Deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of surrounding rock of high-stress large-diameter cylindrical caverns
-
摘要: 针对高应力大直径圆筒形洞室出现的岩爆、喷层开裂和钢绞线弹出等变形破坏现象,通过现场破坏调查、岩体位移和锚索应力监测,详细说明了围岩变形破坏的发展演化过程,并通过钻孔摄像观测了围岩内部破裂特征,进而总结了围岩变形破坏的演化模式。通过数值模拟揭示了洞室围岩变形破坏机制,并提出了合理的支护建议。高应力大直径圆筒型洞室变形破坏是一个链动灾害过程,围岩内部开裂导致了岩体位移和锚索荷载增加,锚索荷载超限时钢绞线断裂弹出,失去约束的洞壁围岩和喷层在卸荷作用下鼓胀开裂。高初始地应力和开挖后诱发的应力集中,玄武岩起裂强度低,临近洞室开挖诱发应力叠加,应力集中区支护强度较弱等综合因素导致了围岩内部开裂的产生。在洞室围岩应力集中区设置足够的预应力长锚索和合理的张拉力,可以有效减弱围岩内部破裂深度和程度。Abstract: Aiming at the deformation and damage phenomena such as rock burst, spray layer cracking and steel strand ejection in high-stress large-diameter cylindrical caverns, the development and evolution process of deformation and damage of the surrounding rock is explained through field investigation, observation of displacement of rock mass and stress of anchor cable. The internal fracture characteristics of the surrounding rock are observed through borehole camera, and the evolution mode of the deformation and failure of the surrounding rock is summarized. The deformation and failure mechanism of the surrounding rock of the cavern is revealed through numerical simulation, and reasonable support suggestions are put forward. The deformation and failure of the high-stress large-diameter cylindrical caverns is a chain-driven disaster process. The internal cracking of the surrounding rock leads to the increase in the displacement of the rock mass and the load of anchor cable. The steel strands break and pop out when the load of anchor cable exceed the limit. The surrounding rock and sprayed layer of unconstrained cave wall bulge and crack under the action of unloading. The high initial ground stress and the stress concentration induced after excavation, the low crack initiation strength of basalt, the superposition of stress induced by excavation adjacent to the cavern, and the weak support strength in the stress concentration areas lead to the occurrence of internal cracking in the surrounding rock. Setting enough pre-stressed long anchor cables and reasonable tension force in the stress concentration areas of the surrounding rock of the cavern can effectively reduce the depth and degree of internal fracture of the surrounding rock.
-
0. 引言
中国水利水电、能源矿山等大型地下洞室群开挖规模越来越大,且逐渐向深部地下空间转移,初始高应力及开挖诱发的二次应力集中导致大型地下洞室岩体破裂问题越来越突出[1-3],如锦屏一级水电站地下厂房的深部岩体大变形问题,白鹤滩水电站右岸地下厂房的深层破裂及深部变形问题等[4-6]。大型地下洞室围岩内部破裂会进一步导致工程灾害的链动效应,诱发岩体大变形和支护结构失效,比如喷层开裂、锚索弹出及荷载突降等[7-8]。研究高应力大型地下洞室岩体破裂及链动灾害的形成机制,建立合理的开挖支护设计原则,对于未来深部地下洞室的安全稳定建设具有重要意义。
目前,国内外已有较多学者对高应力大型地下洞室的岩体破裂与支护失效机制进行研究,江权等[9]通过现场调查和钻孔摄像观测了白鹤滩水电站地下厂房玄武岩内部破裂的演化全过程,揭示了高应力下岩体破裂的空间非连续及破裂深度、裂隙宽度的时效增长现象。戴峰等[10]通过常规测试和微震监测技术,揭示了猴子岩水电站地下厂房开挖卸荷过程围岩裂隙的萌生、发育和扩展的演化过程,分析了围岩裂隙演化与施工动态之间的相互关系。卢波等[11]研究了锦屏一级水电站地下厂房岩体开裂及大变形、喷层开裂等与地应力场的关系。其他学者也通过现场调查、原位监测、地质力学机制分析或者数值模拟方法研究了锦屏一级水电站、白鹤滩水电站等高应力大型地下洞室的岩体变形破坏规律,并从地应力、地质构造、地下洞室群空间结构等方面分析了其形成机理[12-15]。前人关于高应力大型地下洞室岩体变形破坏与支护失效机制的研究主要集中在地下厂房等长条形地下洞室,对于采用圆筒形结构的尾调室等大型地下洞室岩体变形破坏特征的研究还不是很多,特别是含大型地质构造和复杂工程布置条件下圆筒形地下洞室岩体变形破坏特征与形成机制需要研究,其围岩变形破裂及链动灾害的发展演化过程、形成机制及合理的开挖设计还需进一步探讨。
本文主要以白鹤滩水电站#8尾水调压室为例,通过现场调查、原位监测和数值模拟等方法研究含大型地质构造条件下高应力大型圆筒形地下洞室岩体变形破裂及支护失效、喷层开裂等链动灾害的形成过程,揭示大型圆筒型洞室围岩内部破裂的形成机制,并基于裂化抑制思想探讨高应力大型圆筒形地下洞室的开挖支护设计原则,提出合理的支护建议。
1. 工程概况
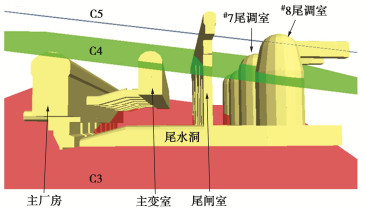
白鹤滩水电站左右岸地下洞室群是目前世界上开挖规模最大的地下洞室群,具有初始地应力高(初始最大主应力超过30 MPa)、岩体硬脆性显著、地质条件复杂(多条错动带切割)的典型特征[16],图 1为白鹤滩水电站右岸地下洞室群,图中C3、C4和C5为切割洞室群的错动带,四大洞室轴线方向为NW10°。地下洞室群区域岩性为块状玄武岩,主要分为隐晶玄武岩、杏仁状玄武岩和斜斑玄武岩,第一主应力方向为N0°—20°E,量值约为22~26 MPa,属高地应力区。岩石天然单轴抗压强度约为120~150 MPa。岩体级别以Ⅲ1类为主,地下厂房等洞室群开挖期间出现了显著的片帮、喷层开裂、深层变形等变形破坏问题[5-6, 17],图 2为白鹤滩水电站右岸地下厂房上游侧拱肩在Ⅲ层开挖时出现的长达近百米的大范围喷层开裂剥落破坏。
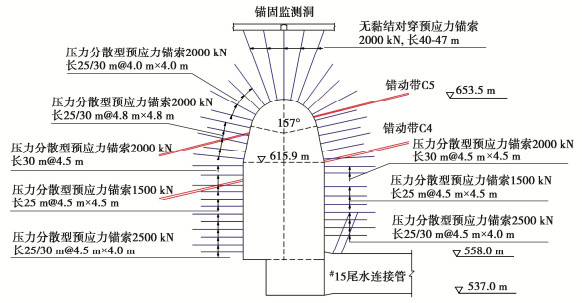
地下洞室群中的尾水调压室采用穹顶圆筒形式,其中右岸#8尾调室的体型、地质条件较为复杂,其穹顶直径为40 m,下部井身直径48 m,洞室总高116.5 m。层间错动带C4、C5分别斜切尾调室的井身上部和穹顶,两条错动带近于平行,产状为N40°—50°E,SN∠15°—20°。尾调室垂直埋深约450 m,水平埋深约670 m。尾调室采用自上而下、分层分块的开挖方式,穹顶段分层开挖高度4~12 m,井身段分层开挖高度3.5 m,且开挖一层,支护一层。尾调室采用喷锚支护,其中穹顶部位初喷CF30钢纤维混凝土10 cm,挂网复喷C25混凝土10 cm,6 m长C28普通砂浆锚杆与9 m长C32预应力锚杆间隔布置,预应力为150 kN,间距为1.5 m×1.5 m。尾调室穹顶与上部锚固监测洞采用无黏结对穿锚索,预应力为2000 kN,长度40~47 m,间距为4.0 m×4.0 m,穹顶其他部位采用压力分散型锚索,预应力为2000 kN,长度为25/30 m间隔布置,间距为4.0 m×4.0 m,4.8 m×4.8 m。井身部位:挂网喷C25混凝土15 cm,6 m长C28普通砂浆锚杆与9 m长C32普通砂浆锚杆间隔布置,间距为1.5 m×1.5 m。井身部位采用系统压力分散型锚索,错动带出露附近区域采用加强锚索,井身上部锚索预应力为1500 kN,长度25 m,间距4.5 m×4.5 m,井身下部锚索预应力为2500 kN,长度为25 m/30 m间隔布置,间距为4.5 m×4.0 m,其中2500 kN锚索仅在洞室方位角280°~330°,90°~145°部位布置。#8尾调室工程布置及锚索支护参见图 3。
2. 围岩变形破坏特征
2.1 围岩变形破坏过程
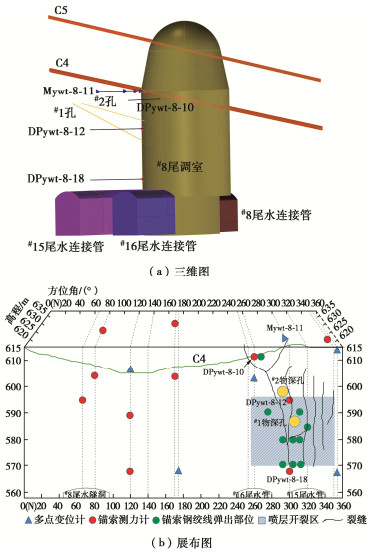
#8尾调室井身段开挖过程中曾出现围岩片帮、喷射混凝土开裂掉块,钢筋网鼓胀等破坏,在尾调室开挖接近完成时,又发生了较为严重的岩爆、喷层开裂、锚索钢绞线弹出等破坏现象,此次变形破坏过程从2019年4月初开始,持续近1个月,主要破坏发生在2019年5月1日前后。#8尾调室洞周布置有大量的多点位移计、锚索应力计(见图 4),结合现场破坏调查、围岩位移和锚索应力变化,详述本次洞室围岩变形破坏的发展演化过程如下:
(1)2019年4月10日开始,位于方位300°、高程617.8 m的多点位移计Mywt-8-11孔口测点位移持续增长,周增量为2~3 mm,此时3 m测点位移的周增量较小。位于方位角260°、高程610 m的锚索测力计DPywt-8-10,位于方位角300°、高程595 m的锚索测力计DPywt-8-12的荷载都不断增长。
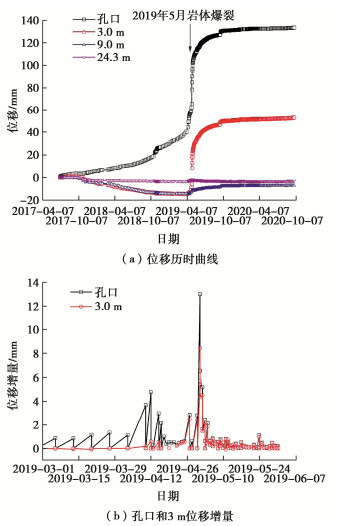
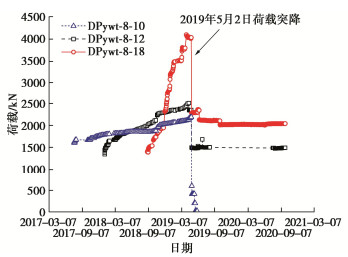
(2)从2019年4月27日开始,Mywt-8-11孔口位移和3 m处位移的两日增量分别达到2.26,1.99 mm。4月28日15:00,DPywt-8-10荷载达到最大值2200.28 kN。DPywt-8-12的荷载为2359.33 kN,位于方位角301°高程568 m的锚索测力计DPywt-8-18的荷载为4033.98 kN。4月30日16:00,DPywt-8-10荷载为2199.00 kN,DPywt-8-12的荷载仍为2359.33 kN,DPywt-8-18的荷载为4011.78 kN。4月30日18:00起,Mywt-8-11孔口位移和3 m测点位移迅速增长,5月1日9:00相比4月30日18:00,孔口位移增量为12.99 mm。多点位移发生突变后,#8尾水调压室跟着发生了岩爆和开裂掉块现象。9:30—10:45连续发生5次岩爆,震动较大,井壁两侧有小石掉落,11:00—14:30,又连续发生3次响岩爆,13:50岩爆震动较大,岩爆过程中有碎石掉落。
(3)5月1日16:00时相比9:00时,Mywt-8-11孔口位移增量为6.55 mm,孔口和3m处累积位移分别为84.85,8.42 mm。5月1日22:00相比16:00,位移增量又分别为5.40,4.35 mm。5月1日相比4月30日,多点位移计Mywt-8-11的孔口和3m位移日增量总计为24.94,18.46 mm,累积位移分别为90.25,12.77 mm。多点位移计Mywt-8-11的位移时程演化曲线参见图 5。
(4)2019年5月2日从9:15至16:29,又前后发生6次岩爆,其中16:29时岩爆响声较大,岩爆过程中有块体掉落,其他为岩爆过后有少量碎石掉落。5月3日9:20和10:17,发生两次岩爆,伴有少量块体掉落。多点位移计Mywt-8-11在5月2日、5月3日的孔口位移和3 m位移日增量为3~4 mm。5月2日16:00,DPywt-8-10荷载骤降到601.09 kN,DPywt-8-12荷载降到1499.83kN,DPywt-8-18荷载降到2284.94 kN。锚索测力计DPywt-8-10、DPywt-8-12和DPywt-8-18荷载时程演化曲线参见图 6。
(5)5月4日从3:28至14:37发生6次岩爆,伴有少量块体或碎石掉落,其中两次岩爆声音较小,无块体或碎石掉落。5月6日发生2次岩爆,分别在21:10,21:51,有少量碎石掉落。5月7日发生1次岩爆,时间为21:50,有少量碎石掉落。5月4日至5月9日多点位移计Mywt-8-11的日变形增量稳定在1 mm。5月4日9:00,DPywt-8-10荷载又降低到414.73 kN,5月17日荷载又减小到202.45 kN。DPywt-8-12荷载未再有明显变化。
从5月1日至5月7日,累计发生25次岩爆,每次岩爆后都伴随有小的喷层掉块出现,5月1日和5月2日两天的岩爆较为剧烈,从5月3日至5月7日岩爆次数、震动程度总体呈逐渐减弱趋势。从4月27日开始,孔口位移和3 m处位移的增量均有显著增长。可见,距洞壁3 m处已经出现了较为显著的开裂。此后在整个岩爆发生过程中孔口位移和3 m位移保持了量值接近的增量,说明此后位移的增长主要是3 m与9 m测点之间的岩体开裂引起的。
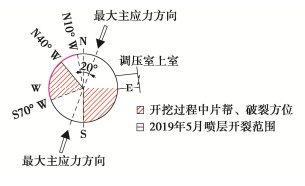
2019年5月3日现场调查发现,尾调室高程572.5~610 m、方位263°—310°有约10束锚索钢绞线弹出,每束弹出1—2股,弹出长度约为2 m。在高程570~616 m、方位角260°~350°形成大范围的喷层开裂,并出现8条明显裂缝,裂缝迹线主要以竖直方向为主,裂缝最大长度近46 m,开裂部位喷层表面鼓胀30~50 cm,喷层开裂之前岩体内部听到爆裂声响,参见图 7。
2.2 围岩内部破裂
为了精细判断岩体内部破裂情况,在喷层开裂区钻设#1、#2两个地质钻孔,通过钻孔摄像观察岩体内部破裂分布。#1孔高程588.6 m,方位323°,长度为59.0 m,#2孔高程599.2 m,方位335°,长度为50.8 m,两孔均斜向上,两钻孔起点均在尾闸室。图 8为两孔的钻孔摄像展布图,#1孔距洞壁5.4 m(孔深50.3 m)至孔口范围围岩破裂严重,破裂面间距5~30 cm,一般10 cm左右,距洞壁7.0~5.4 m(孔深48.3~50.3 m)微破裂,发育5条破裂面,破裂面间距0.1~1.0 m。#2孔距洞壁1.7 m(孔深48.9 m)至孔口范围围岩破裂程度相对较严重,破裂面间距10~30 cm,距洞壁5.2~1.7 m(孔深45.0~48.9 m)微破裂,发育3条微破裂面,破裂面间距1 m左右。故可判断#1孔与#2孔所在位置洞室围岩严重破裂区深度约为1.7~5.4 m,损伤破裂区范围约为5.2~7.0 m。
2.3 围岩变形破坏演化模式
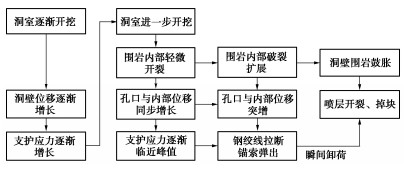
分析整个围岩变形破坏过程可得,随着洞室开挖,洞壁围岩位移不断增长,导致支护应力也呈现逐渐增长趋势,不过此时岩体内部尚未产生明显开裂。随着洞室进一步开挖,围岩应力集中区逐渐向深部围岩转移,围岩内部逐渐产生轻微开裂,导致开裂位置和洞壁之间的围岩位移产生近于同步的增长。随着围岩位移的不断增长,支护应力逐渐增加,直至达到峰值。随着围岩内部破裂扩展加剧,围岩位移迅猛增长,洞壁围岩产生明显鼓胀,此后孔口位移和破裂范围与洞壁之间的内部测点位移增量保持同一数量级快速增长。当围岩位移增加到超出锚索可承受拉伸范围时,部分钢绞线断裂,并从锚墩头弹出。由于围岩内部破裂增长导致表层围岩鼓胀不断加大,同时由于钢绞线断裂瞬间卸荷,失去约束的表层围岩和混凝土喷层在鼓胀、锚索卸载和巨大的震动冲击影响下快速碎裂掉块,并出现明显声响。断续的鼓胀和喷层开裂逐渐贯通形成裂缝和大面积的掉块。整个围岩变形破坏的演化模式如图 9所示。
观测围岩内部破裂可见,在距洞壁5~7 m的位置仍有较为显著的开裂,此即是距洞壁3 m测点位移也出现突增的主要原因。从整个岩体内部破裂、位移增长和支护应力演化过程看,三者既有依次先后顺序影响,又形成闭环的致灾效应。岩体内部破裂引发了位移增长,由于岩体破裂和位移增长又导致了支护应力的逐渐增长,当锚索应力超出承受极限时,钢绞线断裂瞬间卸荷,围岩约束减弱,内部开裂迅速扩展,位移进一步增长,同时导致了表层围岩鼓胀和喷层开裂的出现。
3. 围岩变形破坏机制
#8尾调室岩体喷层开裂和钢绞线弹出等围岩破坏主要发生在洞室开挖临近完成时,围岩变形破坏主要集中在方位角260°~350°范围。考虑到白鹤滩水电站右岸地下洞室群最大主应力方向为NE0°—20°,尾调室岩体破裂范围与初始最大主应力方向夹角较大,符合洞室围岩应力型破坏发生位置及延伸方向与洞室横剖面内最大主应力近于平行的认识[18],可见初始地应力场对本次洞室围岩变形破坏具有重要影响,参见图 10。
图 11为建立的包含#5~#8四个尾调室,C3、C4和C5三个错动带,以及临近的进场交通洞、尾水连接管和尾水隧洞等交叉洞室的三维数值计算模型,其中尾水连接管尺寸为23.8 m×16.0 m(高×宽),尾水隧洞尺寸为22.0 m×18.5 m(高×宽),进场交通洞尺寸为11.5 m×10.6 m(高×宽)。按照各洞室开挖顺序模拟其开挖过程,岩体本构模型采用可反映硬岩脆性破坏的应变软化模型,错动带采用莫尔-库仑理想弹塑性模型,岩体和错动带的力学参数分别见表 1,2。
表 1 岩体力学参数Table 1. Mechanical parameters of surrounding rock弹性模
量/GPa泊松比 初始黏聚
力/MPa残余黏聚
力/MPa初始内摩擦
角/(°)残余内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强
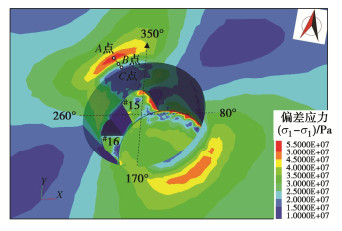
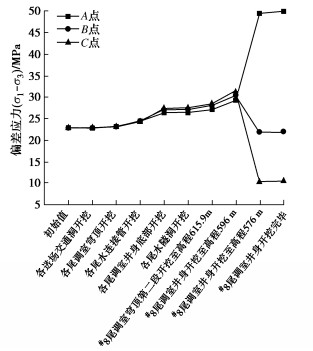
度/MPa黏聚力等效塑性剪应变 内摩擦角等效塑性剪应变 15.1 0.25 15 3 21.8 42 1.2 3×10-4 4×10-4 表 2 错动带力学参数Table 2. Mechanical parameters of dislocation zone错动带 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强度/MPa C4 2.0 0.32 1.2 32 0.2 C3、C5 5.0 0.32 1.5 35 0.5 图 12为#8尾调室开挖完毕后580 m高程剖面围岩偏差应力($ {\sigma _1} - {\sigma _3} $)的分布云图,可见尾调室NW和SE方位围岩处于应力集中区,由于#15和#16尾水连接管开挖引起的应力叠加的影响,NW方位的应力集中程度强于SE方位,NW方位局部围岩偏应力超过了45 MPa,甚至超过了50 MPa。已有研究显示隐晶玄武岩硬脆性特征明显,岩样启裂时有明显声响,临近破坏时岩片迅猛弹射,内部含有隐微裂隙,启裂强度较低,当岩体应力超过45 MPa就有大量的微破裂声发射信号产生[19-20],故洞室NW方位围岩内部破裂风险较高。在图 13中A点、B点和C点距洞壁分别约为9,4,1 m,提取3点偏差应力随洞室开挖过程的演化曲线可见,在尾调室井身开挖之前,各测点偏差应力只有轻微增长,随着尾调室井身下挖,偏差应力逐渐增大。当尾调室井身开挖至高程596 m时,三点偏差应力分别达到了29.2,30.4,31.3 MPa,当尾调室井身开挖至高程576 m时,3个测点所在断面已经开挖,此时3点偏差应力分别为49.5,21.9,10.2 MPa,从B、C两点偏差应力的迅速减小可推测B点和C点已经进入了塑性区,由于计算采用的本构模型为应变软化模型,其偏差应力逐渐变小,并且C点的应力莫尔圆更小。由于临近洞壁岩体进入损伤破坏阶段,应力集中区向深部围岩转移,A点偏差应力迅速增加。洞室开挖完毕后三点不同的偏差应力揭示的岩体损伤破坏演化结果与钻孔摄像显示的围岩破裂区范围具有同样的趋势,临近洞壁的1.7~5.4 m范围岩体破裂较为严重,该范围内岩体进入残余阶段偏差应力较小,5.4~7.0 m范围岩体仍有轻微破裂出现,此段范围内岩体进入峰后损伤破坏阶段,偏差应力也有明显降低,而对于临近峰值的峰前损伤区和弹性区,其偏差应力将逐渐增大,直至达到45 MPa。可见数值模拟分析的岩体变形破裂位置、深度等与现场观测结果一致,分析结果可用于工程实践应用。
可见,#8尾调室的岩体破裂部位初始地应力较大,随着尾调室逐渐下挖,位于方位260°~350°范围围岩应力集中逐渐增强,隐晶玄武岩启裂强度较低,易发生由表及里的渐进破坏。当洞室开挖至临近尾水连接管上方时,受到交叉洞口应力叠加影响,同时应力集中区预应力锚索数量不足,在多方面综合因素影响下导致了围岩内部的严重开裂。岩体破裂范围内的非弹性位移出现突增,锚索由于无法承受巨大位移引起的荷载增长而拉断,从而导致了钢绞线拉断弹出。在围岩内部开裂和锚索失效情况下,洞壁表层围岩和喷层受到的约束减弱,发生鼓胀开裂。
4. 开挖支护建议
高应力硬岩地下洞室围岩内部开裂诱发了位移突增、锚索失效和喷层开裂等变形破坏,故应以控制围岩内部开裂为目的,通过开挖优化和支护优化降低岩体破裂深度和破裂程度[1],其中开挖优化主要包括开挖高度、开挖顺序、开挖进尺,支护优化主要包括支护参数(结构形式、支护长度、支护刚度)和支护时机等。在洞室围岩应力集中部位应及时喷射混凝土和施加预应力锚杆,给围岩提供初期围压,提高岩体的起裂强度,减轻洞壁表层岩体破裂程度,增强表层围岩的承载能力,这有助于减轻应力集中向深部围岩的转移深度。对于高应力硬岩大型地下洞室,在应力集中区部位应设置足够数量和长度的预应力锚索,预防围岩深层破裂的出现,考虑到可能的岩体开裂、岩体位移突增及引起的锚索荷载迅猛增长,预应力锚索的初期张拉力不应大于设计强度的70%~80%。在洞室群的交叉部位,也需要及时施做一定长度的预应力锚杆和预应力锚索,减轻多面卸荷诱发的岩体开裂,增强应力集中转移的深部围岩稳定。在洞室开挖过程中加强围岩内部开裂、围岩位移和支护应力监测,必要时考虑增加微震、扰动应力和声发射等监测手段,实现全过程多方位洞室围岩稳定性的控制与预警。
考虑到#8尾调室圆筒形的体型及玄武岩硬脆性特点,核心关键在于抑制应力集中区围岩的渐进性开裂。#8尾调室井身段开挖分层高度为3.5 m,每层采用由内到外分块开挖,且支护基本紧跟开挖[21],但其应力集中区的支护锚固力偏弱,仅在洞室井身中下部#15、#16尾水连接管上方高程586.00~572.50 m、方位角280°~330°布置了4排2500 kN锚索,支护作用效果有限。针对此次破坏,设计单位提出了以下补强措施:
(1)重新挂设主动防护网,将喷层开裂掉块部位彻底清撬,重新挂网喷射C25混凝土12 cm。
(2)在高程606.25~565.75 m、方位角223°~345°范围内插10排全长黏结型预应力锚索,预应力3000 kN,长度30 m/35 m间隔布置;高程587.25~564.75 m、方位角99°~175°范围内插6排全长黏结型预应力锚索,预应力3000 kN,长度30 m/35 m间隔布置。
(3)在#15,#16尾水连接管与尾水调压室交岔口顶拱分别布置4排有黏结型1500 kN预应力锚索,长度15 m。
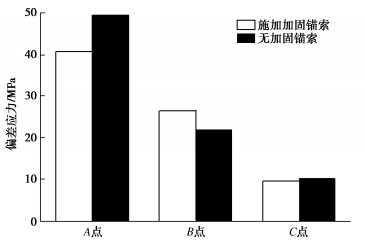
图 14为洞室井身下部#15,#16尾水连接管上方新增锚索布置示意图。图 15为洞室开挖完毕后设计张拉力为2100 kN时各锚索轴力的计算结果,绝大多数锚索轴力基本在2000~2500 kN,但是在#15尾水管上方有7根锚索轴力超过了5000 kN,其中有1根甚至达到了近7000 kN,这说明应力集中区锚索轴力相对较大,也验证了前边应力集中区部分锚索易拉断的事实。但是在补强加固锚索实施后,对整个洞室围岩的应力集中程度有较大程度的改善,图 16为是否施加补强加固锚索情况下A、B、C 3点偏差应力的对比,施加补强加固锚索后A点应力集中程度降低,而B点处偏差应力高于未施加情况,C点处偏差应力相差不大。说明B点处岩体虽然同样进入峰后阶段,但其损伤程度相对无加固锚索时略低,洞壁表层岩体相对完整,承载能力相对较高,位于深部的A点应力集中程度就会有明显降低,从而深部围岩破裂风险降低,洞室稳定性提高。
5. 结论
针对白鹤滩水电站#8尾调室为代表的高应力大直径圆筒形洞室出现的岩爆、喷层开裂、锚索钢绞线弹出等围岩变形破坏问题,通过现场调查、原位监测和数值分析,获得了其形成发展演化过程,揭示了围岩内部破裂特征,分析了其形成机制,并提出了支护建议,得到以下3点结论。
(1)高应力大直径圆筒形地下洞室的岩爆、喷层开裂、锚索弹出等围岩变形破坏问题是链动灾害现象,首先在洞室围岩应力集中区易发生岩体内部开裂,诱发破裂范围内围岩位移突增,进而导致锚索荷载突增,钢绞线在超载时拉断弹出,由于围岩约束减弱,洞室围岩向洞内卸荷膨胀,导致喷层开裂出现。
(2)#8尾调室喷层开裂、锚索弹出等强应力型破坏的发生是地应力、岩性、工程结构布置及支护等综合因素引起的。洞室围岩变形破坏区域位于高应力集中区,而玄武岩起裂强度低、弹脆性显著,尾水连接管等交叉洞室开挖导致应力集中叠加,同时围岩应力集中区预应力锚索数量不足,支护强度较弱。
(3)高应力大直径圆筒形地下洞室应该采用裂化抑制思想进行开挖、支护设计,在分层开挖高度、预应力锚索位置和张拉力等方面进行优化,需加强应力集中区岩体破裂监测,洞室围岩应力集中区应采用表层预应力锚杆和深层预应力锚索的组合支护。
-
表 1 岩体力学参数
Table 1 Mechanical parameters of surrounding rock
弹性模
量/GPa泊松比 初始黏聚
力/MPa残余黏聚
力/MPa初始内摩擦
角/(°)残余内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强
度/MPa黏聚力等效塑性剪应变 内摩擦角等效塑性剪应变 15.1 0.25 15 3 21.8 42 1.2 3×10-4 4×10-4 表 2 错动带力学参数
Table 2 Mechanical parameters of dislocation zone
错动带 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强度/MPa C4 2.0 0.32 1.2 32 0.2 C3、C5 5.0 0.32 1.5 35 0.5 -
[1] 江权, 冯夏庭, 李邵军, 等. 高应力下大型硬岩地下洞室群稳定性设计优化的裂化-抑制法及其应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(6): 1081-1101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201906002.htm JIANG Quan, FENG Xiating, LI Shaojun, et al. Cracking-restraint design method for large underground Caverns with hard rock under high geostress condition and its practical application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(6): 1081-1101. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201906002.htm
[2] 卢波, 丁秀丽, 邬爱清, 等. 高应力硬岩地区岩体结构对地下洞室围岩稳定的控制效应研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(增刊2): 3831-3846. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2012S2052.htm LU Bo, DING Xiuli, WU Aiqing, et al. Study of influence of rock structure on surrounding rock mass stability of underground Caverns in hard rock region with high geostress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(S2): 3831-3846. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2012S2052.htm
[3] 张勇, 肖平西, 丁秀丽, 等. 高地应力条件下地下厂房洞室群围岩的变形破坏特征及对策研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(2): 228-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201202003.htm ZHANG Yong, XIAO Pingxi, DING Xiuli, et al. Study of deformation and failure characteristics for surrounding rocks of underground powerhouse Caverns under high geostress condition and countermeasures[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(2): 228-244. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201202003.htm
[4] 黄润秋, 黄达, 段绍辉, 等. 锦屏Ⅰ级水电站地下厂房施工期围岩变形开裂特征及地质力学机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(1): 23-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201101003.htm HUANG Runqiu, HUANG Da, DUAN Shaohui, et al. Geomechanics mechanism and characteristics of surrounding rock mass deformation failure in construction phase for underground powerhouse of Jinping Ⅰ hydropower station[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(1): 23-35. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201101003.htm
[5] FENG X T, PEI S F, JIANG Q, et al. Deep fracturing of the hard rock surrounding a large underground cavern subjected to high geostress: in situ observation and mechanism analysis[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(8): 2155-2175. doi: 10.1007/s00603-017-1220-4
[6] 孟国涛, 何世海, 陈建林, 等. 白鹤滩右岸地下厂房顶拱深层变形机理分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(3): 576-583. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202003020 MENG Guotao, HE Shihai, CHEN Jianlin, et al. Mechanism of deep deformation of roof arch of underground powerhouse at right bank of Baihetan Hydropower Station[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(3): 576-583. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202003020
[7] 江权, 陈建林, 冯夏庭, 等. 大型地下洞室对穿预应力锚索失效形式与耦合模型[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(8): 2271-2279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201308030.htm JIANG Quan, CHEN Jianlin, FENG Xiating, et al. Failure format and interactive mechanism of prestressed thru-anchor cable in a large underground Caverns[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(8): 2271-2279. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201308030.htm
[8] 董志宏, 丁秀丽, 黄书岭, 等. 高地应力区大型洞室锚索时效受力特征及长期承载风险分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(1): 351-362. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201901037.htm DONG Zhihong, DING Xiuli, HUANG Shuling, et al. Analysis of ageing-stress characteristics and long-term bearing risk of anchor cable for a large cavern in high geo-stress area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(1): 351-362. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201901037.htm
[9] 江权, 樊义林, 冯夏庭, 等. 高应力下硬岩卸荷破裂: 白鹤滩水电站地下厂房玄武岩开裂观测实例分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(5): 1076-1087. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201705004.htm JIANG Quan, FAN Yilin, FENG Xiating, et al. Unloading break of hard rock under high geo-stress condition: inner cracking observation for the basalt in the Baihetan's underground powerhouse[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(5): 1076-1087. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201705004.htm
[10] 戴峰, 李彪, 徐奴文, 等. 猴子岩水电站深埋地下厂房开挖损伤区特征分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(4): 735-746. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201504010.htm DAI Feng, LI Biao, XU Nuwen, et al. Characteristics of damaged zones due to excavation in deep underground powerhouse at houziyan hydropower station[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(4): 735-746. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201504010.htm
[11] 卢波, 王继敏, 丁秀丽, 等. 锦屏一级水电站地下厂房围岩开裂变形机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(12): 2429-2441. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201012010.htm LU Bo, WANG Jimin, DING Xiuli, et al. Study of deformation and cracking mechanism of surrounding rock of Jinping i underground powerhouse[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(12): 2429-2441. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201012010.htm
[12] 魏进兵, 邓建辉, 王俤剀, 等. 锦屏一级水电站地下厂房围岩变形与破坏特征分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(6): 1198-1205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201006016.htm WEI Jinbing, DENG Jianhui, WANG Dikai, et al. Characterization of deformation and fracture for rock mass in underground powerhouse of Jinping ⅰ hydropower station[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(6): 1198-1205. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201006016.htm
[13] 李仲奎, 周钟, 汤雪峰, 等. 锦屏一级水电站地下厂房洞室群稳定性分析与思考[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(11): 2167-2175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200911003.htm LI Zhongkui, ZHOU Zhong, TANG Xuefeng, et al. Stability analysis and considerations of underground powerhouse Caverns group of Jinping i hydropower station[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(11): 2167-2175. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200911003.htm
[14] 刘国锋, 冯夏庭, 江权, 等. 白鹤滩大型地下厂房开挖围岩片帮破坏特征、规律及机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(5): 865-878. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201605001.htm LIU Guofeng, FENG Xiating, JIANG Quan, et al. Failure characteristics, laws and mechanisms of rock spalling in excavation of large-scale underground powerhouse Caverns in Baihetan[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(5): 865-878. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201605001.htm
[15] 韩刚, 赵其华, 彭社琴. 白鹤滩水电站坝区深部破裂岩体地应力演化特征[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(增刊1): 583-589. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2011S1103.htm HAN Gang, ZHAO Qihua, PENG Sheqin. In-situ stress field evolution of deep fracture rock mass at dam area of Baihetan hydropower station[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(S1): 583-589. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2011S1103.htm
[16] 樊启祥, 汪志林, 何炜, 等. 金沙江白鹤滩水电站地下厂房玄武岩洞室群施工技术创新[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2021, 51(9): 1088-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JEXK202109009.htm FAN Qixiang, WANG Zhilin, HE Wei, et al. Technological innovations in construction of underground Caverns in basaltic rocks at Baihetan Hydropower Station on Jinsha River[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2021, 51(9): 1088-1106. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JEXK202109009.htm
[17] 裴书锋, 赵金帅, 于怀昌, 等. 考虑洞室岩体应力型破坏特征的局部地应力反演方法及应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(12): 4093-4104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202012030.htm PEI Shufeng, ZHAO Jinshuai, YU Huaichang, et al. Inversion method for local in situ stress considering stress-induced damage of cavern surrounding rock and its application[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(12): 4093-4104. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202012030.htm
[18] MARTIN C D, CHRISTIANSSON R. Estimating the potential for spalling around a deep nuclear waste repository in crystalline rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2009, 46(2): 219-228.
[19] 张传庆, 刘振江, 张春生, 等. 隐晶质玄武岩破裂演化及破坏特征试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(7): 2487-2496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201907003.htm ZHANG Chuanqing, LIU Zhenjiang, ZHANG Chunsheng, et al. Experimental study on rupture evolution and failure characteristics of aphanitic basalt[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(7): 2487-2496. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201907003.htm
[20] 张春生, 朱永生, 褚卫江, 等. 白鹤滩水电站隐晶质玄武岩力学特性及Hoek-Brown本构模型描述[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(10): 1964-1978. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201910003.htm ZHANG Chunsheng, ZHU Yongsheng, CHU Weijiang, et al. Mechanical behaviors of basalt at Baihetan hydropower station and simulation with Hoek-Brown constitutive model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(10): 1964-1978. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201910003.htm
[21] 周涛, 张发斌, 徐宇, 等. 复杂地质条件下特大直径尾水调压室开挖支护施工[J]. 云南水力发电, 2020, 36(8): 187-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNSD202008043.htm ZHOU Tao, ZHANG Fabin, XU Yu, et al. Excavation support construction of large diameter tailwater surge chamber under complex geological conditions[J]. Yunnan Water Power, 2020, 36(8): 187-192. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNSD202008043.htm
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 裴书锋,郝文锋,樊义林,陈浩,李文涛. 大型水利水电工程锚固系统运行状况分析. 长江科学院院报. 2024(02): 142-150 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 苏都都,范勇,吴进高,杨广栋,冷振东. 穿越断层破碎带深埋洞室爆破开挖围岩破坏机理研究进展. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(04): 25-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 周嵩,潘岳,刘永胜,谢韬,张理蒙,张继超. 极高地应力破碎地层斜井进正洞力学行为分析及施工优化研究. 现代隧道技术. 2024(04): 142-150 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: