,本文将着重阐述支护结构与主体地下结构相结合技术、微扰动土体加固技术、混凝土支撑主动变形控制技术以及承压水控制超深帷幕技术4个方面的主要成果。
4.1 支护结构与主体地下结构相结合技术
支护结构与主体地下结构相结合是指采用部分或全部主体地下结构构件作为基坑支护结构,是一种基于支护结构刚度的变形控制设计方法。根据结合方式的不同可以分为围护墙与地下室外墙相结合(即两墙合一、桩墙合一)、支撑与水平梁板相结合以及竖向构件相结合等不同形式[34],如图 31所示。
以支护结构与主体地下结构全面相结合为例,一方面,可以利用基坑围护墙作为永久地下室的外墙,既提高了地下空间的利用率也节省了工程造价。另一方面,采用逆作法施工时,可利用逐层浇筑的地下室结构梁板作为基坑围护墙的内部支撑,由于地下结构水平构件与临时支撑相比刚度大得多,所以围护结构在侧向水土压力作用下的变形相对较小。与此同时,采用地下结构梁板作为基坑水平支撑,无需拆除支撑,避免了常规支撑开挖完成后即被废弃造成的资源浪费和环境污染,并能有效减小支撑拆除引起的围护结构和周边环境的二次变形。因此,结构梁板代替支撑有利于减小基坑变形,缓解基坑开挖对邻近建构筑物、地铁隧道、地下管线等敏感环境设施的影响。
根据大量工程案例的实测数据分析,对比了顺作法和逆作法基坑在控制基本变形方面的效果(见图 9)。对于顺作法基坑,94个采用地下连续墙和79个采用钻孔灌注桩围护的基坑工程最大侧移δhm与开挖深度H的比例关系分别为δhm=0.42%H,δhm=0.44%H。而对于采用支护结构与主体地下结构相结合的逆作法基坑工程这一比例关系的平均值约为δhm=0.25%H[35],仅为顺作法基坑的60%,表明支护结构与主体地下结构相结合且采用逆作法施工能够有效地控制基坑的变形,进而减少基坑开挖对周边环境的影响。
基于大量工程的实际需求,笔者和团队系统建立了基坑支护结构与主体地下结构相结合成套技术,进一步提出了上下同步逆作、跃层逆作、顺作逆作交叉实施等新型逆作法技术,并在全国大量复杂环境条件下基坑工程项目中成功应用[34-36],既控制了基坑变形和环境影响同时也避免了大量临时支护结构的使用,相关技术纳入了国家标准《建筑地基基础设计规范》[6]和行业标准《建筑工程逆作法技术标准》[37]。
4.2 土体加固评估与数字化微扰动搅拌桩技术
(1)土体加固效果评估
土体加固通过改善土体的物理力学性能、提高被动区土体抗力从而达到减小基坑变形并增强其整体稳定性的目的。根据不同环境保护要求,基坑被动区土体加固一般采用墩式、裙边、抽条和满堂等几种平面布置形式。加固后其水平基床系数kH=mz(其中m为比例系数,z为开挖对土体的影响深度)将会发生改变,加固后土体刚度是控制基坑开挖变形的关键因素。
为了研究土体加固的效果,收集了上海地区多个邻近地铁隧道、采用搅拌桩进行地基加固的基坑工程案例,对基坑平面杆系结构弹性支点法中土层参数m值进行了反演分析。反演分析时,首先在有限元软件中建立基坑分析模型,得到围护墙变形,然后借助Ucode反分析软件,通过不断改变计算模型参数(如m值)使得围护墙变形计算结果与实测数据吻合,直到计算模型能够反映实测变形,这样就得到了实际的土体m值[38]。当然,通过反分析得到的m值也同时包含了施工方法、开挖条件和施工过程等因素的影响。
表 6为反演分析得到的加固前后土体m值。对比发现,经过可靠的加固处理后,反算分析得到的加固土体比例系数m值提高了2~3倍,说明加固后土体的抗变形能力得到了增强,对控制基坑变形效果显著。
表 6 加固前后土体m值对比Table 6. Comparison of m values of soil prior to and after ground improvement加固土层 原状土性质 未加固m值/
(kN·m-4)加固后m值/
(kN·m-4)③淤泥质粉质黏土 流塑,高压缩性 [800, 1800]
平均值1300[2700, 3900]
平均值3300④淤泥质黏土 流塑—软塑 [600, 1900]
平均值1300[2700, 3900]
平均值3300⑤1黏土 软塑 [700, 2600]
平均值1700[3700, 5800]
平均值4800(2)DMP工法数字化微扰动搅拌桩
水泥土搅拌桩因其施工高效、经济性好等特点在基坑工程中被广泛用于土体加固。随着基坑工程呈现新的发展趋势,对于水泥土搅拌桩技术也有了新的需求。一方面,随着项目规模越来越大,对搅拌桩智能化控制和自动化施工水平的要求越来越高;其次,为保证日益复杂环境设施的安全,控制水泥土搅拌桩的施工质量和降低施工扰动也至关重要。
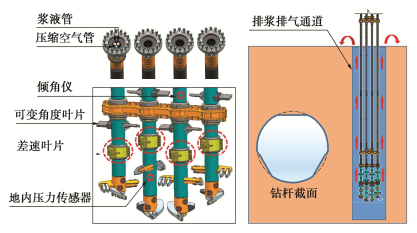
基于上述工程需求,研发了DMP工法数字化微扰动搅拌桩新技术。如图 32所示,该技术采用浆气同轴多通道异形钻杆,每根钻杆内部均同时配置喷浆管和喷气管,成桩过程中同时喷射浆液和压缩空气,解决了桩身强度平面分布不均匀的问题。通过多层可变角度的搅拌叶片和差速叶片,同时采用上下转换喷浆工艺,使下沉和搅拌全过程浆液和土体都能得到充分搅拌,增强了水泥土搅拌均匀性、降低了置换土量。现场试验表明,在采用15%的水泥掺量的情况,桩体28 d无侧限抗压强度均达到了0.8 MPa;施工过程中产生的置换土量约为加固土体积的25%,降低了材料消耗。
DMP工法通过数字化控制系统自动完成下沉、复搅和提升等施工环节,能实时记录施工全过程参数和对成桩过程进行监控,并对异常情况进行报警,施工全过程自动化控制大大提高了搅拌桩的施工效率。借助数字化施工控制系统,减小了施工过程中人为因素对搅拌桩质量的影响,施工数据通过设备上的网络模块上传到云平台,提升了搅拌桩施工过程的透明度和可回溯性。
工程实践中发现搅拌桩施工引起的变形量也不容忽视。为了降低施工影响,在搅拌钻头上配备了地内压力传感器,通过数字化控制系统能够实现地内压力自动控制和自主排浆,减小了搅拌和喷浆过程中对原位土体应力场的影响。同时,下沉和提升过程采用不同水胶比的水泥浆液,下沉过程中水胶比稍大,可以进一步降低下钻过程搅拌原位土体的阻力。工程实践表明,DMP工法搅拌桩能够将距离桩身2 m处的土体变形控制在5 mm,适用于城市敏感环境条件的基坑土体加固施工[39]。
DMP工法是一种自动化程度高、绿色节能、微扰动搅拌桩新技术,已在全国多地的基坑围护、土体加固、截水帷幕、顶管洞口加固、堤坝加固等不同类型的工程项目中应用,如上海浦东国际机场扩建项目、东方枢纽上海东站、东莞港沙田港四期工程、广南铁路联络线等,为保障重大工程项目的建设和周边环境的安全提供了重要的技术手段。
4.3 混凝土支撑主动变形控制技术
紧邻敏感环境设施的基坑工程对于变形控制的要求很高,很多项目需要实现毫米级微变形的要求。以邻近地铁的基坑工程为例,为了达到微变形控制要求,目前通常将面积较大的基坑分成大小坑先后实施,在先实施的大基坑中采用混凝土支撑,而在邻近地铁的小基坑内采用轴力伺服钢支撑[40]。常规的钢筋混凝土支撑受到侧向水土压力、混凝土徐变、温度收缩等因素的影响,往往难以满足微变形的控制要求。
为了进一步减小采用混凝土支撑的大基坑的变形,提出了一种新型轴力伺服混凝土支撑形式。如图 33所示,将支撑端部截面扩大并将轴力伺服千斤顶设置在凹槽内,开挖过程中根据变形要求启动伺服千斤顶进行分级加载。未施加轴力前,由端部支墩将围护结构上的侧向水土压力传递至围檩和支撑;当千斤顶施加轴力后,支墩与围檩脱开并退出受力,侧向压力转为由千斤顶传递至牛腿和支撑上。需要注意的是,伺服千斤顶施加轴力的过程中,支墩与围檩间的空隙不断增大,会导致支墩和围檩呈脱开状态,在下一皮土方开挖前以及千斤顶泄压前应对脱开的空隙采用高强灌浆料填实,以保证支撑与围檩之间水平传力可靠。该技术融合了混凝土支撑刚度大和轴力伺服系统主动控制的优点,在支撑端部设置伺服千斤顶,施加的预应力直接传递到支撑杆件上、受力直接。这种轴力伺服钢筋混凝土支撑技术不仅适用于地下连续墙围护,也适用于排桩、工法桩等离散型的围护结构,不需要另外多设置一道围檩,节省了工期与造价。
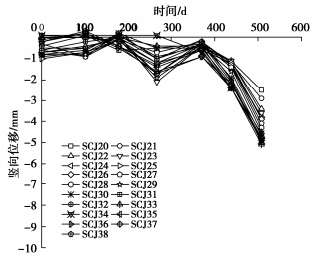
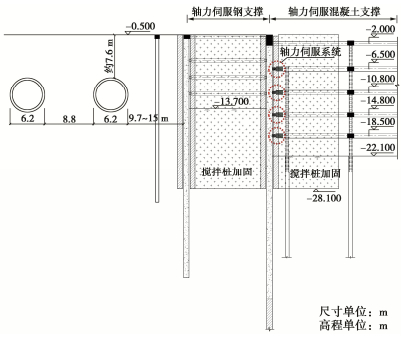
上海浦东新区某基坑邻近地铁隧道,基坑挖深21.6~22.1 m,距离隧道最小净距约9.7 m,如图 34所示。采用地下连续墙结合大小坑的分区设计方案,小的窄条基坑采用轴力伺服钢支撑,大基坑采用五道十字正交钢筋混凝土支撑。为了进一步减小大基坑施工对地铁隧道的影响,在第二至第五道支撑临近隧道一侧设置了轴力伺服千斤顶。按照3 m间距布置,其中第二道支撑千斤顶保压值为2000 kN,第三至第五道支撑千斤顶保压值为3000 kN。第二道支撑施工完成后根据变形监测数据开启伺服系统进行加载,其中第二至第五道混凝土支撑最终施加的预应力分别为3300 kN(分4级)、2500 kN(分5级)、3000 kN(分5级)和3000 kN(分5级)。从开始施加预应力到大基坑基础底板施工完成,地铁侧地下连续墙最大测斜小于20 mm,隧道的收敛变形和竖向沉降增量分别为1.6 mm和2.6 mm,轴力伺服混凝土支撑有效控制了基坑开挖对隧道变形的影响。
4.4 承压水控制的超深帷幕技术
超深基坑工程长时间大面积开敞抽降承压水将引起周边大范围地面沉降,危及周边建构筑物的安全,对深层承压水通常采取设置帷幕隔断的措施,传统的水泥土搅拌桩作为帷幕最大隔水深度仅30 m左右,而钢筋混凝土地下连续墙作为隔水帷幕,槽段接头易渗漏,且造价高。为解决深大地下空间开发面临的深层承压水控制安全问题,超深帷幕新技术的研发应需而生,包括超深水泥土搅拌墙技术和超深超高压喷射注浆技术,笔者和团队对这两项新技术开展了系统性研究[41-42],并率先在全国开展推广应用[43-50],为承压水的安全控制提供了高效的手段。这两项技术均以水泥土为介质构筑形成超深隔水帷幕,大幅降低了钢筋和混凝土的材料消耗。
(1)超深水泥土搅拌墙技术
超深水泥土搅拌墙技术可用于形成竖向超深隔水帷幕,根据不同成墙工艺分为渠式切割水泥土搅拌墙技术(下文简称TRD工法)和铣削式水泥土搅拌墙技术(下文简称SMC工法),相比水泥土搅拌桩和混凝土地下连续墙,这两项技术适应地层广、隔渗性能好、成墙工效高、工程造价低,是一种节能降耗的承压水控制新技术。
如图 35所示,TRD工法通过链锯型刀具插入地基至设计深度后,全深度范围对成层地基土整体上下回转切割喷浆搅拌,并持续横向推进,构筑成连续无缝的水泥土搅拌墙。该工法适用于软黏土、标贯击数100以内的密实砂土、粒径10 cm以内的卵砾石及单轴抗压强度不超过10 MPa的软岩等地层。成墙厚度介于550~1200 mm,深度可达85 m,垂直度可达1/300。成层土体经链锯型刀具全断面搅拌形成的墙体连续无缝,均匀性好,强度高(25%水泥掺量搅拌墙可达1~3 MPa),抗渗性能好(可达10-7 cm/s量级)。
目前国内应用较多的中国自主研发的TRD工法施工设备有TRD-60D/E型、TRD-70D/E型、TRD- 80E/EA型等,最大施工深度达到86 m,切割箱中部和底部可同时喷浆,确保超深墙体的搅拌均匀性。TRD工法施工设备的最大高度一般不超过12 m,施工机架重心低,安全稳定性好,可满足城市狭小低空环境的施工需求。TRD工法用于超深隔水帷幕均采用三工序成墙工艺:先行挖掘、回撤挖掘、成墙搅拌,先行挖掘工序注入挖掘稳定液,成墙搅拌工序注入水泥浆固化液。根据诸多工程实践,三工序成墙先行挖掘工序推进速度一般控制在0.2~2.0 m/h,回撤挖掘速度一般控制在5~10 m/h,成墙搅拌推进速度一般控制在1~3 m/h。
如图 36所示,SMC工法是通过钻具底端的两组铣轮竖向掘削地基土至设计深度后,提升喷浆搅拌形成一定宽度的水泥土墙幅,并通过对相邻已施工墙幅的铣削连接构筑成水泥土搅拌墙。该工法可适用软黏土、密实砂土、粒径20 cm内的卵砾石和单轴抗压强度达20 MPa的岩层等多种地层。成墙厚度介于640~1200 mm,单幅墙长度为2.8 m,成墙深度视设备而异,导杆式设备最大施工深度可达60 m,悬吊式设备可达80 m,垂直度可达1/500。铣削搅拌形成的墙幅质量高,强度可达1~5 MPa(水泥掺量20%~25%),渗透系数可达10-7 cm/s量级。
目前国内应用的SMC工法施工设备主要有中国自主研发的SMC-SC系列机型和XCM80机型。SMC-SC系列机型均为导杆式,是国内应用的主要机型。导杆式设备虽机架高度较高,但钻具主要重量均位于铣削钻头,整机重心低,安全稳定性较好。SMC工法用于超深隔水帷幕时单幅墙体施工采用双浆液方式,铣削头在掘削下沉过程中注入膨润土浆液,搅拌提升时注入水泥浆液。铣轮下沉搅拌速度一般控制在1.0 m/min内,提升搅拌速度一般控制在0.3~0.8 m/min。墙幅之间的铣削咬合连接施工采用跳槽式,两侧先行施工墙幅具有一定强度后施工中间墙幅,确保超深墙幅施工的垂直度。
TRD工法和SMC工法通过不同工艺构筑成等厚度水泥土搅拌墙,各具特点,可应对不同工程应用需求,如表 7所示。相比混凝土地下连续墙帷幕技术,水泥土搅拌墙工效提高逾50%,造价降低逾50%。目前TRD工法和SMC工法已在全国各地千余项工程中应用,水泥土搅拌墙应用方量累计超1000万立方米。
表 7 TRD工法与SMC工法对比Table 7. Comparison between TRD and SMC methods施工工法 TRD工法 SMC工法 成墙方式 水平掘削,整体搅拌 竖向掘削,分层搅拌 适用性 适用软土、硬土和软岩等多种地层,应对城市狭小低空环境的施工需求 应对高标贯击数的密实砂土、大粒径卵砾石、岩石等复杂地层以及多转角墙幅的施工需求 成墙效果 连续无缝,抗渗性能优异,深度达80m 高效成墙,抗渗性能好,导杆式设备深度达60 m,悬吊式设备深度达80 m 在上海浦东某科学装置矩形工作井深基坑工程中(挖深为42.1~45.45 m),为控制多承压含水层降水对邻近高压铁塔、磁悬浮基础(控制变形小于2 mm)的影响,采用了地下连续墙结合TRD工法水泥土搅拌墙的双帷幕设计方案,在双帷幕之间设置承压水应急备用降水井和观测井。水泥土搅拌墙厚900 mm,深69 m,水泥掺量30%,采用TRD-80E型工法机施工,综合工效为每天5.5延米。搅拌墙28 d龄期芯样强度(0.8~1.0)MPa,芯样渗透性由原土层的(10-4~10-3)cm/s级减小至10-8 cm/s量级。通过针对多承压含水层的“隔-降-灌”一体化设计方法及分层减压控制技术,保障了超深基坑的安全,邻近磁悬浮轨道变形控制在1 mm内。
(2)超深超高压喷射注浆技术
超高压喷射注浆技术也为深大地下空间开发面临的深层承压水控制安全问题提供了一种有效的手段,可用于形成超深隔水帷幕、地下连续墙槽段接缝封堵等。目前广泛应用的工艺有RJP工法和MJS工法,但随着超深基坑工程的出现,RJP工法和MJS工法由于施工能力限制仍存在一些不足,一方面其最大施工深度小于70 m,无法实施超过70 m深的帷幕或地墙接头封堵;另一方面,大量工程实测表明深部地层成桩桩径一般2.5 m左右,成桩可靠性降低。基于此研发了成桩深度和直径更大的N-Jet工法超高压喷射注浆技术。
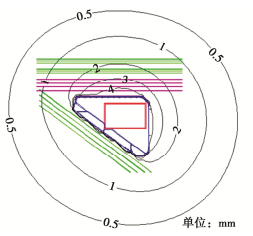
该技术是通过具有多个可变角度喷嘴的前端喷射注浆装置喷射超高压水泥浆液,并与土体混合形成大直径大深度圆形或扇形截面的水泥土加固体。现场试验表明,N-Jet工法在上海浅层黏性土地层中喷射注浆成桩直径达10 m,如图 38所示;在深厚砂层中成桩深度可达115 m,可以适用于黏性土、砂土、卵砾石等多种地层。该工艺喷射形成的大直径加固体质量可靠,可用于形成竖向超深隔水帷幕、水平向封底帷幕、超深地下连续墙槽段接缝封堵等[51],如图 39所示。
N-Jet工法施工过程中由主机控制钻杆旋转速度、提升速度、步进距离和施工角度。钻杆内部包含输送水泥浆液、水、主动空气等8个通道,其中浆液通道可满足多喷嘴最大600 L/min浆液流量的输送要求。钻杆前端的喷射注浆装置可配置1~7个喷嘴,每个喷嘴可承受45 MPa喷射压力,并可设置不同喷射角度,可根据地层条件和喷射成桩直径需求进行选择。施工参数设定和施工过程监控由数字化施工管理系统控制,施工过程中全自动喷射作业、实时显示施工状态、并可将施工状态和参数上传云端实现远程监控,实现了全过程可视化信息化施工管控。
N-Jet工法喷射注浆水泥掺量一般不小于40%,水灰比一般控制在1.0~1.3。成桩直径与土层特性、施工深度、喷嘴数量、喷射压力和流量、喷射装置提升速度等相关,需结合地层条件通过成桩试验进行验证,并通过开挖、声测或设置观测孔等直接或间接的方法进行直径检测。工程实践表明,超百米深注浆成桩直径可以达到3 m左右。
N-Jet工法具有喷射压力大、喷嘴数量多、喷射流量大等特点,相比RJP工法和MJS工法,成桩直径和深度均显著提高,如表 8所示。目前已在上海、宁波、北京等地多个超深基坑工程得到了应用,在上海轨道交通机场联络线某车站工程中施工深度达到107.5 m。
表 8 N-Jet工法与RJP工法、MJS工法主要技术参数对比Table 8. Comparison of parameters of N-Jet method with RJP and MJS methods工法 最大桩径/
m最大深度/
m最大喷射压力/
MPa浆液最大流量/
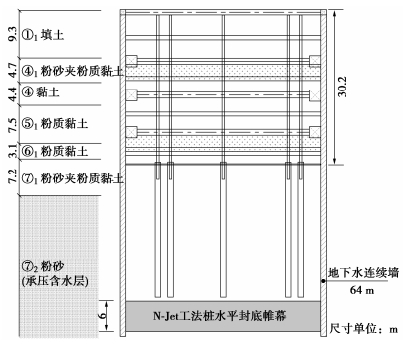
(L·min-1)浆液喷嘴数量 适用地层 RJP工法 3.5 70 40 190 单喷嘴 黏性土、砂土 MJS工法 4 70 40 130 单喷嘴 黏性土、砂土 N-Jet工法 10 115 45 600 1~7喷嘴 黏性土、砂土、卵石 在上海轨道交通机场联络线某风井基坑工程中(平面尺寸30.4 m×25.4 m,挖深30.2 m),场地承压含水层深厚,帷幕无法完全隔断承压含水层。基坑采用地下连续墙(墙深64 m)作为围护结构,为了减小抽降承压水对邻近的沪杭高铁及铁路李莘联络线的影响,在承压含水层中设置一道N-Jet工法水平封底帷幕,如图 40所示。
N-Jet工法桩直径3.5 m,桩中心距2.2 m,帷幕厚度6 m(顶底深度分别为52.5 m和58.5 m)。N-Jet工法桩施工采用双喷嘴单侧水平喷射的方式,水泥掺量45%。基坑实施降水期间,坑内承压水观测井水位从13 m降至33 m,坑外承压水观测井水位变化小于0.2 m,水平封底帷幕止水效果优异。
5. 总结与展望
结合工程需求,针对软土深基坑变形与环境影响评估和控制的技术难题,二十余年来笔者和团队重点围绕变形控制标准、开挖与承压水降水环境影响分析方法、变形控制技术3个方面开展了系统的研究工作,形成的技术成果在全国大量基坑工程中成功应用,为软土深基坑全过程变形的精细化控制和对周边重要设施安全风险的主动防控提供了技术支撑。
(1)制定明确的变形控制指标是进行基坑变形分析及环境影响控制的关键条件,既能保证基坑和周边环境设施的安全,又能避免“过度”设计造成资源浪费。基于大量工程案例的统计分析,揭示了软土深基坑变形与环境影响规律,首次提出了软土深基坑环境保护等级和变形控制指标,建立了基坑变形分级控制标准,为软土深基坑周边不同类型环境设施的保护提供了依据。
(2)合理预估基坑变形及环境影响能够有效指导设计和施工全过程采取更加有效的变形控制措施。为了便于工程使用,建立了基于变形容许值的环境影响简化分析方法;率先提出了通过室内和现场试验确定土体小应变本构模型(HS-Small)参数的实用方法,首次得到了典型黏土层HS-Small模型的全套参数,在分析邻近浅基础建筑、桩基础建筑、地铁隧道和市政管线等复杂环境条件下的基坑工程中广泛应用,提高了软土深基坑变形与环境影响预测的精细度。
(3)随着基坑深度不断增大,深层承压水控制逐渐成为影响深基坑工程变形与安全的重要因素。针对深层承压水无法完全隔断的工程需求,提出了根据群井抽水试验反演确定关键水文地质参数的实用方法,建立了评估深层承压水降水对地层和环境设施变形影响的分析方法,包括渗流计算结合分层总和分析方法和流固耦合分析方法,为深层承压水降水影响的量化评估提供了技术手段。基于群井抽水试验和承压水降水的环境影响分析可以优化承压水处理方案,进一步根据按需减压的原则控制各个工况下承压水的抽降,实现对承压水及周边环境变形影响的安全控制。
(4)系统开展了绿色、低碳、环境低影响变形控制技术的研究。提出了支护结构与主体地下结构相结合变形控制技术,形成了上下同步逆作、跃层逆作、顺作逆作交叉实施等新型逆作法技术,在全国大量复杂环境条件基坑工程项目中成功应用,控制了基坑变形与环境影响也节省了材料消耗;研发了DMP工法数字化微扰动搅拌桩技术,提升了搅拌桩自动化施工水平并减小了环境影响;提出了新型混凝土支撑主动变形控制技术,为基坑工程毫米级微变形控制提供了有效的手段;研发了包括TRD工法渠式切割水泥土搅拌墙、SMC工法铣削式水泥土搅拌墙以及N-Jet工法超高压喷射注浆桩在内的系列超深水泥土隔渗新技术,满足了深层承压水安全控制的工程需求。
随着中国城市建设进入新的发展阶段,深层地下空间开发的需求日益迫切,软土50 m以上的超深基坑工程项目不断涌现。与此同时,伴随着大规模城市更新改造的持续深入,既有建筑地下空间的开发利用逐渐成为新的趋势。合理利用超深地下空间和科学开发既有建筑下的地下空间是岩土工作者面临的新的挑战。在超深基坑工程方面,深层土压力分布规律、超深地下结构分析方法等需要进一步深入研究;而更加高效、深度更大的施工装备的创新对超深基坑工程的发展具有重要的推动作用。在城市更新既有建筑地下空间开发方面,需要因地制宜研发适用狭小空间和低净空等受限条件下的小型化、微扰动地下工程施工设备,以满足城市更新改造过程中复杂环境条件下基坑工程的需求。超深地下工程和既有建筑地下空间的高效利用将大幅拓展地下空间的深入和广度,对我国地下空间资源的合理利用和优化配置具有重要意义。致力探索绿色低碳新技术的研发和应用,不断促进软土深基坑工程精细化设计方法、智能化施工装备和信息化监测技术的创新发展是新时期岩土工作者面临的重要挑战与机遇。
致谢: 感谢土力学和岩土工程界各位同行的信任,让笔者有幸成为今年黄文熙讲座的主讲人。本文内容是笔者在二十余年从业历程中在软土深基坑变形与环境影响分析与控制方面积累的刍荛之见。感谢团队徐中华博士、李青博士、常林越博士在本文撰写过程中提供的帮助,感谢团队吴江斌博士、胡耘博士、戴斌、翁其平、邸国恩、宋青君、沈健、陈畅、李靖、宗露丹等对相关研究内容的贡献;感谢笔者学生王浩然博士、张娇博士在土体小应变特性研究方面的细致工作。感谢上海市基础工程集团有限公司李耀良顾问总工在技术合作研发方面提供的支持和帮助。 -
表 1 基坑环境保护等级的定义
Table 1 Definition of environment protection grade
环境保护对象 保护对象与基坑的距离 环境保护等级 优秀历史建筑、有精密仪器与设备的厂房、采用天然地基或短桩基础的医院、学校和住宅等重要建筑物、轨道交通设施、隧道、防汛墙、原水管、自来水总管、煤气总管、共同沟等重要建(构)筑物或设施 s≤H 一级 H < s≤2H 二级 2H < s≤4H 三级 较重要的自来水管、煤气管、污水管等市政管线、采用天然地基或短桩基础的建筑物等 s≤H 二级 H < s≤2H 三级 注:H为基坑开挖深度,s为保护对象与基坑开挖边线的净距。 表 2 基坑变形设计控制指标
Table 2 Deformation control criterion for deep excavation design
基坑环境保护等级 围护结构最大侧移 坑外地表最大沉降 一级 0.18%H 0.15%H 二级 0.3%H 0.25%H 三级 0.7%H 0.55%H 表 3 HS-Small本构模型参数及获取方法
Table 3 Determination of parameters of HS-Small model
参数类型 参数名称 获取方法 HS模型参数 强度参数 有效内聚力c′ 三轴固结试验有效应力莫尔圆 有效内摩擦角φ′ 剪胀角ψ 三轴试验或经验公式 破坏比Rf 三轴试验 刚度参数 参考切线模量Erefoed 标准固结试验 参考割线模量Eref50 三轴排水试验 参考卸载再加载模量Erefur 三轴排水试验 经验参数 静止侧压力系数K0 现场实测或经验公式 幂指数m 经验公式 泊松比νur 经验值,νur=0.2 参考应力pref 经验值,pref=100 kPa 小应变参数 刚度参数 参考初始剪切模量Gref0 共振柱试验或配有弯曲元及局部位移传感的三轴试验 参考剪应变γ0.7 表 4 HS-Small模型主要参数取值方法
Table 4 Detemination of key parameters for HS-Small model
土层 Erefoed/kPa Eref50/kPa Erefur/kPa Gref0/kPa γ0.7/10-4 νur m Rf ② 0.9Es1 - 2 1.2Erefoed 6Erefoed (2.5~4.9)Erefur 1.5~9.0 0.2 0.8 0.9 ③ 8Erefoed 0.6 ④ 0.6 ⑤ 6Erefoed 0.9 ⑥ 0.9 表 5 反演分析所得的④1及④2层水文地质参数
Table 5 Hydrogeological parameters of layers ④1 and ④2
层号 土层名称 渗透系数平均值/(m·d-1) 贮水系数S 水平向 竖向 ④1 粉细砂 25.0 21.8 2.3×10-3 ④2 中细砂 28.0 24.3 2.4×10-3 表 6 加固前后土体m值对比
Table 6 Comparison of m values of soil prior to and after ground improvement
加固土层 原状土性质 未加固m值/
(kN·m-4)加固后m值/
(kN·m-4)③淤泥质粉质黏土 流塑,高压缩性 [800, 1800]
平均值1300[2700, 3900]
平均值3300④淤泥质黏土 流塑—软塑 [600, 1900]
平均值1300[2700, 3900]
平均值3300⑤1黏土 软塑 [700, 2600]
平均值1700[3700, 5800]
平均值4800表 7 TRD工法与SMC工法对比
Table 7 Comparison between TRD and SMC methods
施工工法 TRD工法 SMC工法 成墙方式 水平掘削,整体搅拌 竖向掘削,分层搅拌 适用性 适用软土、硬土和软岩等多种地层,应对城市狭小低空环境的施工需求 应对高标贯击数的密实砂土、大粒径卵砾石、岩石等复杂地层以及多转角墙幅的施工需求 成墙效果 连续无缝,抗渗性能优异,深度达80m 高效成墙,抗渗性能好,导杆式设备深度达60 m,悬吊式设备深度达80 m 表 8 N-Jet工法与RJP工法、MJS工法主要技术参数对比
Table 8 Comparison of parameters of N-Jet method with RJP and MJS methods
工法 最大桩径/
m最大深度/
m最大喷射压力/
MPa浆液最大流量/
(L·min-1)浆液喷嘴数量 适用地层 RJP工法 3.5 70 40 190 单喷嘴 黏性土、砂土 MJS工法 4 70 40 130 单喷嘴 黏性土、砂土 N-Jet工法 10 115 45 600 1~7喷嘴 黏性土、砂土、卵石 -
[1] 王卫东, 丁文其, 杨秀仁, 等. 基坑工程与地下工程: 高效节能、环境低影响及可持续发展新技术[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020, 53(3): 78-98. WANG Weidong, DING Wenqi, YANG Xiuren, et al. Deep excavation engineering and underground engineering: new techniques of high-efficiency and energy-saving, low environmental impact, and sustainable development[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(7): 78-98. (in Chinese)
[2] 翁其平, 王卫东. 软土超深基坑工程关键技术问题研究[J/OL]. 地基处理, 2022: 1-9(2022-110-115). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1416.TU.20221124.1913.002.html. WENG Qiping, WANG Weidong. Key technical problems of super-deep foundation pit engineering in soft soils[J/OL]. Journal of Ground Improvement, 2022: 1-9(2022- 110-115). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1416.TU.20221124.1913.002.html. (in Chinese)
[3] BURLAND J B, WROTH C P. Settlement of buildings and associated damage[C]// Proceedings of the Conference on Settlement of Structures, London, 1974: 611-654.
[4] BJERRUM L. Allowable settlements of structures[C]// Proceedings of the European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, London, 1963.
[5] OU Changyu. Deep Excavation-Theory and Practice[M]. Leiden: Taylor & Francis, 2006.
[6] 建筑地基基础设计规范: GB50007—2011[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2012. Code for Design of Building Foundation: GB50007—2011[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2012. (in Chinese)
[7] 徐中华, 王卫东. 深基坑变形控制指标研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2010, 6(3): 619-625. XU Zhonghua, WANG Weidong. Deformation control criteria of deep excavations[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2010, 6(3): 619-625. (in Chinese)
[8] 城市轨道交通工程监测技术规范: GB50911—2013[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2013. Code for Monitoring Measurement of Urban Rail Transit Engineering: GB50911—2013[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2013. (in Chinese)
[9] 给水排水管道工程施工及验收规范: GB50268—2008[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2008. Code for Construction and Acceptance of Water and Sewerage Pipeline Works: GB50268—2008[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
[10] 上海市住房和城乡建设管理委员会. 城市轨道交通结构安全保护技术标准: DG/TJ 08-2434-2023[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2023. Department of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of Shanghai. Technical Standard for Protection of Urban Rail Transit Structures: DBJ/T 15-120-2017[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2017. (in Chinese)
[11] 广东省住房和城乡建设厅. 城市轨道交通既有结构保护技术规范: DBJ/T 15-120-2017[S]. 2017. (Department of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of Guangdong Province. Technical Code for Protection of Existing Structures of Urban Rail Transit: DBJ/T 15-120-2017[S]. 2017. (in Chinese)
[12] 城市轨道交通结构安全保护技术规范: CJJ/T202—2013[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2014. Technical Code for Protection Structures of Urban Rail Transit: CJJ/T202—2013[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
[13] CLOUGH G W, O'ROURKE T D. Construction induced movements of in situ walls[C]// Proceedings of Design and Performance of Earth Retaining Structures, Geotechnical Special Publication 25-ASCE, 1990: 439-470.
[14] HSIEH P G, OU C Y. Shape of ground surface settlement profiles caused by excavation[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1998, 35(6): 1004-1017. doi: 10.1139/t98-056
[15] 王卫东, 徐中华, 王建华. 上海地区深基坑周边地表变形性状实测统计分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2011, 33(11): 1659-1666. http://cge.nhri.cn/cn/article/id/14412 WANG Weidong, XU Zhonghua, WANG Jianhua. Statistical analysis of characteristics of ground surface settlement caused by deep excavations in Shanghai soft soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(11): 1659-1666. (in Chinese) http://cge.nhri.cn/cn/article/id/14412
[16] 上海市住房和城乡建设管理委员会. 基坑工程技术标准: DG/TJ 08-61-2018[S]. 2018. (Department of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of Shanghai. Technical Code for Excavation Engineering: DG/TJ 08-61-2018[S]. 2018. (in Chinese)
[17] 徐中华, 王卫东. 敏感环境下基坑数值分析中土体本构模型的选择[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(1): 258-264. XU Zhonghua, WANG Weidong. Selection of soil constitutive models for numerical analysis of deep excavations in close proximity to sensitive properties[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(1): 258-264. (in Chinese)
[18] ATKINSON J H. Non-linear soil stiffness in routine design[J]. Géotechnique, 2000, 50(5): 487-508. doi: 10.1680/geot.2000.50.5.487
[19] BENZ T. Small-Strain Stiffness of Soils and Its Numerical Consequence[D]. Stuttgart: Institute of Geotechnical Engineering, University of Stuttgart, 2007.
[20] 王卫东, 李青, 徐中华, 等. 软黏土小应变本构模型参数研究与应用[J]. 地下空间学报, 2023, 19(3): 844-855. WANG Weidong, LI Qing, XU Zhonghua, et al. Investigation and application of small-strain model parameters for soft clay deposits[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2023, 19(3): 844-855. (in Chinese)
[21] 王卫东, 王浩然, 徐中华. 基坑开挖数值分析中土体硬化模型参数的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(8): 2283-2290. WANG Weidong, WANG Haoran, XU Zhonghua. Experimental study of parameters of hardening soil model for numericalanalysis of excavations of foundation pits[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(8): 2283-2290. (in Chinese)
[22] SCHWEIGER H F. Design of deep excavations with FEM-influence of constitutive model and comparison of EC7 design approaches[C]// The Proceedings of the 2010 Earth Retention Conference. Washington, 2010.
[23] OU C Y, SHIAU B Y, WANG I W. Three-dimensional deformation behavior of the Taipei National Enterprise Center (TNEC) excavation case history[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2000, 37(2): 438-448. doi: 10.1139/t00-018
[24] RAMPELLO S, VIGGIANI G M B, AMOROSI A. Small-strain stiffness of reconstituted clay compressed along constant triaxial effective stress ratio paths [J]. Géotechnique, 1997, 47(3): 475-489. doi: 10.1680/geot.1997.47.3.475
[25] CLAYTON C R I, HEYMANN G. Stiffness of geomaterials at very small strains[J]. Géotechnique, 2001, 51(3): 245-255. doi: 10.1680/geot.2001.51.3.245
[26] 王浩然. 上海软土地区深基坑变形与环境影响预测方法研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2012. WANG Haoran. Prediction of Deformation and Response of Adjacent Environment of Deep Excavation in Shanghai Soft Deposit[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2012. (in Chinese)
[27] 宗露丹, 徐中华, 翁其平, 等. 小应变本构模型在超深大基坑分析中的应用[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2018, 15(增刊1): 231-242. ZONG Ludan, XU Zhonghua, WENG Qiping, et al. Application of small strain constitutive model in the analysis of a ultra large and deep excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2018, 15(S1): 231-242. (in Chinese)
[28] 李靖, 徐中华, 王卫东. 基础托换对基坑周边建筑物变形控制作用的三维有限元分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(增刊2): 157-161. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2017S2039 LI Jing, XU Zhonghua, WANG Weidong. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of foundation underpinning on deformation control of existing buildings adjacent to a deep excavation [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(S2): 157-161. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2017S2039
[29] 张娇. 上海软土小应变特性及其在基坑变形分析中的应用[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2017. ZHANG Jiao. Small Strain Stiffness Properties of Shanghai Soft Soils and Application in Deformation Analysis of Deep Excavations[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[30] 王卫东, 王浩然, 徐中华. 上海地区基坑开挖数值分析中土体HS-Small模型参数的研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(6): 1766-1744. WANG Weidong, WANG Haoran, XU Zhonghua. Study of parameters of HS-Small model used in numerical analysis of excavations in Shanghai area [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(6): 1766-1744. (in Chinese)
[31] 徐中华, 李靖, 张娇, 等. 基于小应变土体本构模型的逆作法深基坑三维有限元分析[C]// 第九届全国基坑工程研讨会, 郑州, 2016. XU Zhonghua, LI Jing, ZHANG Jiao, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a top-down excavation using small strain soil model[C]// Proceedings of the Ninth Symposium of Excavation Engineering, Zhengzhou, 2016. (in Chinese)
[32] 张娇, 王卫东, 李靖, 等. 分区施工基坑对邻近隧道变形影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 建筑结构, 2017, 47(2): 90-95. ZHANG Jiao, WANG Weidong, LI Jing, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the impact of zoned excavation on adjacent tunnels[J]. Building Structure, 2017, 47(2): 90-95. (in Chinese)
[33] BIOT M A. General theory of three-dimension-consolidation [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1942, 12(2): 155-164.
[34] 王卫东, 王建华. 支护结构与主体结构相结合的设计分析与实例[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2007. WANG Weidong, WANG Jianhua. Design, Analysis and Case Histories of Deep Excavations Supported by Permanent Structures[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2007. (in Chinese)
[35] 王建华, 徐中华, 王卫东. 支护结构与主体地下结构相结合的深基坑变形特性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007, 29(12): 1899-1903. http://cge.nhri.cn/cn/article/id/12713 WANG Jianhua, XU Zhonghua, WANG Weidong. Analysis of deformation behavior of deep excavations supported by permanent structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(12): 1899-1903. (in Chinese) http://cge.nhri.cn/cn/article/id/12713
[36] 王卫东, 徐中华, 宗露丹, 等. 上海国际金融中心超深大基坑工程变形性状实测分析[J]. 建筑结构, 2020, 50(18): 126-135. WANG Weidong, XU Zhonghua, ZONG Ludan, et al. Field measurement and analysis on deformation behavior of extreme deep and large foundation pit engineering of Shanghai International Financial Center[J]. Building Structure, 2020, 50(18): 126-135. (in Chinese)
[37] 建筑工程逆作法技术标准: JGJ 432—2018[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018. Technical Standards for Top-Down Method of Building Engineering: JGJ 432—2018[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2018. (in Chinese)
[38] 徐中华, 李靖, 王卫东. 基坑工程平面竖向弹性地基梁法中土的水平抗力比例系数反分析研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2014, 35(增刊2): 398-404. XU Zhonghua, LI Jing, WANG Weidong. Back analysis of proportional coefficient of horizontal resistance in vertical elastic subgrade beam method for deep excavations [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(S2): 398-404. (in Chinese)
[39] 李青, 杜策, 王理想, 等. 数字化微扰动搅拌桩技术与现场试验研究[J]. 施工技术, 2023, 52(11): 113-118. LI Qing, DU Ce, WANG Lixiang and YU Wenbo. Development and field testing of digital micro-disturbance soil mixing pile technique[J]. Construction Technology, 2023, 52(11): 113-118. (in Chinese)
[40] 徐中华, 宗露丹, 沈健, 等. 邻近地铁隧道的软土深基坑变形实测分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(增刊1): 41-44. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2019S1011 XU Zhonghua, ZONG Ludan, SHEN Jian, et al. Deformation of a deep excavation adjacent to metro tunnels in soft soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(S1): 41-44. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2019S1011
[41] 王卫东. 超深等厚度水泥土搅拌墙技术与工程应用实例[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2017. WANG Weidong. Technology and Practice of Uniformly Thick Soil Mixing Wall[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2017. (in Chinese)
[42] 王卫东. 超深超大直径超高压喷射注浆技术研发与应用[R]. 上海: 华东建筑设计研究院有限公司, 2022. WANG Weidong. Research and Application of Ultra-Deep and Ultra-Large High-Pressure Jet Grouting Technique[R]. Shanghai: East China Architecture Design & Research Institute, 2022. (in Chinese)
[43] 王卫东, 常林越, 谭轲. 超深TRD工法控制承压水的邻近地铁深基坑工程设计与实践[J]. 建筑结构, 2014, 44(17): 56-62. WANG Weidong, CHANG Linyue, TAN Ke. Design and practice of a deep foundation pit project adjacent to subway tunnel usingsuper deep TRD construction method to control confined water[J]. Building Structure, 2014, 44(17): 56-62. (in Chinese)
[44] 谭轲, 王卫东, 邸国恩. TRD工法型钢水泥土搅拌墙的承载变形性状分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(增刊2): 191-196. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2015S2037 TAN Ke, WANG Weidong, DI Guoen. Deformation and bearing characteristics of steel cement-soil wall constructed by TRD method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(S2): 191-196. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2015S2037
[45] 王卫东, 邸国恩. TRD工法等厚度水泥土搅拌墙技术与工程实践[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(增刊1): 628-634. http://cge.nhri.cn/cn/article/id/14829 WANG Weidong, DI Guoen. Engineering practices of constant thickness steel cement-soil wall constructed by TRD method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(S1): 628-634. (in Chinese) http://cge.nhri.cn/cn/article/id/14829
[46] 王卫东, 翁其平, 陈永才. 56 m深TRD工法搅拌墙在深厚承压含水层中的成墙试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2014, 35(11): 3247-3252. WANG Weidong, WENG Qiping, CHEN Yongcai. Experimental investigation of construction of a 56 m deep constant thickness cement-soil wall using trench cutting re-mixing deep wall (TRD) method in deep aquifers[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(11): 3247-3252. (in Chinese)
[47] 王卫东, 陈永才, 吴国明. TRD水泥土搅拌墙施工环境影响分析及微变形控制措施[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(增刊1): 1-5. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2015S1001 WANG Weidong, CHEN Yongcai, WU Guoming. Impact analysis and micro-deformation control measures of TRD construction cement-soil mixing wall[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(S1): 1-5. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2015S1001
[48] 王卫东, 邸国恩, 王向军. TRD工法构建的等厚度型钢水泥土搅拌墙支护工程实践[J]. 建筑结构, 2012, 42(5): 168-171. WANG Weidong, DI Guo'en, WANG Xiangjun. Engineering practice of the constant thickness steel cement-soil wall constructed by TRD method [J]. Building Structure, 2012, 42(5): 168-171. (in Chinese)
[49] 邸国恩, 黄炳德, 王卫东. 敏感环境深基坑工程TRD工法等厚度水泥土搅拌墙设计与实践[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(增刊1): 25-30. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2014S1004 DI Guoen, HUANG Bingde and WANG Weidong. Design and application of constant thickness cement-soil wall constructed by TRD method in deep excavations with sensitive surroundings[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(S1): 25-30. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2014S1004
[50] 黄炳德, 王卫东, 邸国恩. 上海软土地层中TRD水泥土搅拌墙强度检测与分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2015, 48(增刊2): 1-5. HUANG Bingde, WANG Weidong, DI Guoen. Test and analysis of strength of cement-soil wall constructed by TRD method in soft soil of Shanghai [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2015, 48(S2): 1-5. (in Chinese)
[51] 聂书博, 常林越, 朱士传, 等. N-Jet工法在超深基坑工程中对承压水控制应用研究[C]// 第四届全国岩土工程施工技术与装备创新论坛, 无锡, 2023: 180-186. NIE Shubo, CHANG Linyue, ZHU Shichuan, et al. Investigation on application of N-Jet ultra high pressure jet grouting in controlling confined aquifer[C]// The Proceedings of the Fourth Symposium of New Process in Construction Technology and Equipment of Geotechnical Engineering. Wuxi, 2023: 180-186. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(33)
1. 苏宇. 敏感环境下地下水池基坑围护施工技术. 山西建筑. 2025(02): 68-71+81 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘长云. 邻近轨道交通深基坑支护设计实践与变形控制研究. 城市建设理论研究(电子版). 2025(02): 201-204+151 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李成,刘红军,张秋虎. 土体参数对基坑支护及邻近建筑物变形影响的研究. 五邑大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 8-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 姜如英. 黏粉土互层软土环境下深基坑降水技术研究与风险管控. 建筑施工. 2025(01): 94-97+107 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 侯泽洋. 深基坑工程施工对临近地铁隧道结构的安全评价研究. 工程机械与维修. 2025(01): 55-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 喻卫华,马春景. 某超高层建筑深基坑设计与施工技术. 特种结构. 2025(01): 114-118+125 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张普. 装配式高层建筑基坑开挖与联合支护施工技术. 中国建筑金属结构. 2025(04): 70-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 周振,杜策,张振. 复杂环境深基坑中数字化微扰动搅拌桩的应用研究. 地基处理. 2025(01): 76-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 吴钰彬. 软土地区狭长型基坑变形及空间效应分析. 福建建设科技. 2025(02): 28-31+48 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 汪明元,过锦,俞建霖,龚晓南,余少乐. 基坑开挖诱发邻近桩基水平变形的理论分析方法. 建筑结构. 2025(05): 142-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 杨科. 深基坑工程对地铁盾构隧道变形影响的实测数据分析. 建筑施工. 2025(03): 462-466 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 姜文星. 软土地区深基坑双层承压水控制技术分析. 隧道与轨道交通. 2025(01): 32-36+73 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 李堪耀. 深基坑变形控制技术在高层装配式建筑中的应用研究. 科技资讯. 2025(04): 167-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 王文雅,冯冲,邵先飞,王念辉,刘子玉. 浅埋地铁上方路基分段跳仓施工技术方案研究. 湖南文理学院学报(自然科学版). 2025(02): 48-55+82 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 李彧,张力,高天涯,汪优. 富水砂层深基坑开挖风险分析及应对措施研究. 施工技术(中英文). 2025(05): 100-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 胡天亮. 基坑降水方案设计及地下水位变化规律研究. 江西建材. 2024(02): 206-208 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 林生凉. “两墙合一”地下连续墙在深部高承压水地区超深基坑工程中的应用研究. 福建建筑. 2024(06): 71-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 韩爱民. 软土地区紧邻地铁深基坑施工变形控制研究. 建筑施工. 2024(07): 1072-1075 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 张凯,顾宏. 邻近深基坑某老旧建筑基础加固综合治理. 中国水运(下半月). 2024(08): 137-139 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 蔡子勇. 坑底加固对深厚软土狭长基坑变形影响研究. 现代城市轨道交通. 2024(08): 75-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 李昭,陈勇. 软土地区现浇桩基坑监测管理分析. 四川建材. 2024(08): 86-87+103 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 陈文华,张玉山,刘际付,曾维楚. 深基坑混凝土支撑轴力监测与分析. 地基处理. 2024(04): 404-412+420 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 张恒瑞. 紧邻既有建筑物含流砂层深基坑管井降水施工技术研究. 江西建材. 2024(06): 337-340 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 赵攀. 大跨劲性骨架钢筋混凝土拱桥深基坑开挖稳定性分析. 智能城市. 2024(08): 111-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 何林南. 软土地区某复杂边界条件深大基坑支护设计与分析. 建筑施工. 2024(10): 1687-1692 .  百度学术
百度学术
26. 唐浩然,胡垚,雷华阳,路军富,刘婷,王凯. 基于深度学习的基坑开挖引起地表位移时序预测. 岩土工程学报. 2024(S2): 236-241 .  本站查看
本站查看
27. 王伟,邓松峰. 深厚软土区邻近地铁深基坑工程关键技术研究. 江苏建筑. 2024(05): 120-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
28. 张凯,顾宏. 邻近深基坑某老旧建筑基础加固综合治理. 中国水运. 2024(16): 137-139 .  百度学术
百度学术
29. 涂仁盼. 铁路枢纽深基坑混凝土支撑伺服系统应用研究. 铁道建筑技术. 2024(12): 14-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
30. 李迎春,钮玉萍. 地铁超深基坑变形控制成套技术. 江苏建筑. 2024(06): 104-107 .  百度学术
百度学术
31. 余希明. 桥梁基坑施工顺序对挡土墙安全受力特性的影响. 交通世界. 2024(36): 162-164 .  百度学术
百度学术
32. 刘力英,欧振锋,杨春山,段尚磊. 沉管基槽开挖诱发临岸结构变形数值模拟与实测分析. 隧道与地下工程灾害防治. 2024(04): 12-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
33. 孟旭,陈东霞,陈波,袁博. 滨海悬挂式止水帷幕深基坑非稳定渗流模型. 水资源与水工程学报. 2024(06): 149-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)



 下载:
下载: