Experimental study on comparison of consolidation creep characteristics between silty sand and silty soil
-
摘要: 为了解释基坑预降水引发的基坑周边地面沉降的滞后性,依托某地铁车站基坑预降水工程,开展场地中典型粉砂和粉土的一维固结蠕变试验。通过试验结果分析,得到土的压缩指数、回弹指数和次固结系数,给出了回弹指数与压缩指数和次固结系数与压缩指数的经验关系。蠕变试验结果表明,粉砂和粉土的次固结系数与固结荷载之间呈现良好的线性关系,提出了次固结系数与固结压力的经验公式。从固结压力下砂土天然结构破坏的角度,解释了次固结系数随着固结压力的增加而增大的原因,为解释预降水引起的基坑周边地面沉降滞后效应和地面沉降合理估算提供了实验依据。Abstract: In order to explain the lagging settlement in the surrounding ground induced by pre-dewatering of excavations, one-dimensional consolidation creep tests are conducted on typical silty sand and silty soil at a metro station site of Jiangsu Province. Based on the experimental results, the compression index, rebound index and secondary consolidation coefficient of the soil are obtained, and the empirical relationships between the rebound index and the compression index, as well as the secondary consolidation coefficient and the compression index, are given. The results of the creep tests demonstrate a well-defined linear relationship between the secondary consolidation coefficient and the consolidation load for both the silty sand and the silty soil, leading to the development of an empirical formula correlating the secondary consolidation coefficient with consolidation pressure. Furthermore, the increase in the secondary consolidation coefficient with rising consolidation pressure is explained from the perspective of the natural structural breakdown of the sandy soil under consolidation pressure. These findings provide valuable experimental evidence for understanding the lagging effects of ground settlement around the excavations induced by pre-dewatering and for the rational estimation of ground settlement.
-
Keywords:
- silty sand /
- silty soil /
- creep /
- secondary consolidation coefficient /
- compression index /
- swell index
-
0. 引言
长期以来黏性土的蠕变特性得到了更多的关注,而认为无黏性土的变形是瞬时完成的,忽略其蠕变特性。随着工程实践中对无黏性土变形机理认识的深化,发现无黏性土也存在蠕变变形。砂土的蠕变特性不仅得到室内试验所证实,也被现场变形监测数据所证实,由细砂和砂砾石组成的上海第4承压含水层,在水位基本保持不变、甚至略有回升的情况下,出现了砂土蠕变变形[1]。年廷凯等[2]以及Tong等[3]均发现不同含砂量的土体具有不可忽略的非线性蠕变特性。由此可见,工程实践中广泛存在的含砂粒的粉土和粉砂的蠕变特性也应值得关注。
本文依托的工程场地为河漫滩地貌,基坑开挖影响范围内主要分布有新近沉积的粉砂和粉土,粉砂呈稍密—中密状态,中低压缩性,粉土呈稍密状态,中压缩性。在基坑开挖前,坑内预降水期间观测到坑内停止抽水后,场地地下水位恢复过程中周边地面沉降却继续增加,呈现明显的滞后性。由于在预降水后相当长一段时间内场地中无任何造成地面沉降的施工活动。因此,对基坑场地中的粉砂和粉土开展了固结蠕变试验,以认识土的固结蠕变特性,为解释预降水引起的地面沉降和沉降滞后效应提供依据。
1. 固结蠕变试验条件与方案
1.1 试验条件
采用苏州拓测仪器设备有限公司生产的全自动气压固结仪开展了土的一维固结蠕变试验,试验用土采自现场基坑场地,场地岩土工程勘察报告提供土的物理力学参数,如表 1所示。
表 1 土的物理力学参数Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of soils土名 含水率w/% 重度γ/(kN·m-3) 孔隙比e 压缩模量Es1-2/MPa 渗透系数k/(cm·s-1) 黏聚力*c/kPa 内摩擦角*φ/(°) 粉砂 27.4 19.6 0.724 11.57 500×10-6 7.9 31.8 粉土 34.3 18.6 0.940 8.37 50×10-6 12.2 28.5 如图 1所示,粉砂中粒径大于0.075 mm的颗粒质量达到总质量的85.6%,粉土中大于0.075 mm的颗粒质量为总质量的37.3%,且塑性指数Ip为8.4。
1.2 试验方案
试验共采用4组8个试样,试样的直径61.8 mm,高20.0 mm,分别开展粉土和粉砂的固结试验和蠕变试验。为了减小试样差异带来的试验误差,采用了“双样平行”试验,试样的基本物理参数如表 2所示。
表 2 试样的基本物理参数Table 2. Basic physical parameters of samples序号 土样编号 含水率w/% 干密度ρd/(kg·m-3) 天然重度γ/(kN·m-3) 孔隙比e 1 S2 - 1Con 30.3 1.58 18.1 0.704 2 S2 - 2Con 30.6 1.57 18.1 0.723 3 F2 - 1Con 33.4 1.42 19.0 0.902 4 F2 - 2Con 35.3 1.41 19.0 0.915 5 S7 - 1Cre 31.8 1.57 18.1 0.720 6 S7 - 2Cre 33.0 1.54 18.1 0.748 7 F7 - 1Cre 35.0 1.43 19.0 0.887 8 F7 - 2Cre 35.0 1.43 19.0 0.893 注:以S1 - 1Con为例说明试样编号,S代表土样为粉砂,F代表粉土,上标1-1代表第一种加载模式下第一个土样,下标Con为consolidation简写,代表固结试验,下标Cre为creep的简写,代表蠕变试验。 固结试验采用加荷和卸荷两种加载模式,以探讨土的加荷压缩变形和卸荷回弹变形特性。蠕变试验采用分级加载方式,以探讨不同压力下土的蠕变变形特性。试验加载方案如表 3所示。
表 3 试验加载方案Table 3. Loading schemes for tests组号 土类 土样编号 试验方法 试验荷载/kPa 1 粉砂 S2 - 1Con S2 - 2Con 固结试验 50—400—50—400—800 2 粉土 F2 - 1Con F2 - 2Con 3 粉砂 S7 - 1Cre S7 - 2Cre 分级蠕变试验 100,200,400,800 4 粉土 F7 - 1Cre F7 - 2Cre 试验按《土工试验方法标准》(GB/T50123—2019)进行,一维固结试验稳定标准规定为试样变形每小时变化不大于0.01 mm。参考文献[4]给出的黏性软土蠕变试验稳定标准,本次蠕变试验稳定标准采用24 h内试样变形量小于0.01 mm。
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 土的固结变形特性
为了确定粉砂和粉土的固结变形特性,分别对粉砂和粉土开展了加、卸载模式的固结试验,以确定反映土体变形的压缩指数和回弹指数。
粉砂和粉土的固结试验结果如图 2所示,试验在加载过程中土产生压缩变形,卸载导致土发生回弹变形,但回弹变形量明显小于压缩变形量,粉砂和粉土的平均回弹率分别为18.8%和16.3%,说明了粉砂和粉土在固结压力作用下以塑性变形为主,呈现弹塑性变形特性。加卸载过程形成了回滞环,表明了加卸载过程存在能量损失,导致土体进一步压缩变形,再加载至压力400 kPa时,孔隙比要小于卸载时的孔隙比。随着固结压力的继续增加,土的e-lgp曲线呈现线性关系。粉砂和粉土压缩系数和回弹指数如表 4所示。
表 4 压缩指数和回弹指数Table 4. Compression and rebound indices土类 试样编号 Cc Cs 粉砂 S2 - 1Con 0.092 0.010 S2 - 2Con 0.090 0.010 粉土 F2 - 1Con 0.138 0.015 F2 - 2Con 0.156 0.014 2.2 土的蠕变变形特性
土的主固结压缩变形完成后,土进一步发生次固结变形。为了获得粉砂和粉土在恒定荷载下的蠕变特性,分别对粉砂和粉土开展了分级蠕变试验。
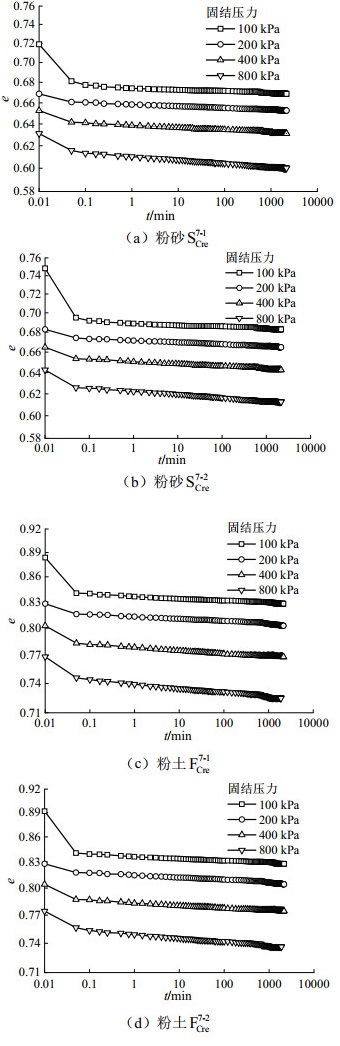
图 3给出了粉砂和粉土的e-lgt曲线,由于粉砂和粉土的渗透性相对较好,主固结结束时间短,加载初期的压缩变形较大,主固结变形结束后进入次固结变形阶段,粉砂和粉土的次固结变形占比的平均值(不同固结压力)分别11.5%和12.2%,明显比软土次固结变形占比(均超过20%[5])要小。
次固结变形是在恒定应力作用下发生的,通常采用次固结系数定量描述次固结变形特性,次固结系数Ca定义为
Ca=Δelg(t2/t2t1)t1), (1) 式中,Δe为时间t1与t2间土的孔隙比变化量,t1和t2为次固结过程中的时刻。
根据分级蠕变试验得到的次固结阶段e-lgt曲线,由公式(1)确定的次固结系数如表 5所示。从表 5中给出的次固结系数与固结压力关系可知,粉砂和粉土的次固结系数均随着固结荷载的增加而增大。粉砂的次固结系数介于0.0013~0.0029之间,粉土的次固结系数介于0.0023~0.0039之间。此外,相同固结压力下,粉土的次固结系数大于粉砂的次固结系数,由此说明了土中黏粒含量对土的蠕变变形特性的影响。
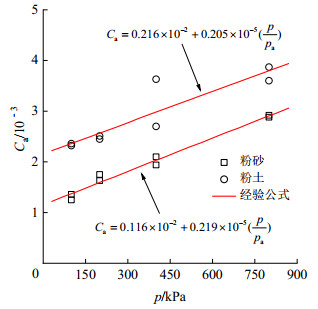
表 5 次固结系数CaTable 5. Coefficients of secondary consolidation Ca固结压力p/kPa 粉砂 粉土 SCre7-1 SCre7-2 FCre7-1 FCre7-2 100 0.0 013 0.0 014 0.0 024 0.0 023 200 0.0 016 0.0 018 0.0 025 0.0 025 400 0.0 019 0.0 021 0.0 036 0.0 027 800 0.0 029 0.0 029 0.0 039 0.0 036 如图 4所示,次固结系数与固结压力呈现良好的线性关系,通过回归分析,得到了粉砂与粉土的次固结系数Ca与固结压力p的关系:
粉砂:Ca=0.116×10−2+0.219×10−5(ppa), (2) 粉土:Ca=0.216×10−2+0.205×10−5(ppa), (3) 式中,p为固结压力(kPa),pa为大气压力(Pa)。
上述经验公式可为类似场地中粉砂和粉土的次固结系数合理取值提供参考。
2.3 Ca与Cc的关系
Mesri等[6]认为Ca和Cc都受有效应力的影响,Ca和Cc之间存在唯一关系,并给出了原状黏性土的Ca/Cc经验值。已有研究成果显示[7],砂土也具有类似特性,对于低黏粒含量的砂土,Ca/Cc的变化范围在0.010至0.030之间[8]。本次试验结果表明,不同压力下粉砂的Ca/Cc变化范围在0.014至0.032之间,粉土的Ca/Cc变化范围在0.016至0.026之间。
Mesri等[6]将Ca/Cc应用于实际工程的次固结沉降预测计算,并利用次固结沉降的长期观察资料验证了其合理性。在在实际工程中,可以根据Ca与Cc的关系,预测地基的工后沉降。
2.4 次固结系数讨论
本次试验发现了砂土和粉土的次固结系数随着固结压力的增加而增大的规律,这一规律在软土的次固结系数研究中同样存在[9],张先伟等[4]通过原状软土与重塑土的对比试验,从固结压力p作用下软土天然结构的屈服过程解释了这一现象产生的原因。
本次试验采用的粉砂和粉土试样均为原状土,保留了土体沉积过程中形成的天然结构。与天然软土不同之处在于,粒径大于0.075 mm的砂粒含量高,土的结构形式不同,土的变形源于土的结构变化。以粉砂为例,在固结压力p作用下,土的天然结构开始逐渐屈服,土颗粒除了粒间滑移外,还伴随着土骨架的压密坍塌,两者造成了土的天然结构逐渐破坏,使得土的压缩变形明显增大,直至土的天然结构完全破坏。其后,土的压缩变形随着 p的进一步增加而增大,但颗粒间滑移成为压缩变形主要原因,且压缩变形增量减小,并渐趋稳定。
相较于软土的次固结系数的变化规律[4],由此推断,粉砂在土骨架压密坍塌阶段,出现次固结系数Ca随固结压力p的增加而增大现象,并在天然土骨架完全破坏时,Ca达到最大值。在其后的颗粒间滑移阶段,次固结系数Ca与随固结压力增加而减小或基本维持不变。由于本次试验固结压力p是根据正常工程应力范围取值,最大值为800 kPa,因此,仅得到了次固结系数Ca随着固结压力p的增加而增大的规律,对粉砂和粉土在高压固结压力下的蠕变特性还需进一步探索。
3. 结论
为了解释基坑预降水引起的基坑周边地面沉降时间效应,采用某地铁车站基坑场地典型的河漫滩原状粉砂和粉土,开展了土的固结试验和蠕变试验。
(1)通过固结试验,得到了压缩指数Cc与回弹指数Cs之间的近似关系,粉砂Cs≈1/9Cc,粉土Cs≈1/10Cc,可为类似场地土回弹指数Cs取值提供参考。
(2)蠕变试验表明,次固结系数与固结荷载之间呈现良好的线性关系,提出了次固结系数与固结压力的经验公式。
(3)给出了不同压力下粉砂和粉土的Ca/Cc范围,粉砂的Ca/Cc在0.014至0.032之间,粉土的Ca/Cc在0.016至0.026之间。可为地基土的固结沉降和蠕变沉降估算提供合理的计算参数。
(4)从固结压力下砂土天然结构破坏的角度,分析了土的结构性与次固结系数的关系,解释次固结系数随着固结压力的增加而增大的原因,对高压固结下砂土次固结系数的变化规律推测有待进一步验证。
-
表 1 土的物理力学参数
Table 1 Physical and mechanical parameters of soils
土名 含水率w/% 重度γ/(kN·m-3) 孔隙比e 压缩模量Es1-2/MPa 渗透系数k/(cm·s-1) 黏聚力*c/kPa 内摩擦角*φ/(°) 粉砂 27.4 19.6 0.724 11.57 500×10-6 7.9 31.8 粉土 34.3 18.6 0.940 8.37 50×10-6 12.2 28.5 表 2 试样的基本物理参数
Table 2 Basic physical parameters of samples
序号 土样编号 含水率w/% 干密度ρd/(kg·m-3) 天然重度γ/(kN·m-3) 孔隙比e 1 S2 - 1Con 30.3 1.58 18.1 0.704 2 S2 - 2Con 30.6 1.57 18.1 0.723 3 F2 - 1Con 33.4 1.42 19.0 0.902 4 F2 - 2Con 35.3 1.41 19.0 0.915 5 S7 - 1Cre 31.8 1.57 18.1 0.720 6 S7 - 2Cre 33.0 1.54 18.1 0.748 7 F7 - 1Cre 35.0 1.43 19.0 0.887 8 F7 - 2Cre 35.0 1.43 19.0 0.893 注:以S1 - 1Con为例说明试样编号,S代表土样为粉砂,F代表粉土,上标1-1代表第一种加载模式下第一个土样,下标Con为consolidation简写,代表固结试验,下标Cre为creep的简写,代表蠕变试验。 表 3 试验加载方案
Table 3 Loading schemes for tests
组号 土类 土样编号 试验方法 试验荷载/kPa 1 粉砂 S2 - 1Con S2 - 2Con 固结试验 50—400—50—400—800 2 粉土 F2 - 1Con F2 - 2Con 3 粉砂 S7 - 1Cre S7 - 2Cre 分级蠕变试验 100,200,400,800 4 粉土 F7 - 1Cre F7 - 2Cre 表 4 压缩指数和回弹指数
Table 4 Compression and rebound indices
土类 试样编号 Cc Cs 粉砂 S2 - 1Con 0.092 0.010 S2 - 2Con 0.090 0.010 粉土 F2 - 1Con 0.138 0.015 F2 - 2Con 0.156 0.014 表 5 次固结系数Ca
Table 5 Coefficients of secondary consolidation Ca
固结压力p/kPa 粉砂 粉土 SCre7-1 SCre7-2 FCre7-1 FCre7-2 100 0.0 013 0.0 014 0.0 024 0.0 023 200 0.0 016 0.0 018 0.0 025 0.0 025 400 0.0 019 0.0 021 0.0 036 0.0 027 800 0.0 029 0.0 029 0.0 039 0.0 036 -
[1] 张云, 薛禹群, 李勤奋. 上海现阶段主要沉降层及其变形特征分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2003, 30(5): 6-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.05.002 ZHANG Yun, XUE Yuqun, LI Qinfen. Current prominent subsidence layer and its deformation properties in Shanghai[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2003, 30(5): 6-11. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.05.002
[2] 年廷凯, 余鹏程, 柳楚楠, 等. 吹填粉砂土固结蠕变试验及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(3): 918-924. NIAN Tingkai, YU Pengcheng, LIU Chunan, et al. Consolidation creep test and creep model of dredger fill silty sand[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2014, 44(3): 918-924. (in Chinese)
[3] TONG F, YIN J H. Nonlinear creep and swelling behavior of bentonite mixed with different sand contents under oedometric condition[J]. Marine Georesources and Geotechnology, 2011, 29: 346-363. doi: 10.1080/1064119X.2011.560824
[4] 张先伟, 王常明. 软土结构性对次固结系数的影响[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(2): 476-482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.02.025 ZHANG Xianwei, WANG Changming. Effect of soft soil structure on secondary consolidation coefficient[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(2): 476-482. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.02.025
[5] 张义德, 孙红, 牛富俊. 武汉软土次固结特性及其演变分析[J]. 甘肃科学学报, 2023, 35(6): 85-91. ZHANG Yide, SUN Hong, NIU Fujun. Analysis on characteristics and evolution of the secondary consolidation of Wuhan soft soil[J]. Journal of Gansu Sciences, 2023, 35(6): 85-91. (in Chinese)
[6] MESRI G, GODLEWSKI P M. Time-and stress- compressibility interrelationship[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division, 1977, 103(5): 417-430. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0000421
[7] MITCHELL J K, SOGA K. Fundamentals of Soil Behaviour[M]. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2005.
[8] KNAPPETT J A, CRAIG R F. Craig's Soil Mechanics[M]. 9th ed. New York: CRC Press, 2020.
[9] 余湘娟, 殷宗泽, 董卫军. 荷载对软土次固结影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007, 29(6): 913-916. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.06.021 YU Xiangjuan, YIN Zongze, DONG Weijun. Influence of load on secondary consolidation deformation of soft soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(6): 913-916. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.06.021



 下载:
下载: