Influences of rainfall-induced landslides on forces acting on gas pipelines with discontinuous joints
-
摘要: 既有成果还较少涉及降雨条件下滑坡对管道结构时域变形的解析分析,且针对滑坡–管道相互作用的理论研究仅限于连续管道,未考虑管道接口和管内气压的影响。首先,基于Green-Ampt模型得出的边坡降雨入渗规律,以边坡湿润锋作为滑坡滑动面,采用不平衡推力法计算出滑坡推力;其次,将滑坡推力施加到非连续接口管道上,基于Pasternak地基模型并考虑输气压力作用,求解出降雨条件下滑坡区域输气管道任意截面的内力和位移。在此基础上,结合工程实测值与本文解析解进行对比验证,获得了较好的一致性。最后,针对降雨强度参数进行了敏感性分析和输气管道安全评价。结果表明:随着降雨历时发展,降雨强度的增大引起非连续管道的变形值和变形速率显著增大,管道最大位移增长速率开始迅速下降的时间点逐渐提前;管道最大当量应力随着连续降雨历时增长而增大,直至超出输气管道安评范围。Abstract: The analytical analysis of the time-domain deformation of pipeline structure caused by landslides under rainfall conditions is rarely involved in the existing results, and the theoretical researches on the interaction between landslides and pipelines are limited to continuous pipelines without considering the influences of pipeline joints and internal air pressures. Firstly, the Green-Ampt model based on the layered assumption is used to calculate the depth of wet layer of slope under rainfall conditions, and the thrust force of landslides is calculated by the unbalanced thrust method. Secondly, the thrust force of landslides is applied to the discontinuous interface pipeline. Based on the Pasternak foundation model and considering the effects of gas pressure, the internal forces and displacements of any section of the gas pipeline are solved in the landslide area under the rainfall. On this basis, the measured values are compared with the analytical solutions, and a good agreement is obtained. Finally, the sensitivity analysis and the safety evaluation of the gas pipeline are carried out according to the rainfall intensity. The results show that with the development of rainfall duration, the increase of rainfall intensity causes the deformation value and rate of discontinuous pipeline to increase significantly, and the starting time of rapid decline for the maximum displacement growth rate of pipeline is gradually advanced. The maximum equivalent stress of the pipeline increases with the increase of continuous rainfall duration until it exceeds the safety assessment range of the gas pipeline.
-
Keywords:
- rainfall /
- landslide /
- gas pipeline /
- air pressure /
- discontinuous joint /
- Pasternak foundation model
-
0. 引言
山区时常因降雨发生滑坡,而滑坡往往伴随着严重的经济损失,如周边建筑物及管道等地下结构产生严重的变形甚至被破坏。目前,边坡安全问题已经成为地质灾害诱发管道安全问题的重中之重,且由降雨诱发的滑坡高达80%以上[1]。所以,研究降雨历时及强度与埋地管道变形破坏的关系有着重大的意义。
国内外学者针对降雨入渗理论进行了大量理论研究[2-6]。张杰等[7]基于分层假定的Green-Ampt模型推导了入渗深度和时间的关系,并将其运用到降雨入渗对边坡安全系数的影响分析中。苏永华等[8]通过改进Green-Ampt模型,使其能综合考虑湿润层含水率分布情况,进而提出了该模型下边坡稳定性系数表达式。进而,相关学者通过解析法对滑坡作用下管道变形特性进行了探究。Sarvanis等[9]基于结构力学杆件受力的理论,提出了一种新的解析方法,用于计算永久性地面变形引起的纵向管道应变。张家铭等[10]为提高弹性地基梁法的计算精度,引入Pasternak双参数模型,考虑土弹簧间相互作用,提出一种滑坡段埋地管道受力分析方法,但未考虑实际工程中管道非连续的情况。Zhang等[11]考虑管土相互作用的非线性和钢管的力学性能,提出了海底滑坡下埋地钢管应力分析的半解析方法,但未考虑管道接口和和管内气压的影响。此外,也有学者通过数值法和模型试验法进行了降雨诱发滑坡作用下管道的内力分析[12-14]。数值法由于模型复杂,一般需要耗费大量运算时间,模型试验法不仅耗费时间且需要大量人力、财力,所以解析法的研究显得尤为重要。且在以上的研究中,对于滑坡引起埋地管道变形量的计算都是将管道视作连续管道,然而实际工程中的埋地管道多为接口管道,接口处的薄弱会导致接口管道整体抗弯刚度明显小于连续管道。因此滑坡作用下非连续接口管道的变形会明显大于连续管道,埋地接口管道的结构连续性假定大大低估了管道沉降量。
目前,对于非连续埋地接口管道变形的研究方法主要有数值模拟法、模型试验法和解析解法。李大勇等[15]运用三维有限元法,求解了受基坑开挖导致的柔性接口地下管线位移和内力。史江伟等[16]通过土工离心模型试验和有限元参数分析,系统研究了盾构下穿不同接口刚度管线的变形特性。Klar等[17]、林存刚等[18]分别基于有限差分法推导出了盾构隧道开挖地层损失下考虑接口效应的管线的挠曲解答。但这些仅限于隧道和基坑开挖对周边非连续管线的影响,还未将其运用到滑坡对非连续管道变形影响的研究中,且在计算管道变形时,未考虑输气管道输气压力引起的轴向力对非连续管道的影响。更是鲜少有人考虑随降雨历时的增长诱发滑坡作用下的非连续输气管道变形的动态过程。
本文基于Green-Ampt降雨入渗模型和Pasternak地基模型,尝试性提出了一种考虑输气压力影响的降雨诱发滑坡导致非连续接口输气管道受力的解析计算方法。首先,基于分层假定下的Green-Ampt模型计算出不同降雨历时下边坡土体的湿润锋深度。其次,将边坡湿润锋作为滑坡滑动面,通过不平衡推力法计算出滑坡对非连续接口输气管道的推力。最后,将前一阶段计算出的滑坡推力施加到横穿滑坡体的非连续接口管道上,基于Pasternak地基模型对管道微元进行受力分析,并考虑输气压力的影响,得到了随持续性降雨发展非连续输气管道位移动态规律的解答。此外,本文使用工程实例结果验证该方法的正确性,并针对降雨强度参数进行了影响因素分析。本研究成果可对多雨滑坡地区埋地管道的安全状况进行评估,为其以后维修加固提供一定的理论依据。
1. 考虑降雨入渗的滑坡推力计算
1.1 基于分层假定的Green-Ampt模型
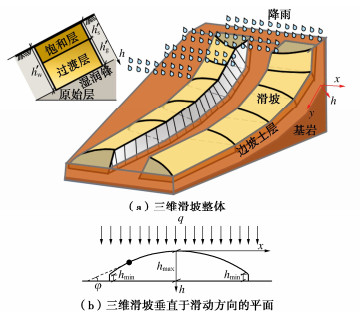
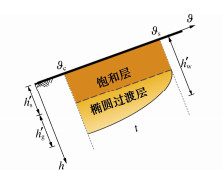
Bodman等[3]在干土积水条件下的垂直一维入渗试验中,提出了一种土体分层假定。彭振阳等[4]在此基础上根据含水率的变化将土体分为饱和层、过渡层和原始层。饱和层和过渡层合称为湿润层,其与原始层的分界面被称为湿润锋,如图 1所示,各土层的含水率为
$$ \vartheta (h)=\left\{ \begin{array}{l}{\vartheta }_{\text{s}}\begin{array}{cc}& 0\le h\le h'_{\text{s}}\begin{array}{cc}& \end{array}(饱和层)\end{array}\\ {\vartheta }_{\text{g}}{\begin{array}{cc}& h'_{\text{s}}\le h\le {h}'_{\text{w}}\end{array}}{{}}{}(过渡层)\\ {\vartheta }_{\text{c}}\begin{array}{cc}& h\ge h'_{\text{w}}\begin{array}{cc}& {{}}{{}}{}\end{array}\text{ }(原始层)\end{array}\end{array} \right. \\ = \left\{ \begin{array}{l}{\vartheta }_{\text{s}}\begin{array}{cc}& 0\le h\le h'_{\text{s}}\end{array}\\ {\vartheta }_{\text{s}}-({\vartheta }_{s}-{\vartheta }_{\text{c}})\sqrt{1-{(h-h'_{\text{s}})}^{2}/{(h'_{\text{g}})}^{2}}, h'_{\text{s}}\le h\le h'_{\text{s}}\\ {\vartheta }_{\text{c}}\begin{array}{cc}& h\ge h'_{\text{w}}\end{array}\end{array} \right. , $$ (1) 其中,
$$ h'_{\text{w}}=h'_{\text{g}}+h'_{\text{s}}\begin{array}{cc}, & h'_{\text{s}}=(1-\eta )h'_{\text{w}}\end{array} 。 $$ (2) 式中h为距地表深度(m);$\vartheta (h)$为h处土体含水率;${\vartheta _{\text{s}}}$,${\vartheta _{\text{g}}}$和${\vartheta _{\text{c}}}$分别为饱和层、过渡层和原始层含水率(%);$ {h'_{\text{s}}} $和$ {h'_{\text{g}}} $分别为饱和层和过渡层厚度(m);$ {h'_{\text{w}}} $为湿润层厚度(m),即湿润锋深度(m);$\eta $为过渡层占湿润层的比例。
随着降雨时间的增长,湿润锋位置由于雨水入渗逐渐向下推移,饱和层和湿润层占湿润层的比例也不断改变,表现为过渡层占湿润层比例逐渐减小,且所占比例与湿润层厚度呈现出线性关系[4]:
$$ \eta = F{h'_{\text{w}}} + G, $$ (3) 式中,F,G为系数,且F<0,0<G<1。
由式(3)可得,存在某一时刻t=tw使得$\eta $=0,此时湿润层土体全部达到饱和状态,即$ {h'_{\text{w}}} $=$ {h'_{\text{s}}} $,$ {h'_{\text{g}}} $=0。
当$\eta $>0时,将式(3)代入式(2)可得
$$ {h'_{\text{w}}} = \frac{{({\text{1}} - G) - \sqrt {{{(1 - G)}^2} - 4F{h'_{\text{s}}}} }}{{2F}} 。 $$ (4) 基于分层假定Green-Ampt(简称GA)模型[5]将降雨入渗的湿润层区域划为为饱和层和过渡层,分别计算其入渗量,最后叠加成降雨入渗的总入渗量。由于过渡层形态的复杂性,只能通过近似方式等效。过渡层土体的含水率随时间的分布曲线可近似为椭圆曲线[5],如图 1所示,其中拟合椭圆的水平半轴长度为${\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}}$,纵向半轴长度为$ {h'_{\text{g}}} $,其拟合结果与Richards方程计算值吻合性很好。因此,过渡层中的降雨入渗量为1/4椭圆面积。根据分层原理,降雨入渗的总入渗量可表示为
$$ U = {U_{\text{s}}} + {U_{\text{g}}} = \left( {{\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}}} \right){h'_{\text{s}}} + \frac{{\text{π }}}{4}({\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}}){h'_{\text{g}}}\\= ({\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}})\left( {1 - \eta + \frac{{\text{π }}}{{\text{4}}}\eta } \right){h'_{\text{w}}}, $$ (5) 式中,Us为饱和层入渗量(m),Ug为过渡层入渗量(m)。
将式(4)代入式(5)得
$$U = \frac{{({\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}})(4 - {\text{π }})}}{4}{h'_{\text{s}}}{\text{ + }}\frac{{{\text{π }}({\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}})({\text{1}} - G)}}{{8F}} -\\ \frac{{{\text{π }}({\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}})}}{{{\text{8}}F}}\sqrt {{{(1 - G)}^2} - 4F{h'_{\text{s}}}} 。 $$ (6) 基于GA模型,可以将降雨入渗的发展过程随降雨时长可以分成3个时段[5-6]。第一时段$ t $<$ {t_{\text{q}}} $,降雨初期,边坡土体处于非饱和状态,土体入渗率由降雨强度控制。第二时段$ {t}_{\text{q}}\le t $<$ {t_{\text{w}}} $,饱和层土体处于饱和状态,降雨已不能完全入渗,坡体表面产生雨水径流,降雨入渗率由土体入渗能力控制。第三时段$ t \geqslant {t_{\text{w}}} $,过渡层消失,边坡土体已处于饱和状态,降雨入渗率仍由土体入渗能力控制。实际的滑坡形态多如图 2(a)所示,滑坡投影在x–h平面的形状多为弧形。图 2(b)中滑坡在x–h平面的形状表面任意点的切线与x轴的夹角为$ \varphi $。
假设降雨强度为q(m/h),在滑坡沿滑动方向任意剖面,垂直于坡面的降雨入渗率k为
$$ k = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} q\cos \theta \cos \varphi \quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad {\text{ (}}t < {t_{\text{q}}}) \hfill \\ {K_{\text{s}}}\left( {\frac{{{h'_{\text{s}}}\cos \theta \cos \varphi }}{{{h'_{\text{s}}}}} + \frac{{{S_{\text{f}}}}}{{{h'_{\text{s}}}}}} \right)\quad\quad{\text{( }}{t_{\text{q}}} \leqslant t < {t_{\text{w}}}) \hfill \\ {K_{\text{s}}}\left( {\frac{{{h'_{\text{w}}}\cos \theta \cos \varphi }}{{{h'_{\text{w}}}}} + \frac{{{S_{\text{f}}}}}{{{h'_{\text{w}}}}}} \right)\quad\quad{\text{ (}}t \geqslant {t_{\text{w}}}) \hfill \\ \end{array} \right. 。 $$ (7) 式中$ \theta $为边坡坡面的倾角;$ \varphi $为边坡沿滑坡宽度方向弧形边界线切线与滑动面的夹角;Ks为饱和渗透系数;Sf为下层土体作用于饱和层的基质吸力势。当$ t \geqslant {t_{\text{w}}} $时,存在$ {h'_{\text{w}}} $=$ {h'_{\text{s}}} $。
根据降雨入渗率的连续性,存在时刻tq,满足
$$ q\cos \theta \cos \varphi = {K_{\text{s}}}\left( {\frac{{{h'_{{\text{sq}}}}\cos \theta \cos \varphi }}{{{h'_{{\text{sq}}}}}} + \frac{{{S_{\text{f}}}}}{{{h'_{{\text{sq}}}}}}} \right) 。 $$ (8) 式中,$ {h'_{{\text{sq}}}} $为降雨时刻为tq时的饱和层厚度,整理可得$ {h'_{{\text{sq}}}} = {S_{\text{f}}}/\chi $,$ \chi {\text{ = }}{{q\cos \theta \cos \varphi } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{q\cos \theta \cos \varphi } {{K_{\text{s}}} - \cos \theta }}} \right. } {{K_{\text{s}}} - \cos \theta }}\cos \varphi $。
联立式(6)~(8),得降雨入渗临界时刻tq为
$$ {t_{\text{q}}} = \frac{{({\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}})(4 - {\text{π }}){S_{\text{f}}}}}{{4q\chi \cos \theta \cos \varphi }}{\text{ + }}\frac{{{\text{π }}({\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}})({\text{1}} - G)}}{{8Fq\cos \theta \cos \varphi }} - \\ \frac{{{\text{π }}({\vartheta _{\text{s}}} - {\vartheta _{\text{c}}})}}{{{\text{8}}Fq\cos \theta \cos \varphi }}\sqrt {{{(1 - G)}^2} - \frac{{4F{S_{\text{f}}}}}{\chi }} , $$ (9) 式中,Uq为降雨tq时刻降雨总入渗量。
将式(6)等号两边对t求导后代入式(9),再将等式两边积分,得降雨历时t与饱和层厚度$ {h'_{\text{s}}} $关系为
$$ t=\left\{ \begin{array}{l}\frac{({\vartheta }_{\text{s}}-{\vartheta }_{\text{c}})(4-\text{π})h'_{\text{s}}}{4q\mathrm{cos}\theta \mathrm{cos}\varphi }\text{+}\frac{\text{π}({\vartheta }_{\text{s}}-{\vartheta }_{\text{c}})(\text{1}-G)}{8Fq\mathrm{cos}\theta \mathrm{cos}\varphi }-\\ \frac{\text{π}({\vartheta }_{\text{s}}-{\vartheta }_{\text{c}})}{\text{8}Fq\mathrm{cos}\theta \mathrm{cos}\varphi }\sqrt{{(1-G)}^{2}-4Fh'_{\text{s}}} \quad\quad\quad\quad\quad \text{ (}t < {t}_{\text{q}}\text{)}\\ {\displaystyle {\int }_{h'_{\text{sq}}}^{h'_{\text{s}}}{\left\{\frac{{K}_{\text{s}}(h\mathrm{cos}\theta \mathrm{cos}\varphi +{S}_{\text{f}})}{\left[\frac{({\vartheta }_{\text{s}}-{\vartheta }_{\text{c}})(4-\text{π})}{4}\text{+}\frac{\text{π}({\vartheta }_{\text{s}}-{\vartheta }_{\text{c}})}{4\sqrt{{(1-G)}^{2}-4Fh}}\right]h}\right\}}^{-1}\text{d}h+{t}_{\text{q}}}\text{ }\\ \quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad \text{ (}{t}_{\text{q}}\le t < {t}_{\text{w}})\\ {{\displaystyle {\int }_{h'_{\text{sq}}}^{h'_{\text{s}}}\left\{\frac{{K}_{\text{s}}\left(h\mathrm{cos}\theta \mathrm{cos}\varphi +{S}_{\text{f}}\right)}{({\vartheta }_{\text{s}}-{\theta }_{\text{c}})h}\right\}}}^{-1}\text{d}h\text{+}{t}_{\text{q}}\quad\quad\quad\text{ (}t\ge {t}_{\text{w}})\end{array} \right.。 $$ (10) 联立式(4),(10)可得降雨历时与湿润锋深度$ {h'_{\text{w}}} $关系。由于积分后公式过于冗长,在此不再赘述。
1.2 滑坡推力求解
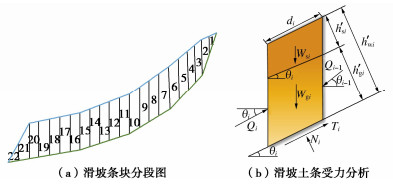
在考虑降雨入渗的条件下,首先沿滑坡滑动方向将滑坡体分成若干竖直条块(图 3(a)),对每个条块进行受力分析并列出平衡方程,其次采用不平衡推力法分别计算其分界面上沿滑坡方向的剩余合力即为该滑块的滑坡推力值。
本文作如下假定:①湿润锋所在的平面为潜在滑动面;滑坡推力方向与潜在滑动方向相同;②对滑坡土块进行受力分析时忽略地表雨水径流产生的冲刷力。对于单个滑块单元采用极限平衡法进行分析时,第i块土条受力分析简图如图 3(b)所示。
(1) 考虑降雨的滑坡推力求解
滑坡推力计算对第i块土条,取土条底面法线方向力平衡可得
$$ {W_{{\text{s}}i}}\cos {\theta _i} + {W_{{\text{g}}i}}\cos {\theta _i} + {Q_{i - 1}}\sin ({\theta _{i - 1}} - {\theta _i}) - {N_i} = 0 。 $$ (11) 对第i块土条,取土条底面轴线方向可得
$$ {W_{{\text{s}}i}}\sin {\theta _i} + {W_{{\text{g}}i}}\sin {\theta _i} + {Q_{i - 1}}\cos ({\theta _{i - 1}} - {\theta _i}) - {T_i} - {Q_i} = 0 。 $$ (12) 将饱和层和过渡层土条剖面形状都近似成平行四边形,来计算其自重。其中,饱和层自重$ {W_{{\text{s}}i}} $为
$$ {W_{{\text{s}}i}} = {\gamma _{\text{s}}}{h'_{{\text{s}}i}}{d_i} 。 $$ (13) 式中$ {h'_{{\text{s}}i}} $为第i块土条饱和层厚度(m),由式(10)计算得到;$ {\gamma _{\text{s}}} $为饱和土体重度(kN/m3);$ {\vartheta _{\text{c}}} $为原始土体含水率(%)。
过渡层土体自重为
$$ {W_{{\text{g}}i}}{\text{ = }}\int_{h_{{\text{s}}i}'}^{h_{{\text{w}}i}'} {{d_i}{\gamma _{{\text{g}}i}}(h)} \text{d} h , $$ (14) 式中,$ {h'_{{\text{w}}i}} $为第i块土条湿润锋的深度(m),由式(4),(10)联立计算得到,$ {\gamma _{{\text{g}}i}}(h) $为第i块土体在h深度时的重度(kN/m3)。
假设过渡层非饱和土体重度和含水率呈线性关系,联立式(1),则过渡层内不同深度的土体重度为
$$ {\gamma _{{\text{g}}i}}(h) = {\gamma _{\text{c}}} + ({\gamma _{\text{s}}} - {\gamma _{\text{c}}})\sqrt {1 - \frac{{{{(h - {h'_{{\text{s}}i}})}^2}}}{{{{({h'_{{\text{g}}i}})}^2}}}} \begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{({h'_{{\text{s}}i}} < h < {h'_{{\text{w}}i}})} \end{array} , $$ (15) 式中,$ {h'_{{\text{g}}i}} $为第i块土条过渡层厚度(m),$ {\gamma _{\text{c}}} $为土体原始重度(kN/m3)。
由Fredlund等[19]提出的非饱和土抗剪强度公式得
$$ {T_i} = \frac{{{c_i}{d_i}}}{{{F_{\text{s}}}}} + \frac{{({N_i} - {u_{\text{a}}}{d_i})\tan {\varphi _i} + ({u_{\text{a}}}{d_i} - {u_{\text{w}}}{d_i})\tan \varphi _i^{\text{b}}}}{{{F_{\text{s}}}}} 。 $$ (16) 式中 $ {c_i} $为第i块土条滑面处的黏聚力(kN);$ {\varphi _i} $为第i块土条滑面处的内摩擦角(°);$ \varphi _i^{\text{b}} $为抗剪强度随基质吸力增大而增大的吸力摩擦角(°);$ {F_{\text{s}}} $为滑坡的稳定系数;$ {u_{\text{a}}} $为滑动面处的孔隙气压,一般默认为大气压强,即$ {u_{\text{a}}} = 0 $;$ {u_{\text{w}}} $为滑动面处的孔隙水压(kPa),$ ({u_{\text{a}}} - {u_{\text{w}}}) $为基质吸力的大小,即[7]
$$ - {u_{\text{w}}} = {\gamma _{\text{w}}}{S_{\text{f}}} , $$ (17) 其中,$ {\gamma _{\text{w}}} $为雨水的重度(kN/m3),$ {S_{\text{f}}} $为下层土体作用于饱和层的基质吸力势(m)。
当降雨时长0<t$ \ll $tw时,滑坡推力计算是将式(16),(17)代入式(11),(12),联立可得
$$ {Q_i} = ({W_{{\text{s}}i}}\sin {\theta _i} + {W_{{\text{g}}i}}\sin {\theta _i}){\text{ + }}{Q_{i - 1}}{\psi _i} - $$ $$ \left[ {\frac{{{c_i}{d_i}}}{{{F_{\text{s}}}}} + \frac{{({W_{{\text{s}}i}} + {W_{{\text{g}}i}})\cos {\theta _i}\tan {\varphi _i} + {\gamma _{\text{w}}}{S_{\text{f}}}{d_i}\tan \varphi _i^{\text{b}}}}{{{F_{\text{s}}}}}} \right] , $$ (18) 式中,传递系数$ {\psi _i} = [\cos ({\theta _{i - 1}} - {\theta _i}) - {{\tan {\varphi _i}\sin ({\theta _{i - 1}} - {\theta _i})]} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\tan {\varphi _i}\sin ({\theta _{i - 1}} - {\theta _i})]} {{F_{\text{s}}}}}} \right. } {{F_{\text{s}}}}} $。
为简化计算采用超载法进行第i块土条的剩余下滑力$ Q_i $计算得
$$ Q_i = K({W_{{\text{s}}i}}\sin {\theta _i} + {W_{{\text{g}}i}}\sin {\theta _i}){\text{ + }}{Q_{i - 1}}{\psi '_i} -\\ [{c_i}{d_i} + ({W_{{\text{s}}i}}\cos {\theta _i} + {W_{{\text{g}}i}}\cos {\theta _i})\tan {\varphi _i} + {\gamma _{\text{w}}}{S_{\text{f}}}{d_i}\tan \varphi _i^{\text{b}}] 。 $$ (19) 式中 $ {\psi '_i} = \cos ({\theta _{i - 1}} - {\theta _i}) - \tan {\varphi _i}\sin ({\theta _{i - 1}} - {\theta _i}) $;K为安全系数,根据《岩土工程勘察规范:GB50021—2001(2009年版)》[20]验算边坡稳定时,取1.10~1.25。
当降雨时长t>tw时,边坡土体已经完全饱和,过渡层消失,基质吸力$ ({u_{\text{a}}} - {u_{\text{w}}}) $的大小为0。将$ {W}_{\text{g}i}=0, $ $ {u_{\text{w}}} = 0 $代入式(19),可得
$$ Q_i = K{W_{{\text{s}}i}}\sin {\theta _i}{\text{ + }}{Q_{i - 1}}{\psi '_i} - ({c_i}{d_i} + {W_{{\text{s}}i}}\cos {\theta _i}\tan {\varphi _i}) 。 $$ (20) 由式(19),(20)归纳的降雨条件下,第i个滑块上的滑坡推力$ Q_i $为
$$ {Q}_{i}=\left\{ \begin{array}{l}\begin{array}{l}\begin{array}{c}K({W}_{\text{s}i}+{W}_{\text{g}i}\text{)}\mathrm{sin}{\theta }_{i}\text{+}{Q}_{i-1}\psi '_{i}-[{c}_{i}{d}_{i}+\\ {\gamma }_{\text{w}}{S}_{\text{f}}{d}_{i}\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }_{i}^{\text{b}}+({W}_{\text{s}i}+{W}_{\text{g}i})\mathrm{cos}{\theta }_{i}\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }_{i}]\end{array}\text{ (}0\le t < {t}_{\text{w}})\\ \end{array}\\ K{W}_{\text{s}i}\mathrm{sin}{\theta }_{i}\text{+}{Q}_{i-1}\psi '_{i}-({c}_{i}{d}_{i}+{W}_{\text{s}i}\mathrm{cos}{\theta }_{i}{}_{}\mathrm{tan}{\varphi }_{i})\text{ (}t\ge {t}_{\text{w}})\end{array} \right.。 $$ (21) (2) 不考虑降雨的滑坡推力求解
当不考虑降雨时长,滑坡推力计算公式由式(19)变换为
$$ Q_i = K{W_{{\text{c}}i}}\sin {\theta _i}{\text{ + }}{Q_{i - 1}}{\psi '_i} - ({c_i}{d_i} + {W_{ci}}\cos {\theta _i}_{}\tan {\varphi _i}) , $$ (22) 式中,$ {W_{{\text{c}}i}} $为不考虑降雨时滑坡土条i的自重,$ {W_{{\text{c}}i}} = $ $ {\gamma _{\text{c}}}{R_i} $,$ {R_i} $为土条i的面积。
2. 滑坡对非连续接口输气管道作用
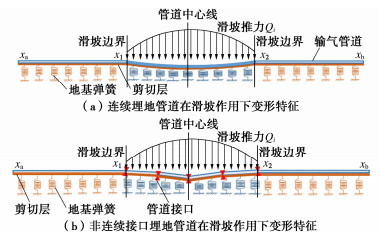
将降雨诱发滑坡产生的滑坡推力作为外界荷载施加于非连续接口输气管道上,基于Pasternak地基模型,将埋地管道简化为弹性地基梁,并采用虚拟节点考虑管道接口处的特性,建立管道单元和节点的力学平衡方程,列出边界条件,求解出管道结构任意截面的内力和位移。图 4为普通连续埋地管道弹性地基梁模型和非连续接口管道的弹性地基梁模型,其两者最大的区别在于接口管道接口两端转角不连续。
基本假设:①在滑坡发生时,导致管道变形的主要作用力为滑坡对管道的推力,忽略管道及管内运输物质的重力作用及管道温差引起的轴向应力;②管道水平埋置于均质各向同性地层中;③管线沿其纵向与周围地层保持接触;④假设管道接口处直径与标准段相同,且忽略接口管道的接口长度;⑤沿管线纵向,无论在标准管段还是接口位置,截面弯矩M均连续,且关于坐标x可导;⑥将接口管道的标准段视作Euler-Bernoulli梁,接口视作旋转弹簧。
2.1 Pasternak地基模型
Pasternak弹性地基梁模型[21]是在Winkler地基梁模型的基础上增加一层剪切层,假设各Winkler地基弹簧之间存在剪切的相互作用。假定管道延任管道横截面走向抗弯刚度无穷大,则土体作用于管道时其沿横截面水平方向产生整体平移;结合管线与周围地层始终接触的假定,则对于管线任一横截面,其接触面上的土体竖向位移$ \omega (x) $沿横截面水平方向不变。因此,管线与土体相互作用时,Pasternak地基模型的二维表达式为
$$ f(x) = k\omega (x) - {G_{\text{p}}}\frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}\omega (x)}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} 。 $$ (23) 式中 f(x)为地基反力(kN/m2);$ k $为地基反力系数(kN/m3);$ {G_{\text{p}}} $为地基剪切刚度(kN/m);$ \omega (x) $为管道位移(m)。$ k $和$ {G_{\text{p}}} $的确定采用Vlazov等[22]提出的公式:$ k = {{(1 - {\nu _{\text{s}}}){E_{\text{s}}}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{(1 - {\nu _{\text{s}}}){E_{\text{s}}}} {[(1 + {\nu _{\text{s}}})(1 - 2{\nu _{\text{s}}})H}}} \right. } {[(1 + {\nu _{\text{s}}})(1 - 2{\nu _{\text{s}}})H}}] $,$ {G_{\text{P}}} = {{{E_{\text{s}}}H} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{E_{\text{s}}}H} {[6(1 + {\nu _{\text{s}}})}}} \right. } {[6(1 + {\nu _{\text{s}}})}}] $。式中,Es和$ {\nu _{\text{s}}} $分别是土的弹性模量(kN/m2)和泊松比;H是剪切层的厚度(m)。通过Yao等[23]提出的桩侧土受影响范围为11倍桩的直径,可近似取H=11D(D为埋地管道的外径)作为地基土的弹性层厚度。
2.2 输气管道位移方程的建立及求解
选取管道任一接口左右两端微元进行受力分析,微元长度为dx。假定其作用于管线轴线位置且沿管道横截面方向均布。
对接口左侧微元取竖向受力平衡,可得
$$ f(x)D{\text{d}}x - {Q_{}}(x){\text{d}}x - {S_{\text{L}}} + ({S_{\text{L}}} - {\text{d}}{S_{\text{L}}}) = 0 。 $$ (24) 式中 $ f(x) $为弹性地基梁作用于管道的地基反力(kN/m2);$ D $为管道外径(m);$ {\text{d}}x $为管道微元的宽度(m),$ {S_{\text{L}}} $为管道接口左侧横截面剪力(kN),$ {\text{d}}{S_{\text{L}}} $为沿着管道轴向x方向增加$ {\text{d}}x $长度时管道截面剪力的增量(kN);$ {Q_{}}(x) $为单位管道截面的滑坡推力(kN/m),$ {Q_{}}(x) = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} Q\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{{x_1} < x < {x_2}}&{} \end{array} \hfill \\ 0\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{{x_{\text{a}}} \leqslant x < {x_1}, {x_2} < x \leqslant {x_{\text{b}}}} \end{array} \hfill \\ \end{array} \right. $,$ Q $值由式(21)或(22)求得。其中,$ {x_1} $,$ {x_2} $分别为滑坡的左右边界轴向坐标,$ {x_{\text{a}}} $,$ {x_{\text{b}}} $分别为管道的左右边界轴向坐标,如图 4所示。
对式(24)进行变换,得
$$ \frac{{{\text{d}}{S_{\text{L}}}}}{{{\text{d}}x}} = f(x)D - {Q_{}}(x) 。 $$ (25) 对接口左侧微元取弯矩平衡,可得
$$ {M_{\text{L}}} - {S_{\text{L}}}{\text{d}}x - T{\text{d}}\omega - ({M_{\text{L}}} - {\text{d}}{M_{\text{L}}}) + \frac{{f(x)D{{({\text{d}}x)}^2}}}{2} - \frac{{Q(x){{({\text{d}}x)}^2}}}{2} = 0 。 $$ (26) 式中 $ {M_{\text{L}}} $为接口左侧弯矩($ {\text{kN}} \cdot {\text{m}} $);$ {\text{d}}{M_{\text{L}}} $为沿着管道轴向x方向增加$ {\text{d}}x $长度时管道截面弯矩的增量($ {\text{kN}} \cdot {\text{m}} $);$ T $为管道边界的轴向力,由管道的输送压力$ p $($ {\text{kPa}} $)决定,$ T = \frac{{{\text{π }}{D_1}^2p}}{4} $,$ {D_1} $为管道内径;$ {\text{d}}\omega (x) $为沿着管道轴向x方向增加$ {\text{d}}x $长度时管道截面位移的增量(m)。
对式(26)进行二阶求导并略去三阶微量后联立式(25)可得
$$ f(x) = \frac{1}{D}\frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{M_L}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} + \frac{{{Q_{}}(x)}}{D} - \frac{{T{{\text{d}}^2}\omega (x)}}{{D{\text{d}}{x^2}}} 。 $$ (27) 由Pasternak地基模型的二维方程(23)联立式(27),且由管道接口左、右两侧弯矩连续可得
$$ \frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}M}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} = - Q(x) + kD\omega (x) - ({G_{\text{p}}}D - T)\frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}\omega (x)}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} , $$ (28) 式中,M为管道任意截面的弯矩。
对于标准连续管段,其位移满足微分方程:
$$ EI\frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}\omega (x)}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} + M = 0 , $$ (29) 式中,E为管道弹性模量(kN/m2),I为管道横截面惯性矩(m4),EI为管道的等效抗弯刚度。
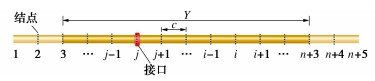
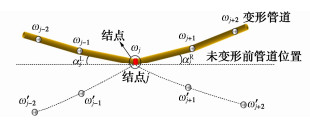
将长度为Y的管道沿长度方向分为n个单元,每段长为c。构建(n+1)个有限差分结点,分别为i=3,4,…,n+3。假设结点都处于地基模型弹簧上,其中有m个接口结点。为构建管道两端部结点(i=3,4,n+2,n+3)的差分方程,增加4个虚拟差分结点,分别为i=1,2,n+4,n+5,管道单元模型如图 5所示。对于非连续接口管道位移方程的差分法解答分为3个部分:接口结点位移方程、接口相邻结点位移方程、标准管段结点位移方程。其中,当m=0时,管道位移方程的解答即为连续管道挠曲方程的解答。
(1) 接口结点处差分方程的建立
柔性接口管道在接口两端位移和弯矩连续,转角不连续,通过增加虚拟结点的方式来满足差分条件。如图 6所示,接口结点位移为$ \omega _j $,接口左右最近的两个结点位移分别为$ \omega _{j{\text{ - }}2} $,$ \omega _{j{\text{ - }}1} $,$ \omega _{j{\text{ + }}1} $,$ \omega _{j{\text{ + }}2} $,左右两边各增加2个虚拟结点,虚拟结点位移分别为$ \omega '_{j - 2} $,$ \omega '_{j - 1} $,$ \omega '_{j{\text{ + }}1} $,$ \omega '_{j{\text{ + }}2} $,以满足接口位移可导的条件。接口所在结点j的弯矩为
$$ {M_j} = {k_j}(\alpha _j^{\text{L}} - \alpha _j^{\text{R}}) , $$ (30) 式中,$ {k_j} $为管道的接口转动刚度(kN•m/rad);$ \alpha _j^{\text{L}} $,$ \alpha _j^{\text{R}} $分别为第j节点所在管道左右两侧的转角,可以通过标准一阶差分算子计算[24]得到:
$$ \alpha _j^{\text{L}} = \frac{{{\text{d}}\omega _{j1}}}{{{\text{d}}x}}\left| {_{x = {x_j}}} \right. = \frac{{\omega '_{j + 1} - \omega _{j - 1}}}{{2c}} , $$ (31) $$ \alpha _j^{\text{R}} = \frac{{{\text{d}}\omega _{j2}}}{{{\text{d}}x}}\left| {_{x = {x_j}}} \right. = \frac{{\omega _{j + 1} - \omega '_{j - 1}}}{{2c}} , $$ (32) 式中,c为每个管道微元段的长度。
联立式(30)~(32)得$ {M_j} $的一阶差分式:
$$ {M_j} = {k_j}\frac{{\omega '_{j{\text{ + }}1} + \omega '_{j{\text{ - }}1} - \omega _{j{\text{ - }}1} - \omega _{j{\text{ + }}1}}}{{2c}} 。 $$ (33) 由式(29)和标准一阶差分中心公式可得结点j左右两边弯矩的一阶差分格式为
$$ M_j^{\text{L}} = - EI\frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{\omega _{j1}}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} = - EI\frac{{{\omega _{j - 1}} - 2{\omega _j} + \omega {'_{j + 1}}}}{{{c^2}}} , $$ (34) $$ M_j^{\text{R}} = - EI\frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{\omega _{j2}}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} = - EI\frac{{{\omega '_{j - 1}} - 2{\omega _j} + {\omega _{j + 1}}}}{{{c^2}}} 。 $$ (35) 由式(33)~(35)及结点两边弯矩连续$ M_j^{\text{R}}{\text{ = }}M_j^{\text{L}} $,可得虚拟结点位移$ \omega '_{j - 1} $,$ \omega '_{j{\text{ + }}1} $为
$$ {\omega '_{j - 1}}{\text{ = }}\frac{{{k_j}c{\omega _{j - 1}} + 2EI{\omega _j} - EI{\omega _{j + 1}}}}{{EI + {k_j}c}} , $$ (36a) $$ {\omega '_{j{\text{ + }}1}}{\text{ = }}\frac{{ - EI{\omega _{j - 1}} + 2EI{\omega _j}{\text{ + }}{k_j}c{\omega _{j + 1}}}}{{EI + {k_j}c}} 。 $$ (36b) 管道接口所在j结点两侧的转角$ \alpha _j^{\text{L}} $,$ \alpha _j^{\text{R}} $还可以通过高阶差分算子计算[24]得到:
$$ \alpha _j^{\text{L}} = \frac{{{\text{d}}\omega _{j1}}}{{{\text{d}}x}}\left| {_{x = {x_j}}} \right. = \frac{{ - \omega '_{j + 2}{\text{ + 8}}\omega '_{j + 1} - 8\omega _{j - 1}{\text{ + }}\omega _{j - 2}}}{{12c}} , $$ (37a) $$ \alpha _j^{\text{R}} = \frac{{{\text{d}}\omega _{j2}}}{{{\text{d}}x}}\left| {_{x = {x_j}}} \right. = \frac{{ - \omega _{j + 2}{\text{ + 8}}\omega _{j + 1} - 8\omega '_{j - 1}{\text{ + }}\omega '_{j - 2}}}{{12c}} 。 $$ (37b) 联立式(30),(37a),(37b),可得$ {M_j} $高阶差分方程为
$$ \begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {M_j} = \frac{{{k_j}}}{{12c}}( - \omega '_{j{\text{ + 2}}} + 8\omega '_{j{\text{ + 1}}} - 8\omega _{j - {\text{1}}} + \omega _{j - 2} + \\{\omega _{j{\text{ + 2}}} - 8\omega _{j{\text{ + 1}}} + 8\omega '_{j - {\text{1}}} - \omega '_{j - 2})} 。 \end{array} $$ (38) 对式(30)进行二次求导后结合梁转角方程的一阶差分形式,再联立式(29),(36a),(36b),(38)以及弯矩的高阶差分格式可得
$$ \begin{array}{l} \frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{M_{}}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}}\left| {_{x = {x_j}}} \right. = \frac{{{k_j}}}{{2{c^3}}}\left\{ {\frac{{ - 2EI}}{{EI + 2{k_j}c}}({\omega _{j - 2}} + {\omega _{j + 2}}) + } \right. \hfill \\ \begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{} \end{array}}&{} \end{array}{\text{ }}\left[ {2 - \frac{{ - 2({k_j}c - EI)}}{{EI + B}}} \right]({\omega _{j - 1}} + {\omega _{j + 1}}) + \hfill \\ \left. {\left[ {\frac{{8EI}}{{EI + 2{k_j}c}}\left( { - 1 + \frac{{8(EI + {k_j}c)}}{{EI + 2{k_j}c}}} \right) - 60\frac{{EI}}{{EI + 2{k_j}c}}} \right]{\omega _j}} \right\} 。 \end{array} $$ (39) 联立式(28),(34),(35),(36a),(36b),(38),(39)可得
$$ \begin{array}{l} - \frac{{{k_j}}}{{2{c^3}}}\left\{ {\frac{{ - 2EI}}{{EI + 2{k_j}c}}({\omega _{j - 2}} + {\omega _{j + 2}}) + \left[ {2 - \frac{{ - 2({k_j}c - EI)}}{{EI + {k_j}c}}} \right]({\omega _{j - 1}} + {\omega _{j + 1}}) + } \right. \hfill \\ \left. {\left[ {\frac{{8EI}}{{EI + {k_j}c}}\left( { - 1 + \frac{{8(EI + {k_j}c)}}{{EI + 2{k_j}c}}} \right) - 60\frac{{EI}}{{EI + 2{k_j}c}}} \right]{\omega _j}} \right\} \hfill \\ = - {Q_j} + kD{\omega _j} - \frac{{({G_{\text{p}}}D - T){k_j}}}{{(EI + {k_j}c)c}}({\omega _{j - 1}} - 2{\omega _j} + {\omega _{j + 1}}) , \end{array}$$ (40) 式中,$ {Q_j} $为管道接口节点j所在管道单元所受的滑坡推力,其值由滑坡推力公式(21)或(22)求得。
由式(40)可列出m个管道接口结点差分方程。
(2) 接口相邻结点的差分方程的建立
将式(29)求二阶导数再联立标准一阶中心差分公式可得
$$ \frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{M_{}}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}}\left| {_{x = {x_{j - 1}}}} \right.{\text{ = }} - \frac{{EI}}{{{c^4}}}(\omega {'_{j + 1}} - 4{\omega _j} + 6{\omega _{j - 1}} - 4{\omega _{j - 2}} + {\omega _{j - 3}}) , $$ (41a) $$ \frac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{M_{}}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}}\left| {_{x = {x_{j{\text{ + }}1}}}} \right.{\text{ = }} - \frac{{EI}}{{{c^4}}}({\omega _{j + 3}} - 4{\omega _{j + 2}} + 6{\omega _{j{\text{ + }}1}} - 4{\omega _j} + \omega {'_{j - 1}}) , $$ (41b) 式中,$ {\omega _{j + 3}} $,$ {\omega _{j + 2}} $,$ {\omega _{j - 2}} $,$ {\omega _{j - 3}} $分别为结点$ j + 3 $,$ j + 2 $,$ j - 3 $,$ j - 2 $处管道的位移。
联立式(28),(36b),(41a),可得
$$\begin{array}{l} \frac{{EI}}{{{c^4}}}\left[ {\frac{{{k_j}c}}{{EI + {k_j}c}}{\omega _{j + 1}} + \left( {4 - \frac{{2EI}}{{EI + {k_j}c}}} \right){\omega _j}} \right. + \hfill \\ \left. {{\text{ }}\left( {6 - \frac{{EI}}{{EI + {k_j}c}}} \right){\omega _{j - 1}} - 4{\omega _{j - 2}} + {\omega _{j - 3}}} \right] \hfill \\ = {Q_{j - 1}} - kD{\omega _{j - 1}} + \frac{{{G_{\text{p}}}D - T}}{{{c^2}}}({\omega _{j - 2}} - 2{\omega _{j - 1}} + {\omega _j}) 。 \end{array} $$ (42) 联立式(28),(36a),(41b)可得
$$ \begin{array}{l} \frac{{EI}}{{{c^4}}}\left[ {{\omega _{j + 3}} - 4{\omega _{j + 2}} + \left( {6 - \frac{{EI}}{{EI + {k_j}c}}} \right){\omega _{j + 1}}} \right. + \hfill \\ \left. {{\text{ }}\left( {4 - \frac{{2EI}}{{EI + {k_j}c}}} \right){\omega _j} + \frac{{{k_j}c}}{{EI + {k_j}c}}{\omega _{j - 1}}} \right] \hfill \\ = {Q_{j{\text{ + }}1}} - kD{\omega _{j + 1}}{\text{ + }}\frac{{{G_{\text{p}}}D - T}}{{{c^2}}}({\omega _{j + 2}} - 2{\omega _{j + 1}} + {\omega _j}) 。\end{array} $$ (43) 由式(42),(43)可列出2m个管道接口相邻结点处的差分方程。
(3) 标准连续管段结点差分方程的建立
在管道构建的(n+1)个有限差分结点中,共有(n+1-3m)个标准连续管段结点。联立式(28),(29)进行中心差分可得连续管段位移差分方程为
$$\frac{{EI}}{{{c^4}}}({\omega _{i{\text{ - }}2}} - 4{\omega _{i - 1}} + 6{\omega _i} - 4{\omega _{i + 1}} + {\omega _{i + 2}})\\ = {Q_i} - kD{\omega _i}{\text{ + }}\frac{{{G_{\text{p}}}D - T}}{{{c^2}}}({\omega _{i + 1}} - 2{\omega _i} + {\omega _{i - 1}}) 。 $$ (44) 式中,$ {\omega _{i - 2}} $,$ {\omega _{i - 1}} $,$ {\omega _i} $,$ {\omega _{i + 1}} $,$ {\omega _{i + 2}} $分别为结点$ i - 2 $,$ i - 1 $,$ i $,$ i{\text{ + }}1 $,$ i + 2 $处管道的位移。由式(44)可列出(n+1-3m)个标准连续管段结点处的差分方程。
因管线的长度相对截面尺寸非常大,可以认为管线两端为自由端,没有约束。边界条件为管线端部弯矩、剪力都为零,可得到
$$ {M}_{3}=0, \begin{array}{cc}& {M}_{n\text{+3}}\end{array}=0, {S}_{3}=0, \begin{array}{cc}& {S}_{n+3}\end{array}=0 。 $$ (45) 式中 $ {M_3} $为管道最左端弯矩;$ {M_{n{\text{ + }}3}} $为管道最右端弯矩;$ {S_3} $为管道最左端剪力;$ {S_{n{\text{ + }}3}} $为管道最右端剪力。
进一步,可得到管道位移差分方程的矩阵形式:
$$ [{\boldsymbol{K}_{\text{p}}}]\{ \boldsymbol{\omega} \} = [\boldsymbol{R}]\{ \boldsymbol{\omega }\} + [\boldsymbol{H}]\{ \boldsymbol{Q}\} , $$ (46) 式中,$ [{\boldsymbol{K}_{\text{p}}}] $为管道刚度矩阵,$ \{ \boldsymbol{\omega} \} $为管道结点位移列向量,$ [\boldsymbol{R}] $为地基反力刚度矩阵,$ [\boldsymbol{H}] $为滑坡推力列向量$ \{\boldsymbol{ Q}\} $的影响系数矩阵。由于篇幅,矩阵不再细列出。
3. 实例验证
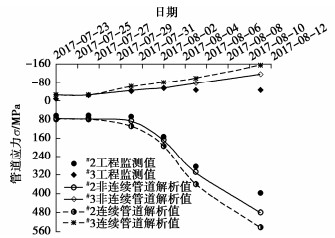
为了更好地反映本文解析方法的正确性和在工程中的应用价值,基于文献[25]中关于降雨诱发横向滑坡对长输管道应力影响的监测数据与本文解析解进行对比。工程背景中的滑坡位于四川省广安市,有一条长输管道横穿其中。计算参数:土体基本参数见表 1中实例;滑坡倾角为55°;管道上方滑坡滑动面长度d为25 m;设定滑坡体在垂直于滑动面的x–h面滑坡表面弧线切线倾角$ \varphi $(°)满足$ \varphi = 0 $°。管道参数见表 2。该地区2017年7月23日至2017年7月29日、2017年8月1日、2017年8月7日、2017年8月9日无雨;2017年7月30日至2017年7月31日降雨强度约0.8 mm/h(中雨);2017年8月2日至2017年8月6日、2017年8月8日降雨强度约为0.9 mm/h(中雨);2017年8月10日、2017年8月11日降雨强度约为1.4 mm/h(大雨)。不同降雨时长的管道应力与工程监测结果对比如图 7所示。其中,非连续接口管道每12 m一个接口。本文不考虑管道温度和管道轴力引起的轴向应力,管道轴向应力$ {\sigma _{\text{l}}} $计算公式为
表 1 土的基本参数Table 1. Physical parameters of soil土体编号 $ {\gamma _{\text{c}}} $/(kN·m-3) $ {\gamma _{\text{s}}} $/(kN·m-3) $ \varphi $/(°) $ c $/kPa $ {\gamma _{\text{w}}} $/(kN·m-3) ${\vartheta _{\text{c}}}$ ${\vartheta _{\text{s}}}$ $ \varphi _{}^{\text{b}} $/(°) G F $ {S_{\text{f}}} $/m $ {K_{\text{s}}} $/(cm·s-1) Es1/MPa $ {\nu _1} $ Es2/MPa $ {\nu _2} $ 实例 18 22.3 25 5.1 9.8 0.2 0.35 2 0.8712 -0.3 5 4.33×10-5 82 0.30 2000 0.28 参数分析 17.8 21.9 7.6 16 9.8 0.2 0.30 2 0.8712 -0.3 10 4.61×10-5 28 0.27 250 0.25 注:$ \varphi $,$ c $分别为滑坡体内原始层内摩擦角和黏聚力;G,F为过渡层在湿润层中占比,即式(3)中系数,取值参照彭振阳等[4]对于积水深度为0条件下的取值;$ {S_{\text{f}}} $为下层土体作用于饱和层基质吸力势,取边坡基岩以上土体厚度;Es1和$ {\nu _1} $为滑体内土体弹性模量和泊松比,滑体内范围为式(24)中[x1, x2]滑体范围内;Es2和$ {\nu _2} $为滑体外土体弹性模量和泊松比,滑体外范围为式(24)中[xa, x1]和[x2, xb]。 表 2 管道的基本参数Table 2. Physical and geometrical parameters of pipeline管道编号 材料类型 接口转动刚度/(kN·m·rad-1) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 外径/mm 厚度/mm 输送压力/MPa 接口数量m 总长/m 滑坡体内长度/m 滑坡体两侧长度/m 实例 X60钢管 2.47×104 210 0.3 475 7.9 2 9 300 100 100 参数分析 L245钢管 4×104 210 0.3 1000 20 4 10 66 22 22 $$ {\sigma }_{\text{l}}={\sigma }_{\text{l}内}\text{+}{\sigma }_{\text{l}外}\text{=}\mu \frac{p{D}_{1}}{2\delta }+\frac{\left|M\right|}{W} 。 $$ (47) 式中$ {\sigma }_{\text{l}内} $为管道内压引起的轴向应力(kPa);$ {\sigma }_{\text{l}外} $为管道外力(如滑坡)引起的轴向应力(kPa);$ \mu $为泊松比,取0.3;$ p $为管道的输送压力(kPa);$ {D_1} $为管道的内径(mm);$ \delta $为管道的壁厚(mm);$ \left| M \right| $为管道弯矩绝对值(kN·m);W为管道截面抗弯模量(m3)。
由于图 7中#1测点离滑坡较远,受滑坡影响很小,故不作分析。图 7中,#2,#3测点分别为距离管道中心线-50,45 m位置处。由图 7可知,2017年7月23日至2017年8月5日,长输管道解析值与工程监测值吻合度非常高;2017年8月11日的管道解析值明显大于工程监测值。非连续接口管道的管道应力值小于连续管道的应力值,更接近于实测结果。由此可证明本文提出的计算接口输气管道内力解析方法的工程适用性和准确性。
4. 参数分析
如上述算例研究所示,本研究中提出的解析解可合理估计非连续接口输气管道对降雨条件下滑坡的响应。在本节中,将进一步研究降雨强度的影响以及对管道进行安全评估。滑坡土体参数如表 1中参数分析所示。滑坡倾角设为50°;滑坡滑动面长度d设为30 m。设定滑坡体在垂直于滑动面的x-h面滑坡表面弧线切线倾角$ \varphi $(°)满足$ \varphi (x)=1.6x $(11 m≤x≤11 m)。设管道位于滑坡最底部。管道参数如表 2中参数分析所示。本文以输气管道为研究对象,在工程使用中强度应满足《输气管道工程设计规范:GB50251—2015》[26]中管道当量应力的失效准则。此外,由《管线钢管规范:API SPEC 5L—2018:L245》钢管极限屈服强度$ {\sigma _{\text{s}}}{\text{ = 245}} $ MPa[27]。
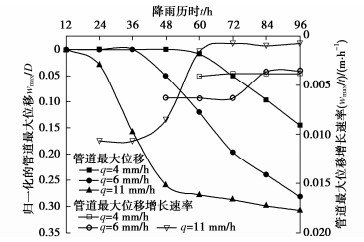
为探究降雨强度对滑坡诱发非连续管道变形的影响,本节选取降雨强度q分别为4 mm/h(暴雨),6 mm/h(大暴雨),11 mm/h(特大暴雨)3种工况来进行对比分析接口管道的随着降雨历时增长的变化情况。
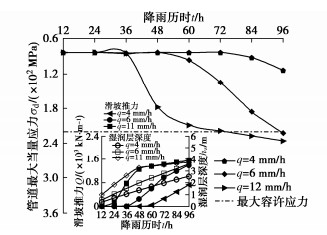
图 8为不同降雨强度下归一化的接口输气管道最大位移对比图。如图 8所示,随着降雨强度的增大,管道最大变形量增大,但最大位移增长速率呈现先保持不变后急剧减小的趋势,管道最大位移增长速率开始变化点出现的时间越早。图 9为不同降雨强度下接口输气管道的安全评估状况。如图所示,当降雨时长为96 h时,降雨强度q分别为4,6,11 mm/h时的接口输气管道的最大当量应力分别为管道最大容许应力的51%,101%,107%。随着降雨强度的增大,管道的最大当量应力不断增大,部分已超出管道最大容许应力。
5. 结论
本文提出了一种降雨诱发滑坡对非连续接口输气管道受力变形影响的简化解析方法,得到了非连续接口输气管道的位移及安全性随降雨发展而变化的动态解。主要得出以下3点结论。
(1) 在相同的降雨强度下,随着降雨时长的增大,边坡土体的湿润锋深度增大,滑动区土体的厚度也随着增大,滑坡推力也随之增大,由此计算出的接口管道位移随着增大。随着降雨历时的增大,在开始时刻,入渗率由降雨强度控制,管道最大位移的增大速率保持不变;随后,降雨已不能完全入渗,降雨入渗率由边坡土体入渗能力控制,管道的变形增长速度开始减小,最后边坡土体完全趋于饱和,湿润层深度增长速率趋于稳定,管道的变形增长速度趋于一个定值。
(2) 管道轴向应力变化结果表明,连续和非连续接口管道随降雨历时变化的轴向应力发展情况具有一定的差别。同一降雨历时和管道位置处,非连续接口管道的轴向应力值小于连续管道轴向应力值,从而更接近于工程实测值,以证明本文受滑坡影响下接口管道受力变形计算方法的准确性。
(3) 分析了降雨强度对接口输气管道的变形特性的影响以及对输气管道进行安全评估。结果表明,随着降雨强度的增大,边坡土体进入完全饱和状态的起始时间点不断提前,接口管道最大位移增长速率开始迅速下降的时间点不断提前。随着降雨强度的增大,相同降雨历时下,边坡土体湿润层深度不断增大,产生的滑坡推力不断增大,进而导致接口管道最大位移和当量应力不断增大,管道安全性降低。
-
表 1 土的基本参数
Table 1 Physical parameters of soil
土体编号 γc/(kN·m-3) γs/(kN·m-3) φ/(°) c/kPa γw/(kN·m-3) ϑc ϑs φb/(°) G F Sf/m Ks/(cm·s-1) Es1/MPa ν1 Es2/MPa ν2 实例 18 22.3 25 5.1 9.8 0.2 0.35 2 0.8712 -0.3 5 4.33×10-5 82 0.30 2000 0.28 参数分析 17.8 21.9 7.6 16 9.8 0.2 0.30 2 0.8712 -0.3 10 4.61×10-5 28 0.27 250 0.25 注:φ,c分别为滑坡体内原始层内摩擦角和黏聚力;G,F为过渡层在湿润层中占比,即式(3)中系数,取值参照彭振阳等[4]对于积水深度为0条件下的取值;Sf为下层土体作用于饱和层基质吸力势,取边坡基岩以上土体厚度;Es1和ν1为滑体内土体弹性模量和泊松比,滑体内范围为式(24)中[x1, x2]滑体范围内;Es2和ν2为滑体外土体弹性模量和泊松比,滑体外范围为式(24)中[xa, x1]和[x2, xb]。 表 2 管道的基本参数
Table 2 Physical and geometrical parameters of pipeline
管道编号 材料类型 接口转动刚度/(kN·m·rad-1) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 外径/mm 厚度/mm 输送压力/MPa 接口数量m 总长/m 滑坡体内长度/m 滑坡体两侧长度/m 实例 X60钢管 2.47×104 210 0.3 475 7.9 2 9 300 100 100 参数分析 L245钢管 4×104 210 0.3 1000 20 4 10 66 22 22 -
[1] 郜泽郑. 镇江地区降雨诱发滑坡机制与降雨阈值研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2019. GAO Ze-zheng. Study on the Mechanism and Rainfall Threshold of Rainfall-Induced- Landslide in Zhenjiang Area[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[2] GREEN W H, AMPT G A. Studies on soil physics: 1. Flow of air and water through soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science, 1911, 4(1): 1–24. doi: 10.1017/S0021859600001441
[3] BODMAN G B, COLMAN E A. Moisture and energy conditions during downward entry of water into soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1944, 8(1): 116–122.
[4] 彭振阳, 黄介生, 伍靖伟, 等. 基于分层假设的Green-Ampt模型改进[J]. 水科学进展, 2012, 23(1): 59–66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201201008.htm PENG Zhen-yang, HUANG Jie-sheng, WU Jing-wei, et al. Modification of Green-Ampt model based on the stratification hypothesis[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2012, 23(1): 59–66. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201201008.htm
[5] YAO W M, LI C D, ZHAN H B, et al. Time-dependent slope stability during intense rainfall with stratified soil water content[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2019, 78(7): 4805–4819.
[6] MEIN R G, LARSON C L. Modeling infiltration during a steady rain[J]. Water Resources Research, 1973, 9(2): 384–394.
[7] 张杰, 韩同春, 豆红强, 等. 基于分层假定入渗模型的边坡安全性分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(9): 3211–3218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201409037.htm ZHANG Jie, HAN Tong-chun, DOU Hong-qiang, et al. Analysis slope safety based on infiltration model based on stratified assumption[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(9): 3211–3218. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201409037.htm
[8] 苏永华, 李诚诚. 强降雨下基于Green-Ampt模型的边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(2): 389–398. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202002005.htm SU Yong-hua, LI Cheng-cheng. Stability analysis of slope based on Green-Ampt model under heavy rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(2): 389–398. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202002005.htm
[9] SARVANIS G C, KARAMANOS S A. Analytical model for the strain analysis of continuous buried pipelines in geohazard areas[J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 152(8): 57–69.
[10] 张家铭, 尚玉杰, 王荣有, 等. 基于Pasternak双参数模型的滑坡段埋地管道受力分析方法[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 51(5): 1328–1336. ZHANG Jia-ming, SHANG Yu-jie, WANG Rong-you, et al. Force analysis method of buried pipeline in landslide section based on Pasternak double-parameter model[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2020, 51(5): 1328–1336. (in Chinese)
[11] ZHANG L, ZHAO X, YAN X, et al. A semi-analytical method of stress-strain analysis of buried steel pipelines under submarine landslides[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2016, 59(5): 38–52.
[12] VASSEGHI A, HAGHSHENAS E, SOROUSHIAN A, et al. Failure analysis of a natural gas pipeline subjected to landslide[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 119(1): 105009.
[13] MA H Q, HE B X, LUO X M, et al. Investigation on strain characteristic of buried natural gas pipeline under longitudinal landslide debris flow[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 86: 103708.
[14] JAHROMI H F, JAFARZADEH F, ZAKARIA M S. Experimental study of burial depth effect on embedded pipe deformations in sandy slopes under dynamic landsliding[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2018, 114(6): 281–297.
[15] 李大勇, 龚晓南. 软土地基深基坑工程邻近柔性接口地下管线的性状分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2003, 36(2): 77–80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC200302014.htm LI Da-yong GONG Xiao-nan. Response of jointed ductile pipeline to deep excavation in soft soil[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2003, 36(2): 77–80. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC200302014.htm
[16] 史江伟, 范燕波, 裴伟伟, 等. 盾构下穿非连续管线变形特性及预测方法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(1): 143–150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202101016.htm SHI Jiang-wei, FAN Yan-bo, PEI Wei-wei, et al. An investigation of deformation mechanisms of jointed pipelines due to underneath tunnel excavation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(1): 143–150. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202101016.htm
[17] KLAR A, MARSHALL A M, SOGA K, et al. Tunneling effects on jointed pipelines[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2008, 45(1): 131–139.
[18] 林存刚, 黄茂松. 基于Pasternak地基的盾构隧道开挖非连续地下管线的挠曲[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(7): 1200–1207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201907004.htm LIN Cun-gang, HUANG Mao-song. Deflections of discontinuous buried pipelines induced by shield tunnelling based on Pasternak foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(7): 1200–1207. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201907004.htm
[19] FREDLUND D G, MORGENSTERN N R, WIDGER R A. The shear strength of unsaturated soils[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1978, 15(3): 313–321.
[20] 岩土工程勘察规范: GB50021—2001[S]. 2009. Code for Investigation of Geotechnical Engineering: GB50021—2001[S]. 2009. (in Chinese)
[21] PASTERNAK P L. Fundamentals of a New Method of Analyzing Structures on an Elastic Foundation by Means of Two Foundation Constants[M]. 2nd ed. Moscow: Gosudarstvennoe Izdatelstro Liberaturi po Stroitelstvui Arkhitekture, 1954: 55–103.
[22] VLASOV V Z, LEONTIEV U N. Beams, Plates and Shells on Elastic Foundation[M]. Moskva: Gosudarstvennoe Izdaterstvo Fiziko-Matematicheskoi Literatury, 1960: 112–170.
[23] YAO W J, YIN W X, CHEN J, et al. Numerical simulation of a super-long pile group under both vertical and lateral loads[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2010, 13(6): 1139–1151.
[24] 王磊, 李家宝. 结构分析的有限差分法[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1982: 4–11. WANG Lei, LI Jia-bao. Finite Difference Method in Structural Analysis[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 1982: 4–11. (in Chinese)
[25] 张航. 管道滑坡应力分析及监测技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2019. ZHANG Hang. Study on Stress Analysis and Monitoring Technology of Pipeline Landslide[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2019. (in Chinese)
[26] 输气管道工程设计规范: GB50251—2015[S]. 2015. Code for Design of Transmission Pipeline Engineering: GB50251—2015[S]. 2015. (in Chinese)
[27] 管线钢管规范: API SPEC 5L—2018[S]. 2018. Specification for Line Pipe: API SPEC 5L—2018[S]. Beijing: 2018. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 江珂,王东源,余志峰,黄栋. 管道受横向滑坡作用破坏分析——以中缅管道贵州晴隆段两次爆炸事故为例. 科学技术与工程. 2023(21): 8988-8995 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 任建东,赵毅鑫,王文,LIU Shimin. 采煤沉陷区油气管道泄漏风险量化分区研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2022(S2): 3353-3368 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: