Influences of antecedent rainfall and change of reservoir water level on seepage and stability characteristics of earth rock dams
-
摘要: 气候变化给水库大坝安全运行管理带来前所未有的挑战,前期降雨、库水位变化是影响坝坡失稳的关键因素,且碾压式土石坝设计规范未考虑降雨对大坝坝坡或浅层坝坡稳定性的影响,水库大坝滑坡或溃坝严重威胁人民的生命安全并造成巨大经济损失。以某水库心墙坝为研究对象,建立了有限元计算模型,研究了前期降雨、库水位变化对心墙坝渗流和稳定特性的影响,揭示了孔隙水压力、渗透比降和坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数的变化规律,并结合高密度电法和安全监测资料验证了计算模型的准确性。研究结果表明:前期降雨对大坝坝坡浅层范围孔隙水压力和抗滑稳定安全系数影响较大,对下游坝坡孔隙水压力影响程度由大到小依次为坡顶 > 坡肩(坡脚),随着降雨量增加下游坝坡10 m范围内孔隙水压力逐渐增大,坝坡表层土体达到饱和,主降雨后下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数减小较大;计算模型的浸润线高程与高密度电法、测压管水位高程均吻合,验证了计算模型的准确性;库水位是影响上游坝坡孔隙水压力和抗滑稳定安全系数的主要因素,对上游坝坡孔隙水压力影响程度由大到小依次为坡脚 > 坡肩 > 坡顶,降雨是导致下游坝坡孔隙水压力和抗滑稳定安全系数变化的主要因素;综合计算模型、高密度电法和安全监测资料,较好地分析了心墙坝孔隙水压力、渗透比降和抗滑稳定安全系数的变化规律,分析前期降雨、库水位变化为完善土石坝设计规范和水库大坝安全评价提供了科学依据。Abstract: The climate change has brought unprecedented challenges to the safe operation and management of reservoir dams. The antecedent rainfall and change of reservoir water level are the key factors affecting the instability of reservoir dam slopes, and the impact of rainfall on the stability of dam slopes or shallow dam slopes is not considered in the existing design code for rolled earth-rock fill dams. The landslide or dam break of reservoir dams seriously threatens human lives and causes huge economic losses. Taking the core wall dam of a reservoir as the research object, a finite element model is established, the influences of the antecedent rainfall and change of reservoir water level on the seepage and stability characteristics of the core wall dam are investigated, the variation rules of pore water pressure, hydraulic gradient and safety factor of anti-sliding stability of the dam slope are released, and the accuracy of the model is verified by using the high-density electrical method and the safety monitoring data. The research results show that the antecedent rainfall has a great impact on the pore water pressure and safety factor of anti-sliding stability in the shallow depth of the dam slope. The influence degree of the antecedent rainfall on the pore water pressure of the downstream dam slope has the descending order: slope top, slope shoulder and slope toe. With the increase of the antecedent rainfall, the pore water pressure within 10 m of the downstream dam slope gradually increases, and the surface soil of the downstream dam slope reaches the saturated state. After the main rainfall, the safety factor of anti-sliding stability of the downstream dam slope greatly decreases. The phreatic line elevation of the proposed model is consistent with the measured water level using the high-density electrical method and the piezometric tube, which verifies its accuracy. The reservoir water level is the main factor affecting the pore water pressure and safety factor of anti-sliding stability of the upstream slope. The influence degree on the pore water pressure of the upstream slope of the dam is in the descending order of slope toe, slope shoulder and slope top. The rainfall is the main factor inducing the change of pore water pressure and affecting the safety factor and anti-sliding stability of the downstream slope. The comprehensive model, high-density electrical method and safety monitoring data can be used to better analyze the change laws of pore water pressure, seepage gradient and safety factor of core wall dam. The analyses of the effects of the antecedent rainfall and change of reservoir water level provide a scientific basis for improving the design specifications of earth-rock dams and the safety evaluation of reservoir dams.
-
0. 引言
气候变化对水利工程,尤其对水库大坝工程产生愈发明显的不利影响已成为不争的事实[1-2]。近年来,降雨和库水位变化诱发水库大坝坝坡失稳现象时有发生[3-4]。2021年7月17日—23日,河南省遭遇历史罕见特大暴雨,发生了严重洪涝灾害,造成重大人员伤亡和特别重大自然灾害,其中,郑州市五星水库在经历数天强降雨后,累计降雨量779.80 mm,达到历史极值,最高库水位218.80 m,超汛限水位(216.00 m)2.80 m,导致下游坝坡发生3处坍塌,出现了明显裂缝。2018年8月21日,青海省石门水库突降大雨,降雨后运行管理人员发现大坝下游坝脚出现数条裂缝,裂缝走向平行坝轴线。因此,研究降雨、库水位变化作用对大坝渗流、稳定和浅层坝坡稳定特性的影响具有重要意义。
降雨是滑坡失稳的主要诱发因素,据统计,20世纪80年代以来,中国大陆发生的大型灾害性滑坡中,约50%由强降雨诱发[5],降雨型滑坡已成为国内外工程地质界的研究热点。Rahardjo等[6]通过室内模型试验探讨了不同降雨条件下,土壤性质、降雨强度、初始水位位置和边坡几何形状在诱发均质土边坡失稳中的重要性。唐栋等[7]基于三峡库区实测降雨资料,采用Geo-studio研究了不同初始条件对砂土和黏土边坡稳定性影响,建议了能够反映边坡含水状态的初始条件选取方法。李卓等[8]基于云南省龙江水电站近坝库岸边坡滑坡区实测降雨资料,通过自行研制模型试验装置,进行前期降雨作用下室内边坡滑坡模型试验,分析了前期降雨作用下的边坡滑坡特性。库水位变化是导致滑坡产生的重要因素,研究库水位变化与边坡稳定性之间的关系,可以有效地减少滑坡灾害的发生。Jia等[9]通过大型模型试验,模拟了砂质土边坡在水位升降作用下的边坡稳定性,在模拟过程中记录了孔隙水压力、总土压力、滑动面和滑坡过程,研究结果对饱和-非饱和土边坡在水位升降作用下的物理特性和破坏模式提供了更好的理解。
近年来,降雨和库水位变化诱发近坝岸坡滑坡引起了国内外广泛的关注。Jian等[10]对三峡库区某边坡进行了数值模拟,根据滑坡的特征和工程条件,重建了滑坡前边坡的地形和地质剖面,查明了滑坡产生的原因。李卓等[11]根据云南省龙江水电站近坝库岸边坡滑坡特点,进行了降雨与库水位共同作用下边坡滑坡大型模型试验研究,揭示了边坡滑坡机理。Sun[12]等采用刚体极限平衡法对周期性降雨和库水位变化作用下库岸滑坡长期稳定性进行了研究。
综上,降雨、库水位变化对近坝岸坡或边坡渗流和稳定性影响的研究已较多,但有关降雨、库水位变化对水库大坝坝坡渗流和稳定性影响的研究较少。《碾压式土石坝设计规范》[13]仅考虑了库水位骤降工况下大坝整体抗滑稳定性,且其在量化研究方面较少,同时未考虑降雨对大坝坝坡或浅层坝坡稳定性影响。考虑前期降雨、库水位变化作用下水库大坝坝坡或浅层坝坡渗流和稳定性的数值模拟与工程验证尚未见报道。因此,研究降雨、库水位变化作用下水库大坝坝坡渗流和稳定特性影响对补充相关规范和水库大坝安全运行都具有重要意义。本文以某心墙坝为研究对象,采用Geo-studio建立有限元数值模型,基于实测降雨资料,研究了前期降雨、库水位变化作用下孔隙水压力、渗透比降和抗滑稳定安全系数的变化规律,并结合高密度电法和安全监测资料验证了模型的准确性。
1. 非饱和渗流与边坡稳定性分析理论
1.1 非饱和土渗流方程
实践证明达西定律适用于非饱和土中水的流动。将降雨入渗作为非饱和带的渗流边界,采用饱和-非饱和渗流理论进行模拟。根据质量守恒原理,非饱和土的渗流方程为[14]
$$ \frac{\partial }{{\partial x}}\left( {{k_x}\frac{{\partial H}}{{\partial x}}} \right) + \frac{\partial }{{\partial y}}\left( {{k_y}\frac{{\partial H}}{{\partial y}}} \right) + Q = {m_{\text{w}}}{\gamma _{\text{w}}}\frac{{\partial H}}{{\partial t}} \text{,} $$ (1) 式中,H为总水头,kx为x方向的渗透系数,ky为y方向的渗透系数,Q为施加的边界流量,mw为储水曲线的斜率,γw为水的重度,t为时间。
有限元方程求解的边界条件:
(1)初始条件
$$ H(x,y,0)={H}_{0} \quad\quad ((x,y)\in \mathit{\Omega} ) \text{,} $$ (2) 式中,H0为初始总水头,Ω为模型的计算面积。
(2)边界条件
$$ H(x,y,t) = {H_t} \quad\quad ((x,y) \in {S_1}) \text{,} $$ (3) $$ k\frac{{\partial H}}{{\partial n'}}\left| {{S_2}} \right. = q(x,y,t) \quad\quad ((x,y) \in {S_2}) \text{,} $$ (4) 式中,Ht为随时间变化的节点水头,k为渗透系数,S1,S2分别为已知水头、流量边界,n′为渗流面法线方向,q(x, y, t)为随时间变化的节点流量。
1.2 非饱和土抗剪强度
非饱和土的抗剪强度公式为[15]
$$ \tau = c' + (\sigma - {u_{\text{a}}})\tan \phi ' + ({u_{\text{a}}} - {u_{\text{w}}})\tan {\phi ^{\text{b}}} \text{,} $$ (5) 式中,τ为抗剪强度,c′为有效黏聚力,$ \sigma $为正应力,ua为孔隙气压力,ϕ′为有效内摩擦角,uw为孔隙水压力,ϕb为与基质吸力(ua-uw)相关的内摩擦角。
1.3 坝坡稳定分析
Bishop提出了一种仅考虑土条间法向力,不考虑土条间剪切力的安全系数计算方法。Bishop法求解边坡安全系数的公式为[16]
$$ {F}_{\text{S}}=\frac{\sum \left({c}^{\prime }\beta R+\left[N-{u}_{\text{w}}\beta \frac{\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }^{\text{b}}}{\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }^{\prime }}-{u}_{a}\beta \left(1-\frac{\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }^{\text{b}}}{\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }^{\prime }}\right)\right]R\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }^{\prime }\right)}{\sum Wx-\sum Nf\pm \sum Dd\pm \sum Aa}\text{,} $$ (6) $$ N=\frac{W-\frac{\left[{c}^{\prime }\beta \mathrm{sin}\alpha +{u}_{\text{a}}\beta \mathrm{sin}\alpha (\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }^{\prime }-\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }^{\text{b}})+{u}_{\text{w}}\beta \mathrm{sin}\alpha \mathrm{tan}{\varphi }^{\text{b}}\right]}{{F}_{\text{s}}}+D\mathrm{sin}\omega }{\mathrm{cos}\alpha +\frac{\mathrm{sin}\alpha \mathrm{tan}{\varphi }^{\prime }}{{F}_{\text{s}}}}\text{,} $$ (7) 式中,Fs为安全系数,$ \beta $为每一条块的底面长度,R为圆弧滑面的半径或与滑动剪力相关的力臂,N为作用在每一条块底部上的总法向力,W为条块重量,x为从每一条块中心线到旋转中心或力矩中心的水平距离,f为法向力与旋转中心或者力矩中心的垂直偏移量,D为外加线荷载,d为从点荷载到旋转中心或力矩中心的垂直距离,A为合成的外部水压力,a为从合成的外部水压力到旋转中心或力矩中心的垂直距离,α为每一条块底面中心切线与水平面的夹角,ω为点荷载与水平面的夹角。
2. 工程概况
某心墙坝于1977年建成,水库总库容1.03×108 m3,设计灌溉面积1.36×108 m2。工程等别为Ⅱ等,工程规模为大(2)型。洪水标准采用500 a一遇洪水设计,1.0×104 a一遇洪水校核,泄洪建筑物消能防冲按50 a一遇洪水设计。设计采用抗震设防烈度为6度。
某水库是一座以防洪、灌溉为主,兼有发电、城镇供水和生态补水等综合效益的水库。工程由大坝、溢洪道、泄洪隧洞、灌溉输水涵管等组成。大坝为黏土心墙坝,坝顶高程112.00 m,坝顶长335.00 m,坝顶宽8.00 m,最大坝高53.00 m。溢洪道位于大坝左岸,长320.00 m。泄洪隧洞位于大坝左侧山体,控制下泄流量30~80 m3/s。灌溉发电输水管位于大坝右岸。上游坝坡坡比由上至下依次为1︰2.5,1︰2.75,1︰4,1︰4,1︰4,1︰3.5,1︰3,下游坝坡坡比由上至下依次为1︰2.288,1︰4.5,1︰1.5,1︰1.5,1︰1.5。
2012年大坝安全鉴定表明,坝体渗透系数较大,坝基基岩破碎,并存在岩溶和多条断层破碎带,坝体和坝肩存在绕渗等问题。2017年,针对水库的病险情况,对水库进行了除险加固,主要建设内容为混凝土防渗墙和帷幕灌浆。
上下游坝体代料均为黏土夹碎(砾)石。心墙填土为高液限黏土夹碎(砾)石。防渗墙墙体采用强度等级为C20混凝土,混凝土抗渗等级为W8。帷幕灌浆灌注材料以水泥灌浆为主,使用强度等级PO42.5级硅酸盐水泥。在上游坡高程95.00 m平台以下至坝基设有36 m高的抛石,其岩性为灰岩,直径约为30~40 cm。在下游坡高程87.00 m平台以下至坝基设有28 m高的三级坡堆石排水陵体,其岩性为灰岩,直径约为30~40 cm。坝址区出露地层岩性多为寒武系中统结晶白云岩,部分夹泥晶白云岩条带,属较强岩溶化岩层,岩溶较为发育。
3. 有限元计算模型
3.1 模型及边界条件
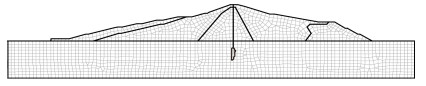
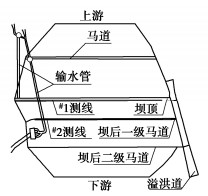
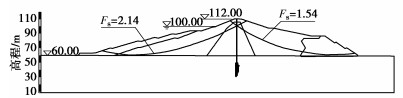
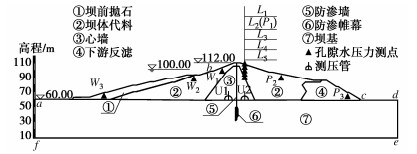
根据某心墙坝桩号0+072典型剖面图,采用Geo-studio建立有限元计算模型,模型和测点布置见图 1,模型网格共划分为2931个节点和2816个单元,数值模拟模型网格剖分见图 2。
模型边界条件:上游坝坡ab为库水位变动边界,bc在有降雨时为流量边界,根据实测资料和现场检测,心墙坝下游无水,故cd为下游水头边界,defa为不透水边界。
3.2 材料参数
某心墙坝坝体分区材料物理力学参数采用地勘报告建议值,见表 1。
表 1 坝体分区材料物理力学参数表Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of dam partition坝体分区 渗透系数/(cm·s-1) 饱和含水率/% 重度/(kN·m-3) 有效黏聚力/kPa 有效内摩擦角/(°) 坝前抛石 1.00×10-3 52.0 21.0 0 35.0 坝体代料 1.43×10-4 40.0 18.5 20.0 16.8 心墙 9.82×10-5 40.0 18.4 23.0 16.5 下游反滤 1.00×10-3 52.0 19.0 0 35.0 坝基 9.62×10-5 36.0 28.7 100.0 45.0 防渗墙 1.00×10-7 2.0 24.0 500.0 35.0 防渗帷幕 1.00×10-7 2.0 24.0 500.0 35.0 3.3 计算工况
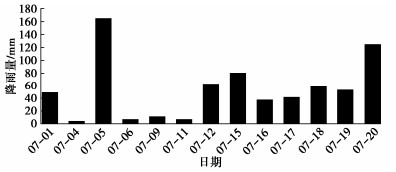
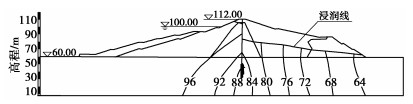
根据某水库实测降雨资料,多年平均降雨量1563 mm,降雨量年内分布不均,4月—10月降雨量占全年降雨量的83%,7月份最大,占全年降雨量的18.2%,降雨量最小为1月份,仅占全年降雨量的1.6%。本文基于2010年—2021年实测降雨资料,选取2020年降雨量最大的7月份作为极端降雨条件下的渗流边界条件,将其设为最不利降雨工况,并根据降雨过程将最不利降雨工况分为2个阶段,其中2020年7月1日—14日为前期降雨阶段,2020年7月15日—20日为主降雨阶段。根据水库实际运行工况,选取了库水位的下降速率。降雨量过程线见图 3,计算工况见表 2。
表 2 计算工况表Table 2. Working conditions计算工况 库水位/m 骤变速率/(m·d-1) 降雨类型 工况一 100.00 — 最不利降雨 工况二 100.00~78.00 1 — 工况三 2 — 工况四 4 — 工况五 100.00~78.00 1 最不利降雨 工况六 2 最不利降雨 工况七 4 最不利降雨 注:2020年7月降雨开始前的初始库水位为100.00 m,死水位为78.00 m。 4. 结果分析
4.1 孔隙水压力分析
(1)前期降雨作用下心墙坝孔隙水压力分析
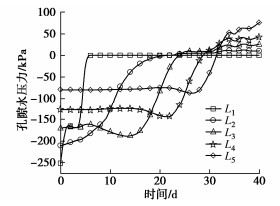
在心墙坝上下游坝坡坡顶、坡肩和坡脚距地表面5 m处各布置1个测点,另外在坝顶距离坡表面每隔5 m设置一个测点,其中上游坝坡测点由上到下依次为W1,W2和W3,下游坝坡测点由上到下依次为P1,P2和P3,坝顶测点由上到下依次为L1,L2,L3,L4和L5。测点布置示意图见图 1。
前期降雨作用下心墙坝孔隙水压力变化见图 4。由图可知,0 h时L1,L2,L3,L4,L5测点的孔隙水压力分别为-252.15,-211.25,-170.83,-127.08,-79.98 kPa。7月1日降雨量为49.1 mm,对应上述不同深度测点的孔隙水压力分别为-160.72,-208.10,-168.23,-127.56,-79.94 kPa,由于降雨量小于坝体代料的渗透系数123.552 mm/d,降雨全部入渗,入渗深度约为5 m。7月5日降雨量为164.7 mm,对应上述不同深度测点的孔隙水压力分别为0,-191.56,-161.05,-128.56,-79.70 kPa,此时,降雨量大于坝体代料的渗透系数,坝坡表层土体达到饱和状态,降雨入渗导致坝坡表层0~5 m范围的土体孔隙水压力快速增大。
7月12日降雨量为63.1 mm,对应上述不同深度测点孔隙水压力分别为0,-72.21,-170.34,-124.62,-78.81 kPa。7月15日—20日为主降雨期,降雨后不同深度测点孔隙水压力分别为0,-1.62,-82.52,-141.69,-75.26 kPa,随着前期降雨增加下游坝坡10 m范围内孔隙水压力逐渐增大,下游坝坡表层土体始终处于饱和状态。
降雨结束20 d后,对应上述不同深度测点孔隙水压力分别为0,10.71,25.22,43.44,75.99 kPa,与0 h相比孔隙水压力分别增大了252.15,221.96,196.04,177.52,155.98 kPa。由此可知,前期降雨对大坝坝坡浅层范围孔隙水压力影响最大,随着降雨入渗,大坝坝坡表层均达到饱和状态,降雨对大坝坝坡的影响深度达到25 m,接近计算浸润线,整个坝体趋于饱和。
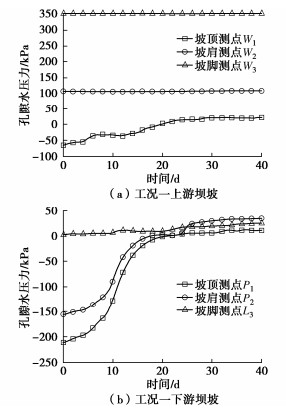
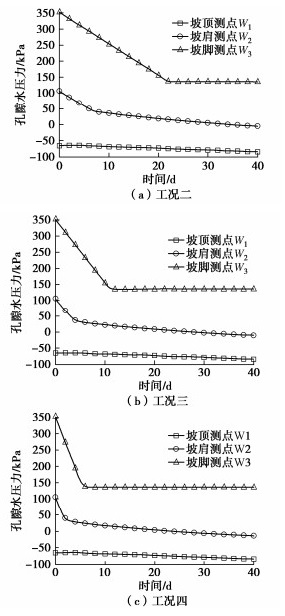
前期降雨作用下上游坝坡孔隙水压力变化见图 5(a)。由图可知,0 h时W1测点孔隙水压力为-65.12 kPa,前期降雨开始后W1测点孔隙水压力缓慢增大;7月5日降雨164.7 mm后,W1测点孔隙水压力为-43.79 kPa,增量为10.72 kPa;7月12日降雨63.1 mm后,W1测点孔隙水压力为-36.52 kPa,孔隙水压力有明显增大趋势,并持续至主降雨期,随后孔隙水压力逐渐稳定;W2和W3测点孔隙水压力变化不大。前期降雨对上游坝坡孔隙水压力影响程度由大到小依次为坡顶 > 坡肩(坡脚)。主要是由于降雨入渗导致W1测点孔隙水压力逐渐增大,降雨强度越大,W1测点孔隙水压力变化越明显,W2,W3测点高程均低于库水位,孔隙水压力与降雨相关性不明显。
前期降雨作用下下游坝坡孔隙水压力变化见图 5(b)。由图可知,P1,P2测点孔隙水压力变化呈现缓增、激增和稳定3个阶段,增量分别为221.96,190.69 kPa,P3测点孔隙水压力变化不大,这是因为P3测点高程低于浸润线高程,前期降雨对浸润线高程抬升较小,因此对P3测点孔隙水压力影响不大。7月5日降雨164.7 mm后,P1,P2测点孔隙水压力急剧增大,表明降雨强度越大,坝坡浅层土体孔隙水压力反应越明显。降雨对下游坝坡孔隙水压力影响程度由大到小依次为坡顶 > 坡肩 > 坡脚。
前期降雨导致心墙坝坝体孔隙水压力不断增大的主要原因是随着前期降雨的增加,浅层土体达到饱和状态,形成暂态饱和区,降雨结束后,原降雨入渗影响区(孔隙水压力增大区域)雨水在重力势能和基质势能综合作用下不断向坝体内部入渗,即湿润锋不断向坝体内部移动,导致不同深度坝体孔隙水压力响应时间滞后于前期降雨,且滞后时间随着距坝顶距离的增加而增加。
不同深度坝体孔隙水压力对前期降雨的响应程度是不同的。坝坡浅层土体(0~5 m)孔隙水压力变化幅度较明显,且孔隙水压力的响应程度随着距坝顶距离的增加而减小,这解释了实际工程中降雨通常诱发浅层滑坡的现象。
(2)库水位变化对心墙坝孔隙水压力影响分析
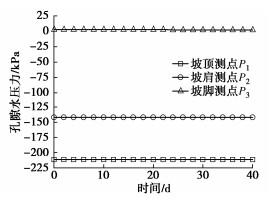
库水位变化作用下上游坝坡孔隙水压力变化见图 6。由图 6可知:W1测点孔隙水压力变化不大;W2测点孔隙水压力在库水位骤降时快速减小,当库水位下降至低于W2测点高程时,W2测点孔隙水压力开始以较慢速率减小;W3测点孔隙水压力在库水位骤降时先以较快速率减小,当库水位停止下降时,孔隙水压力也停止变化。库水位变化对上游坝坡孔隙水压力影响程度由大到小依次为坡脚 > 坡肩 > 坡顶;库水位下降越快,W2,W3测点孔隙水压力变化幅度也越大。
库水位变化作用下下游坝坡孔隙水压力变化见图 7。由图 7可知,工况二、工况三、工况四不同库水位骤降速率对下游坝坡孔隙水压力基本没有影响。
(3)前期降雨和库水位变化共同作用下心墙坝孔隙水压力分析
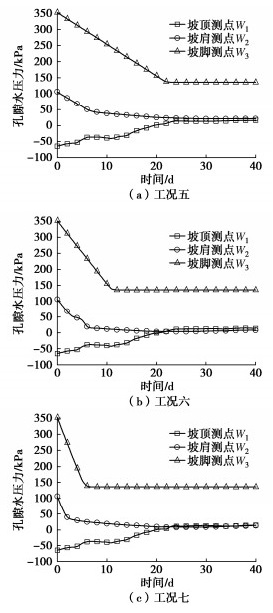
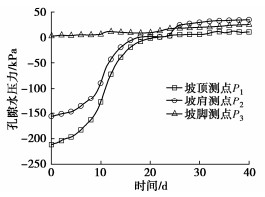
前期降雨和库水位变化共同作用下心墙坝上游坝坡孔隙水压力变化见图 8。由图 8可知,W1测点孔隙水压力主要受降雨入渗影响,孔隙水压力不断增大,W2,W3测点孔隙水压力主要受库水位影响,孔隙水压力不断减小。
前期降雨和库水位变化共同作用下心墙坝下游坡孔隙水压力变化见图 9。由于工况五、工况六、工况七作用下下游坝坡孔隙水压力变化差别不大,因此选取工况五作为典型工况进行分析。由图 9可知,P1,P2,P3测点孔隙水压力主要受降雨入渗影响,孔隙水压力呈增大趋势。
前期降雨和库水位变化共同作用对上游坝坡孔隙水压力的影响与库水位变化对上游坝坡孔隙水压力的影响差别不大,仅在上游坝坡降雨边界存在明显差异;前期降雨与库水位变化共同作用对下游坝坡孔隙水压力的影响与前期降雨对下游坝坡孔隙水压力的影响差别不大。因此,库水位变化是影响上游坝坡孔隙水压力的主要因素,而前期降雨是导致下游坝坡孔隙水压力变化的主要因素。
(4)高密度电法探测结果分析验证
为验证计算模型的准确性,采用高密度电法在大坝坝顶及下游坝坡布置了2条测线,分别位于坝顶下游侧(防渗墙后)、坝后一级马道,对坝体渗漏进行了检测。探测时间为2018年10月29日—11月3日,电极布置方式采用温纳α排列,最大探测深度约为52 m,高密度电法测线布置见图 10。
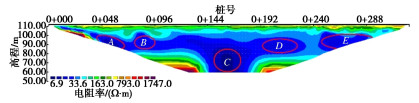
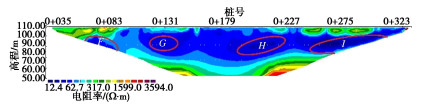
高密度电法视电阻率云图见图 11,12。由图可知,#1,#2测线揭示的浸润线高程分别约为81.27,76.90 m,此时库水位为100.41 m,对比2020年7月1日库水位为100.00 m时,计算模型相同位置处浸润线高程分别为80.31,77.24 m。计算模型的浸润线高程与高密度电法实测浸润线高程吻合,验证了计算模型的准确性。
#1测线D区域(桩号0+192—0+225,高程83.00~93.00 m)、E区域(桩号0+249—0+290,高程88.00~99.00 m),#2测线H区域(桩号0+180—0+230,高程73.00~88.00 m)、I区域(桩号0+251—0+308,高程80.00~92.00 m)为低阻异常区,由此可知桩号0+200—0+300大坝下游侧含水量偏高,推测该区域可能存在渗漏路径。根据工程资料记录,此段为1971年多次滑坡后重新填筑坝体,存在填筑土料含水量大,碾压不密实等质量问题,经检测,该区域心墙渗透系数为3.69×10-4 cm/s,不满足规范要求,坝体代料渗透系数为2.99×10-4 cm/s,大于坝体代料渗透系数平均值;根据地勘报告,桩号0+250—0+335坝基岩体上部10~20 m内,岩体透水率q=19.7~35.8 Lu,为中等透水性岩体。地勘资料揭示的渗漏通道与高密度电法探测结果吻合。
(5)安全监测资料分析验证
为进一步验证计算模型的准确性,在心墙坝桩号0+072断面布置U1,U2两根测压管,其中U1位于防渗墙前,U2位于防渗墙后,测压管布置见图 1。选取工况一进行验证,测压管实测值与数值计算值对比见表 3,由表可知,2020年7月1日库水位为100.00 m,U1测压管水位为95.29 m,U2测压管水位为79.50 m,对应计算模型在初始时刻相同位置浸润线高程分别为96.20,80.31 m,差值分别为0.91,0.81 m;7月20日库水位为102.76 m,U1测压管水位为97.89 m,U2测压管水位为79.45 m,对应计算模型在7月20日相同位置浸润线高程分别为98.55,80.37 m,差值分别为0.66,0.92 m。由此可知测压管实测水位高程与模型浸润线高程差别不大,说明计算模型是准确的。
表 3 测压管实测值与计算模型计算值对比表Table 3. Comparison between measured values by pressure tube and calculated values(m) 日期 U1 U2 实测值 模拟值 差值 实测值 模拟值 差值 07-01 95.29 96.20 0.91 79.50 80.31 0.81 07-20 97.89 98.55 0.66 79.45 80.37 0.92 4.2 渗透比降分析
心墙坝在典型工况下的水头等值线、渗透比降分别见图 13和表 4。由表可知,防渗墙最大渗透比降为39.13,小于防渗墙允许渗透比降100,心墙最大渗透比降为0.26,小于心墙允许渗透比降0.48,坝体代料最大渗透比降为0.14,小于坝体代料允许渗透比降0.40,下游逸出处最大渗透比降为0.14,小于排水棱体允许渗透比降0.20。由此可见,从渗透比降角度分析,坝体渗流稳定满足要求。前期降雨和库水位变化主要影响防渗墙和心墙的渗透比降,对坝体代料渗透比降影响较小。
表 4 渗透比降统计表Table 4. Statistical list of infiltration ratio工况 渗透比降 防渗墙 心墙 坝体代料 下游逸出处 初始状态 24.53 0.11 0.13 0.14 一 37.38 0.22 0.14 0.11 二 16.53 0.26 0.13 0.11 三 18.58 0.24 0.13 0.10 四 19.02 0.21 0.13 0.11 五 37.38 0.25 0.13 0.11 六 38.20 0.23 0.13 0.10 七 39.13 0.21 0.13 0.10 4.3 坝坡抗滑稳定性分析
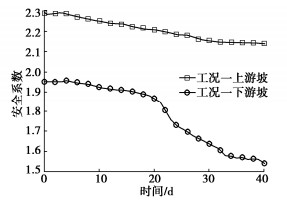
(1)前期降雨作用下心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数分析前期降雨作用下心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数变化见图 14。由图 14可知,上游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数在降雨后缓慢减小,减小幅度不大。7月1日—4日下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数变化不大;7月5日降雨164.7 mm后,下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数开始缓慢减小;7月20日主降雨结束后,下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数快速减小,并在降雨结束20 d后降至1.54。前期降雨对大坝下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数影响较小,主降雨后下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数减小值较大。因此,心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数变化相对前期降雨过程呈现出明显的滞后性。
(2)库水位变化作用下心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数分析
库水位变化作用下心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数变化见图 15。由图 15(a)可知,库水位骤降时,上游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数变化较大,当库水位停止下降时,抗滑稳定安全系数开始缓慢增大,抗滑稳定安全系数减小速率与库水位下降速率成正相关。由图 15(b)可知,下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数随着库水位的下降缓慢增大,抗滑稳定安全系数增大速率与库水位下降速率成正相关。
库水位骤降时坝体浸润线下降存在滞后,在坝体内形成较大的水力梯度,作用在坝坡上的静水压力消失,导致坝体内部的超孔隙水压力和渗透力指向坡外,在坝坡表面形成反向渗流场,产生向外的拖拽力,坝坡土体下滑力增大,抗滑稳定安全系数不断减小,对坝坡稳定十分不利。库水位下降越快,坝体内渗透力越大,越不利于坝体稳定。
(3)降雨和库水位变化共同作用下心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数分析
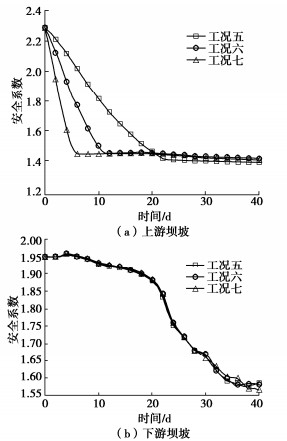
前期降雨和库水位变化共同作用下心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数变化见图 16。由图 16(a)可知,上游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数不断减小并最终趋于稳定;由图 16(b)可知,下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数先缓慢减小,后以较快速度减小,最后趋于稳定。
心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数见图 17和表 5。由表可知,心墙坝在前期降雨作用下,上下游坝坡最小抗滑稳定安全系数分别为2.14,1.54,对比0 h时分别降低了6.56%,21.08%;上游坝坡在库水位变化作用下,最小抗滑稳定安全系数分别为1.53,1.54,1.55,对比0 h时约降低了33%,下游坝坡在库水位变化作用下,最小抗滑稳定安全系数均为1.97,对比0 h时均增大了0.96%;前期降雨和库水位变化共同作用下,上下游坝坡最小抗滑稳定安全系数分别约为1.40,1.58,对比0 h时分别约降低了39%,19%。
表 5 心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数统计表Table 5. Statistical list of safety factor of anti-sliding stability of core dam工况 上游坡最小抗滑稳定安全系数 降幅/% 下游坡最小抗滑稳定安全系数 增幅/% 降幅/% 工况一 2.14 6.56 1.54 — 21.08 工况二 1.53 33.19 1.97 0.96 — 工况三 1.54 32.76 1.97 0.96 — 工况四 1.55 32.32 1.97 0.96 — 工况五 1.39 39.31 1.59 — 18.52 工况六 1.41 38.43 1.58 — 19.03 工况七 1.40 38.87 1.57 — 19.54 由此可知,库水位变化是影响上游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数的主要因素,前期降雨是导致下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数变化的主要因素。前期降雨与库水位变化共同作用对上游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数的影响大于前期降雨或库水位变化作用对上游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数影响。前期降雨与库水位变化共同作用对下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数的影响小于前期降雨作用对下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数影响,表明库水位骤降对下游坝坡稳定是有利的。
受库水位骤降影响,上游坝坡土体抗剪强度大幅降低,坝坡上部土体受前期降雨入渗影响,孔隙水压力和自重不断增大,抗剪强度不断降低,对坝坡稳定不利,上游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数的降低是由降雨和库水位变化共同作用导致。
5. 结论
本文采用Geo-studio对某心墙坝在前期降雨、库水位变化作用下大坝孔隙水压力、渗透比降和抗滑稳定安全系数的变化规律进行了研究,并结合高密度电法、安全监测数据和地勘资料验证了模型的准确性,得出6点结论。
(1)采用高密度电法和安全监测数据对计算模型的准确性进行了验证。高密度电法实测浸润线高程与计算模型的浸润线高程吻合,测压管实测水位高程与计算模型的浸润线高程差值均小于1 m,表明计算模型是准确的。
(2)前期降雨导致心墙坝坝体孔隙水压力不断增大的主要原因是随着前期降雨的增加,浅层土体达到饱和状态,形成暂态饱和区,降雨结束后,原降雨入渗影响区(孔隙水压力增大区域)雨水在重力势能和基质势能综合作用下不断向坝体内部入渗,即湿润锋不断向坝体深部移动,导致不同深度坝体孔隙水压力响应时间滞后于前期降雨,且滞后时间随着距坝顶距离的增加而增加。
(3)前期降雨对上游坝坡孔隙水压力影响程度由大到小依次为坡顶 > 坡肩(坡脚),前期降雨对下游坝坡孔隙水压力影响程度由大到小依次为坡顶 > 坡肩 > 坡脚,库水位骤降对上游坝坡孔隙水压力影响程度由大到小依次为坡脚 > 坡肩 > 坡顶,库水位骤降对下游坝坡基本没有影响。
(4)前期降雨对大坝下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数影响较小,主降雨后下游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数减小值较大。心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数变化相对前期降雨呈现滞后性。因此,需重视前期降雨对大坝下游坝坡浅层土体稳定性的影响。前期降雨、库水位变化作用主要影响防渗墙和心墙的渗透比降,且不同坝体分区渗透比降在不同工况作用下均小于允许渗透比降,坝体渗流稳定满足要求。
(5)受库水位骤降影响,上游坝坡土体抗剪强度大幅降低,坝坡上部土体受前期降雨入渗影响,孔隙水压力和自重不断增大,抗剪强度不断降低,对坝坡稳定不利,上游坝坡抗滑稳定安全系数的降低是由降雨和库水位变化共同作用导致。
(6)研究表明,综合计算模型、高密度电法和安全监测资料较好地分析了心墙坝孔隙水压力、渗透比降和抗滑稳定安全系数的变化规律,为完善土石坝设计规范和水库大坝安全评价提供了科学依据。
-
表 1 坝体分区材料物理力学参数表
Table 1 Physical and mechanical parameters of dam partition
坝体分区 渗透系数/(cm·s-1) 饱和含水率/% 重度/(kN·m-3) 有效黏聚力/kPa 有效内摩擦角/(°) 坝前抛石 1.00×10-3 52.0 21.0 0 35.0 坝体代料 1.43×10-4 40.0 18.5 20.0 16.8 心墙 9.82×10-5 40.0 18.4 23.0 16.5 下游反滤 1.00×10-3 52.0 19.0 0 35.0 坝基 9.62×10-5 36.0 28.7 100.0 45.0 防渗墙 1.00×10-7 2.0 24.0 500.0 35.0 防渗帷幕 1.00×10-7 2.0 24.0 500.0 35.0 表 2 计算工况表
Table 2 Working conditions
计算工况 库水位/m 骤变速率/(m·d-1) 降雨类型 工况一 100.00 — 最不利降雨 工况二 100.00~78.00 1 — 工况三 2 — 工况四 4 — 工况五 100.00~78.00 1 最不利降雨 工况六 2 最不利降雨 工况七 4 最不利降雨 注:2020年7月降雨开始前的初始库水位为100.00 m,死水位为78.00 m。 表 3 测压管实测值与计算模型计算值对比表
Table 3 Comparison between measured values by pressure tube and calculated values
(m) 日期 U1 U2 实测值 模拟值 差值 实测值 模拟值 差值 07-01 95.29 96.20 0.91 79.50 80.31 0.81 07-20 97.89 98.55 0.66 79.45 80.37 0.92 表 4 渗透比降统计表
Table 4 Statistical list of infiltration ratio
工况 渗透比降 防渗墙 心墙 坝体代料 下游逸出处 初始状态 24.53 0.11 0.13 0.14 一 37.38 0.22 0.14 0.11 二 16.53 0.26 0.13 0.11 三 18.58 0.24 0.13 0.10 四 19.02 0.21 0.13 0.11 五 37.38 0.25 0.13 0.11 六 38.20 0.23 0.13 0.10 七 39.13 0.21 0.13 0.10 表 5 心墙坝抗滑稳定安全系数统计表
Table 5 Statistical list of safety factor of anti-sliding stability of core dam
工况 上游坡最小抗滑稳定安全系数 降幅/% 下游坡最小抗滑稳定安全系数 增幅/% 降幅/% 工况一 2.14 6.56 1.54 — 21.08 工况二 1.53 33.19 1.97 0.96 — 工况三 1.54 32.76 1.97 0.96 — 工况四 1.55 32.32 1.97 0.96 — 工况五 1.39 39.31 1.59 — 18.52 工况六 1.41 38.43 1.58 — 19.03 工况七 1.40 38.87 1.57 — 19.54 -
[1] 张建云. 气候变化与水利工程安全[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2009, 31(3): 326–330. http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract13166.shtml ZHANG Jian-yun. Climate change and safety of water conservancy projects[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(3): 326–330. (in Chinese) http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract13166.shtml
[2] 张建云, 向衍. 气候变化对水利工程安全影响分析[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2018, 48(10): 1031–1039. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JEXK201810002.htm ZHANG Jian-yun, XIANG Yan. Analysis on the impact of climate change on the water conservancy project safety[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2018, 48(10): 1031–1039. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JEXK201810002.htm
[3] 徐旺敏, 傅琼华, 马秀峰, 等. 滨田水库大坝滑坡机理分析及防治对策[J]. 人民长江, 2012, 43(20): 36–38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201220012.htm XU Wang-min, FU Qiong-hua, MA Xiu-feng, et al. Analysis of landslide mechanism of Bintian reservoir dam and countermeasures[J]. Yangtze River, 2012, 43(20): 36–38. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201220012.htm
[4] HUANG Q X, WANG J L, XUE X. Interpreting the influence of rainfall and reservoir infilling on a landslide[J]. Landslides, 2016, 13(5): 1139–1149. doi: 10.1007/s10346-015-0644-8
[5] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(3): 433–454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200703000.htm HUANG Run-qiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(3): 433–454. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200703000.htm
[6] RAHARDJO H, ONG T H, REZAUR R B, et al. Factors controlling instability of homogeneous soil slopes under rainfall[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2007, 133(12): 1532–1543. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:12(1532)
[7] 唐栋, 李典庆, 周创兵, 等. 考虑前期降雨过程的边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(11): 3239–3248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201311032.htm TANG Dong, LI Dian-qing, ZHOU Chuang-bing, et al. Slope stability analysis considering antecedent rainfall process[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(11): 3239–3248. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201311032.htm
[8] 李卓, 何勇军, 李宏恩, 等. 前期降雨作用下边坡滑坡模型试验[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(5): 400–405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHDX201605004.htm LI Zhuo, HE Yong-jun, LI Hong-en, et al. Model test on slope landslides under antecedent rainfall[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2016, 44(5): 400–405. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHDX201605004.htm
[9] JIA G W, ZHAN T L T, CHEN Y M, et al. Performance of a large-scale slope model subjected to rising and lowering water levels[J]. Engineering Geology, 2009, 106(1/2): 92–103.
[10] JIAN W X, XU Q, YANG H F, et al. Mechanism and failure process of Qianjiangping landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 72(8): 2999–3013.
[11] 李卓, 何勇军, 盛金保, 等. 降雨与库水位共同作用下近坝库岸边坡滑坡模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(3): 452–459. http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract16853.shtml LI Zhuo, HE Yong-jun, SHENG Jin-bao, et al. Landslide model for slope of reservoir bank under combined effects of rainfall and reservoir water level[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(3): 452–459. (in Chinese) http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract16853.shtml
[12] SUN G H, YANG Y T, CHENG S G, et al. Phreatic line calculation and stability analysis of slopes under the combined effect of reservoir water level fluctuations and rainfall[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2017, 54(5): 631–645.
[13] 碾压式土石坝设计规范: SL274—2020[S]. 2020. Design Code for Rolled Earth-Rock Fill Dams: SL274—2020[S]. 2020. (in Chinese)
[14] Geo-Slope International Ltd. Seepage Modeling with SEEP/W 2007[R]. Calgary: Geo-Slope International Ltd, 2007.
[15] FREDLUND D G, MORGENSTERN N R, WIDGER R A. The shear strength of unsaturated soils[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1978, 15(3): 313–321.
[16] Geo-Slope International Ltd. Stability Modeling with SLOPE/W 2007[R]. Calgary: Geo-Slope International Ltd, 2007.
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 江超,薛小荣,曹昕,欧阳辉,祖安君,张宏瑞,丁博杰,马万存. 坝脚鱼塘对水库大坝安全影响数值模拟分析与对策研究. 中国水利. 2025(01): 60-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 梁俊群,罗滔,易宇. 基于COMSOL的不同库水位条件下土石坝坝坡稳定性分析. 中国农村水利水电. 2024(01): 251-256 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 庄燕珍. 库水位涨落条件下挡墙坡体渗流特征数值模拟. 水利与建筑工程学报. 2024(02): 32-39+65 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 钟亮. 基于有限元法的兴宁市新陂镇响水寨水库大坝渗流稳定性分析. 陕西水利. 2024(07): 199-201 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 邓志平,邹艺,潘敏,郑克红,牛景太,蒋水华. 考虑多参数空间变异性的非饱和土石坝坝坡可靠度分析. 应用基础与工程科学学报. 2024(04): 1108-1123 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 荣威,秦宇,张坤勇. 水库土石坝坝坡稳定性分析. 江西建材. 2024(12): 109-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 杨会刚,刘得潭,商永喜,王峻峰,徐力群,黄章鑫. 特高心墙堆石坝蓄水工况非稳定渗流分析. 人民珠江. 2023(06): 70-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 袁凤娟. 基于Autobank水库大坝的一些稳定渗流分析. 水利科技与经济. 2023(08): 96-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈建华. 基于有限元分析的土石坝防渗加固效果研究. 水利科技与经济. 2023(09): 139-142 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 曹思源,张淼,袁颖. 不同库水位下均质土石坝稳定性分析. 河北地质大学学报. 2023(05): 53-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 郭秋金. 水位下降条件下挡土墙参数对渗流特征的影响. 中国市政工程. 2023(05): 105-109+127-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 邵志一,肖珍珍. 下游鱼塘对水库大坝渗流稳定及抗滑稳定的影响——以阳春市湴濛仔水库大坝为例. 人民珠江. 2023(S2): 216-221 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(12)



 下载:
下载: