Dynamic strength of temperature-controlled MICP-treated calcareous sand
-
摘要: 利用微生物温控加固技术对南海某岛钙质砂进行了MICP加固砂柱试验,并通过循环三轴试验开展了MICP加固钙质砂的动强度特性试验研究,探讨了不同MICP加固程度、相对密实度以及有效围压对钙质砂动强度与液化特性的影响。研究发现,经过MICP加固后松散钙质砂的动力液化特性由“流滑”逐渐演变为“循环活动性”;相较于未加固中密砂试样,MICP加固中密钙质砂试样表现出更加明显的“循环活动性”特点。MICP加固钙质砂的动强度随着MICP加固程度、相对密实度以及有效围压的提高表现出不同程度的提高。针对MICP加固钙质砂提出了优化动强度经验公式,建立了MICP加固钙质砂的统一动强度准则。该研究成果将为MICP加固技术在南海岛礁建设发展和应用中提供重要的理论基础。Abstract: A series of undrained cyclic triaxial tests are carried out for calcareous sand treated by temperature-controlled MICP (microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation) technology, and the dynamic strength characteristics of MICP-treated calcareous sand are thoroughly investigated. The in-depth discussion is conducted for the effects of biocementation level, relative density and effective confining pressure on dynamic strength and liquefaction characteristics. The dynamic and liquefaction characteristics of loose calcareous sand gradually change from flow slide to cyclic mobility after MICP treatment. Compared with the untreated medium dense calcareous sand, the MICP-treated medium dense calcareous sand shows more obvious characteristics of cyclic mobility. An increase in biocementation level, relative density and effective confining pressure leads to an increase in the dynamic strength of MICP-treated calcareous sand in different extents. Based on the optimized empirical formula of dynamic strength for MICP-treated calcareous sand, a uniform dynamic strength criterion is further established for MICP-treated calcareous sand. The unified dynamic strength criterion in this study will provide an important theoretical basis for the development and application of MICP treatment technology in the construction of islands and reefs in South China Sea.
-
0. 引言
土的动强度特性一直是土动力学研究中的重点问题。南海海域钙质砂广泛分布,该地区在历史上发生过多次地震,砂土液化以及结构的破坏,造成人民的财产损失甚至威胁人民的生命安全[1-3]。因此,学者们针对钙质砂的基本力学特性[4-5]、颗粒破碎特性[6-7]以及动力液化特性[8-9]等展开了系统研究。研究发现钙质砂是一种特殊的海洋岩土材料,它具有高压缩性、低强度且易发生颗粒破碎的特点,其静动力学特性与传统陆源砂(如石英砂等)存在明显差异,钙质砂场地的桩基侧阻力和端阻力较低,传统桩基础工程经验并不适用于钙质砂地基[10]。同时,南海地区常年高温、高湿,岛礁面积小、生态环境较脆弱,岛礁工程建设环境较恶劣、生态要求较高,水泥注浆等地基处理方法也不适于南海岛礁建设大面积应用[11]。微生物诱导碳酸钙沉淀(MICP)技术作为一种环境友好的新型岩土加固手段为南海岛礁加固建设带来了新的机遇[12-18]。方祥位等率先利用MICP技术对钙质砂开展MICP单元试验,研究发现MICP加固钙质砂试样的强度与刚度较未加固钙质砂试样有显著改善,其强度与变形特性也有别于水泥、石膏、高聚物等砂土加固试样[19-22]。Xiao等[23-24]开展了不同MICP加固程度、相对密实度、有效围压下MICP加固钙质砂的动强度、动孔压以及动变形特性研究,提出了砂土抗液化性能指标,揭示了MICP加固对钙质砂抗液化性改善的机理。总体来说,目前关于MICP加固钙质砂动力特性的研究仍处于起步阶段,为完善MICP加固钙质砂工程力学特性理论体系,有必要进一步开展MICP加固钙质砂的动强度特性试验与理论研究。
本文首先利用温控MICP技术开展了钙质砂的微生物加固试验,随后开展了MICP加固钙质砂的动强度特性研究。全文探讨了不同MICP加固程度、相对密实度以及有效围压对钙质砂动强度与液化特性的影响,针对MICP加固钙质砂提出了优化动强度经验公式,最后建立了MICP加固钙质砂的统一动强度准则。本文的研究成果将为MICP加固技术在南海岛礁建设发展和应用中提供重要的理论基础。
1. 温控MICP加固钙质砂试验
1.1 试验材料
本次试验所用钙质砂取自南海某岛,其相对质量密度Gs为2.79,最大孔隙比emax为1.79,最小孔隙比emin为1.13,不均匀系数Cu为2.26,曲率系数Cc为1.03,主要粒径参数D10=0.19 mm,D30=0.29 mm,D50=0.38 mm,D60=0.43 mm。试验用砂属于级配不良砂(SP)[25]。
1.2 温控MICP加固钙质砂
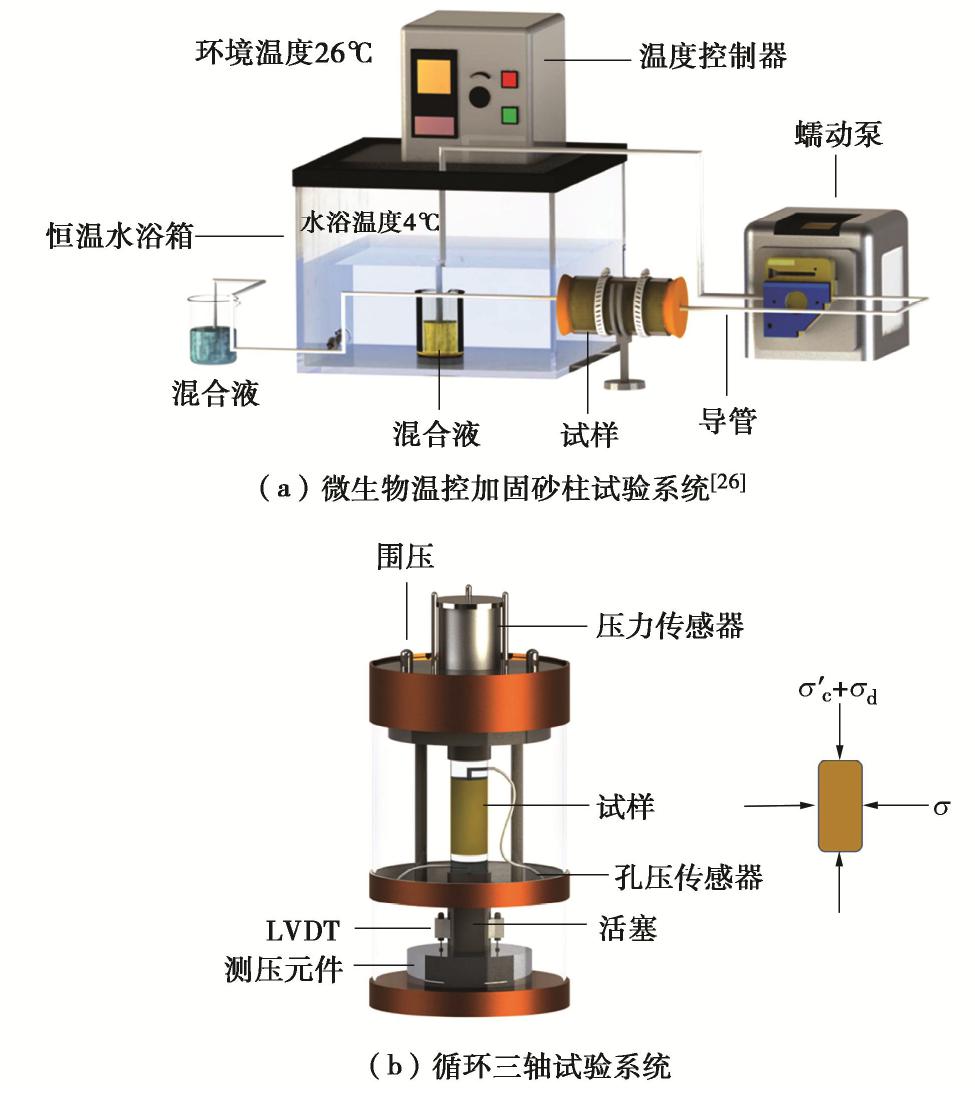
本次钙质砂砂柱的MICP加固采用团队提出的温控MICP加固技术进行[27]。温控MICP加固试验系统如图1(a)所示,试验的主要步骤包括低温菌液和反应液制备、低强度微生物加固钙质砂三轴试样装样以及MICP灌浆加固。本次温控MICP加固钙质砂试验中所用细菌为巴氏芽孢八叠球菌(S. pasteurii),菌液浓度为107 cell/ml,OD600值为0.8~1.2,环境温度为26℃,反应液为体积比为1∶1的CaCl2和尿素的溶液,浓度为0.5 mol/L,加固时所用混合液为体积比为1∶4的菌液与反应液的混合液,环境温度为26℃,养护时间12 h。
2. 循环三轴试验
2.1 循环三轴试验
本次试验采用DDS-70微机控制电磁式振动三轴试验系统,如图1(b)所示。本文开展了86组不同MICP加固程度、相对密实度、有效围压以及动应力比的钙质砂循环三轴试验。对于未加固的天然钙质砂试样,本文采用湿装法制备[28],对于MICP加固钙质砂试样,本文利用低强度微生物加固钙质砂三轴试样制样装置制备[24]。试样为直径39.1 mm,高80 mm,均采用等压排水固结,振动频率为1 Hz,荷载采用单向加载振动,选择孔压达到95%有效围压的孔压标准作为试样的破坏标准选择。表1给出了本次循环三轴试验的具体试验工况。
Table 1. Cyclic triaxial test conditions of MICP-treated calcareous sand试样编号 相对密实度/% 有效围压/kPa 反压/kPa B值 频率/Hz 固结比 循环应力比 UL1-12 10 50
100
200300 ≥0.95 1.0 1.0 0.125~0.167 UM1-12 47 0.146~0.292 UD1-13 80 0.208~0.375 T1L1-12 10 0.167~0.333 T1M1-12 47 0.167~0.375 T2L1-12 10 0.333~0.500 T2M1-13 47 0.292~0.500 2.2 试验结果
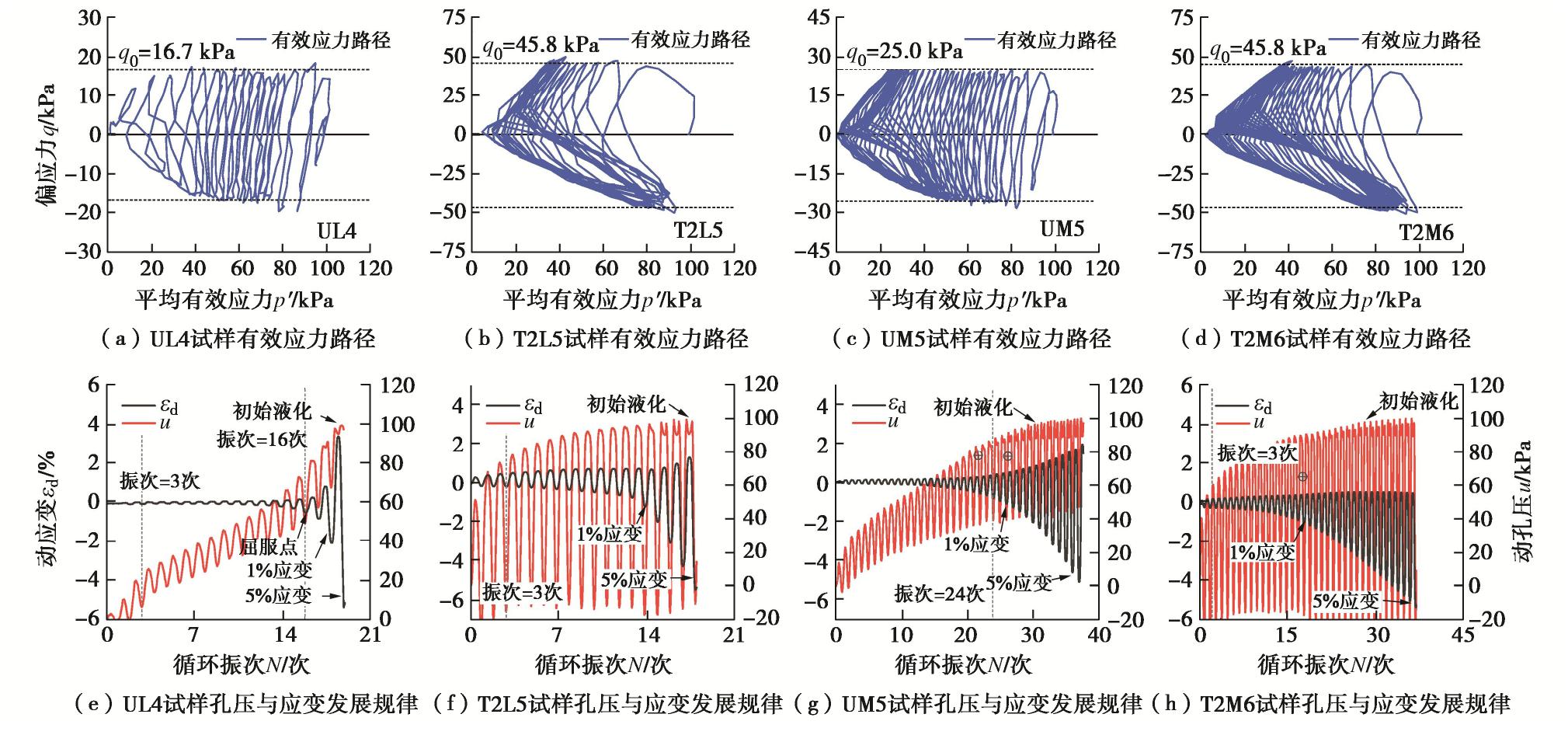
为讨论MICP加固对钙质砂动力特性的影响,图2给出了初始相对密实度为10%和47%的未加固钙质砂和MICP加固钙质砂的有效应力路径、孔压发展以及变形发展规律。为便于对比MICP胶结作用对动力特性的影响,这里选取循环振次相近的两组工况进行讨论。
对于天然未加固松散钙质砂试样,例如UL4试样(图2(a),(e)),在循环荷载作用下有效应力路径整体向左演化;在循环加载的前3周,应力路径迅速向左发展,同时孔压比迅速增长至20%左右;随着循环振动的发展,在3~16周内,有效应力路径以较小的速率逐渐向左移动,孔压和应变以较小的幅值缓慢增长;当循环振次为16周次时,试样达到屈服应变;当循环发展达到屈服点后,平均有效应力迅速减小并迅速接近0,试样在17~18周达到1%应变,在19周左右同时达到初始液化和5%应变,试样发生破坏。未加固松散钙质砂试样的动力液化特性符合“流滑”特点。对于MICP加固两次的松散钙质砂试样,例如T2L5试样(图2(b),(f)),其动力特性曲线的发展明显有别于未加固试样。当循环振动为3周次时,试样孔压比迅速达到0.7,并伴有明显的剪胀特性,此时平均有效应力迅速减小,有效应力路径迅速向左发展并接近原点;当循环振动为14周次左右,试样轴向应变达到1%,此后孔压在峰值处出现凹槽现象,应力路径出现蝴蝶状的循环发展模式;试样在18周次左右达到初始液化和5%应变。MICP加固松散钙质砂试样的动力液化特性更符合“循环活动性”的特点。
对于天然未加固中密钙质砂试样,例如UM5试样(图2(c),(g)),其有效应力路径发展较松砂更稳定,在循环加载前期应力路径逐渐向左发展;当循环振次为3周次时,孔压比达到0.3;当循环振动达到24周次时应变达到1%,1%应变对应的循环振次比为0.65;当循环振次发展到31周次时,平均有效应力减小到0,此时试样达到初始液化;当循环振次为36周次时应变达到5%,试样开始表现出明显的蝴蝶状循环发展模式。未加固中密钙质砂的液化特性比较符合“循环活动性”的液化特点。对于MICP加固两次的中密钙质砂试样,例如T2M6试样(图2(d),(h)),其动力特性曲线的发展明显有别于未加固试样。当循环振次为3周次时,T2M6试样的孔压比由UM试样的0.3增长到0.6;孔压在每个循环周次的循环波动增大,在卸载阶段甚至出现负值,这表明试样有较大的剪胀趋势。当循环振动为19周次时,试样应变达到1%;相较于UM5试样,T2M6试样1%应变对应的循环振次比由0.65提前到0.5。随着循环振动的发展,试样的有效应力路径的斜率在受拉部分的变化增大,试样在28周次时发生初始液化,37周次时达到5%应变拉伸破坏,试样破坏时对应的压应变减小。
总体来说,对于松散钙质砂试样,随着MICP加固程度的提高,试样的动应变发展在循环加载前期逐渐明显,而应变屈服点变得不再明显,试样的变形破坏模式从“崩塌型失稳破坏”演变为“渐进型变形破坏”;试样的有效应力路径逐渐表现出蝴蝶状的循环发展模式,试样的动力液化特性逐渐由“流滑”演变为“循环活动性”;松散钙质砂试样在不同MICP加固程度下达到初始液化与5%应变的循环周次基本一致。对于中密钙质砂试样,随着MICP加固程度的提高,试样达到1%应变对应的循环振次比逐渐减小,应变发展逐渐平缓,有效应力路径在受拉部分斜率的变化逐渐加快,剪胀性逐渐增大;试样均发生拉伸破坏,但破坏时对应的压缩变形随着MICP加固程度的提高而逐渐变小。对于未加固中密砂试样,MICP加固中密钙质砂试样表现出更明显的“循环活动性”特点。
3. MICP加固钙质砂动强度特性
3.1 动强度曲线特性
本文选取的破坏标准为孔压标准,土的动强度规律可用动应力
与破坏振次 间的关系表示。本节通过 关系讨论了MICP加固程度、相对密实度以及有效围压对钙质砂动强度曲线发展特性的影响;同时,这里利用动强度经验公式 对各工况下的 关系进行拟合,其中a,b均为经验参数。 (1)MICP加固程度的影响
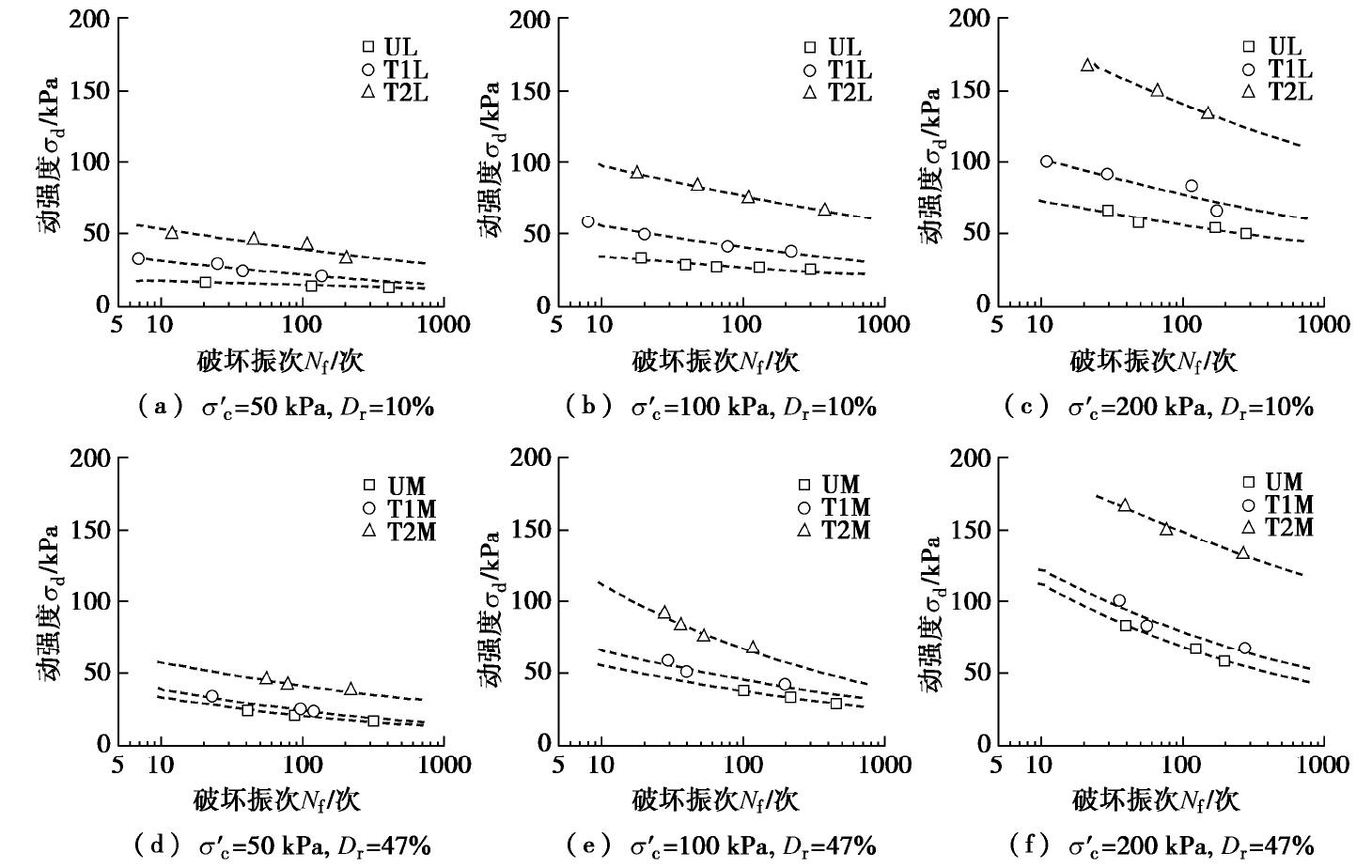
图3给出了不同MICP加固程度的松散钙质砂和中密钙质砂的动强度曲线发展规律。图中可以看出,相同有效围压下各工况试样的破坏振次均随着动强度的增加而减少;随着MICP加固程度的提高,试样在相同循环振次下发生破坏所需的动强度也明显增大。
![]() 图 3 不同MICP加固程度钙质砂的动强度曲线(部分数据来自文献[24])Figure 3. Dynamic strength curve of MICP-treated calcareous sand with different biocementations
图 3 不同MICP加固程度钙质砂的动强度曲线(部分数据来自文献[24])Figure 3. Dynamic strength curve of MICP-treated calcareous sand with different biocementations当有效围压为100 kPa、破坏振次为50次时,对于松散钙质砂试样,MICP加固一次试样的动强度较未加固试样提高了56.4%,MICP加固两次试样的动强度较未加固和MICP加固一次试样分别提高了187.1%和83.6%;对于中密钙质砂试样,MICP加固一次试样的动强度较未加固试样提高了15.6%,MICP加固两次试样的动强度较未加固和MICP加固一次试样分别提高了77.1%和53.2%。同样的,对于有效围压为50,200 kPa的MICP加固钙质砂试样,其动强度变化规律与100 kPa时基本一致[29-30]。该结论与前人研究的水泥改良土动强度特性规律一致。同时,试验结果还表明,在本试验条件下,温控MICP加固钙质砂试样第二次的MICP加固对动强度的提升比第一次MICP加固对动强度的提升更显著。
(2)相对密实度的影响
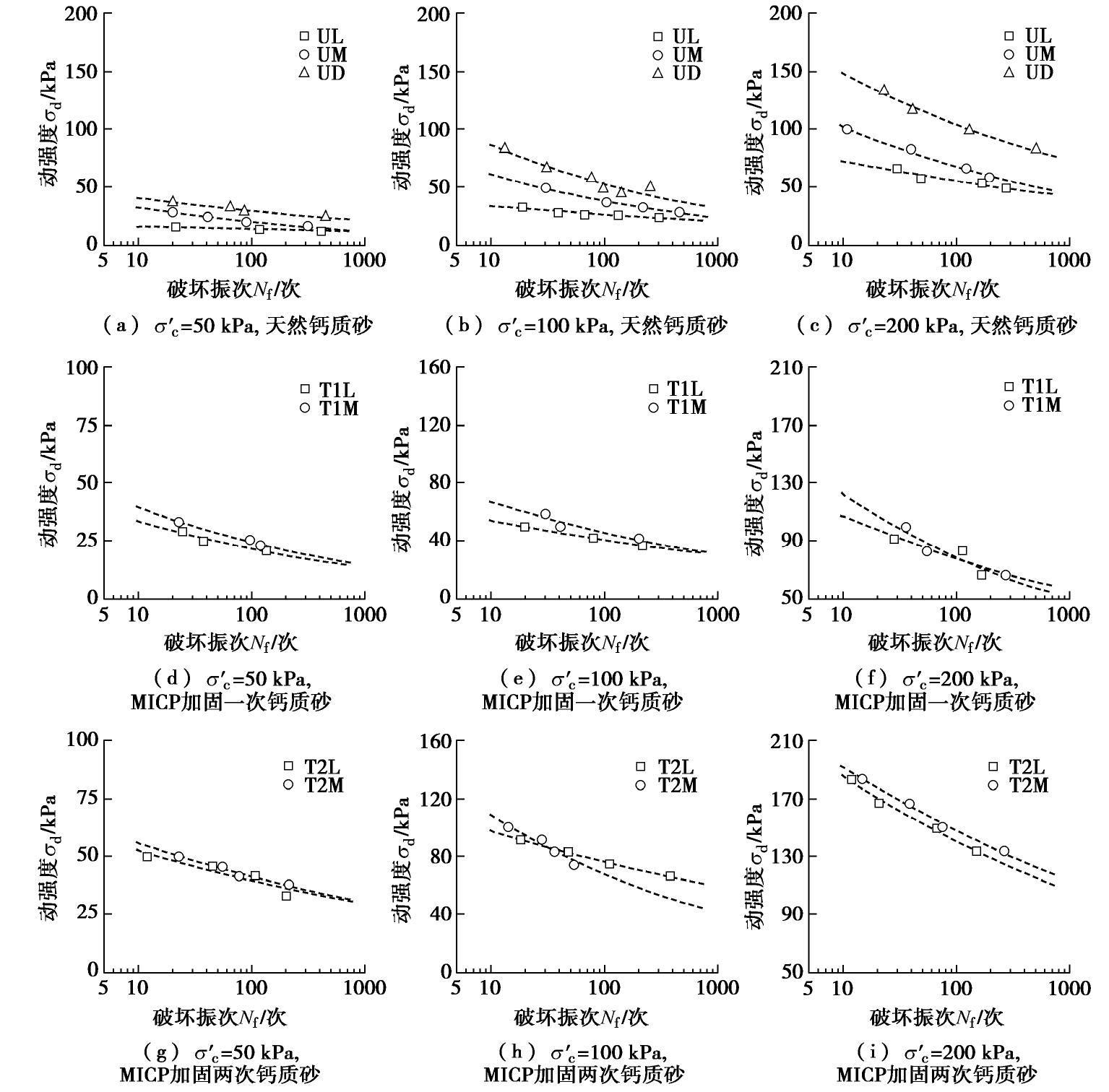
图4为不同相对密实度的天然钙质砂和MICP加固钙质砂的动强度曲线发展规律。图中可以看出,相对密实度对动强度曲线的变化规律有明显的影响。随着相对密实度的增大,各组试样的动强度表现出不同程度的增长趋势;同时,相同有效围压下MICP加固钙质砂的破坏振次随动强度的增大而减小。对于未加对密实度对动强度曲线的变化规律有明显的影响。随固天然钙质砂,当破坏振次为50次时,中密砂试样在有效围压为50,100,200 kPa下的动强度较松砂分别提高了52.2%,51.7%和26.2%。
![]() 图 4 不同相对密实度钙质砂的动强度曲线(部分数据来自文献[24])Figure 4. Dynamic strength curve of calcareous sand with different relative densities
图 4 不同相对密实度钙质砂的动强度曲线(部分数据来自文献[24])Figure 4. Dynamic strength curve of calcareous sand with different relative densities对于MICP加固处理后的钙质砂,相对密实度对试样动强度的影响有减弱的趋势。经过一次加固处理后,中密砂试样在破坏振次为50次、有效围压为50~200 kPa下对应的动强度较松砂提高了约5%~14%。经过两次MICP加固处理后,相对密实度对试样动强度的影响进一步减小,此时中密砂试样与松砂试样的动强度基本相同。当破坏振次为50次时,中密砂试样在有效围压为50 kPa和200 kPa时对应的动强度较松砂仅提高了约5%,而在有效围压为100 kPa时,中密砂试样的动强度甚至略小于松砂,这可能是由于循环三轴试验或者MICP加固试验中的离散性造成的动强度大小偏差。
总体来说,相对密实度对MICP加固钙质砂的动强度有一定影响。相对密实度越大,试样的动强度越大;随着MICP加固程度的提高,相对密实度对钙质砂的动强度影响逐渐减弱。试验结果表明了松散钙质砂的MICP加固效率高于中密砂的加固效率,同时MICP加固程度越高,该差异越明显。
(3)有效围压的影响
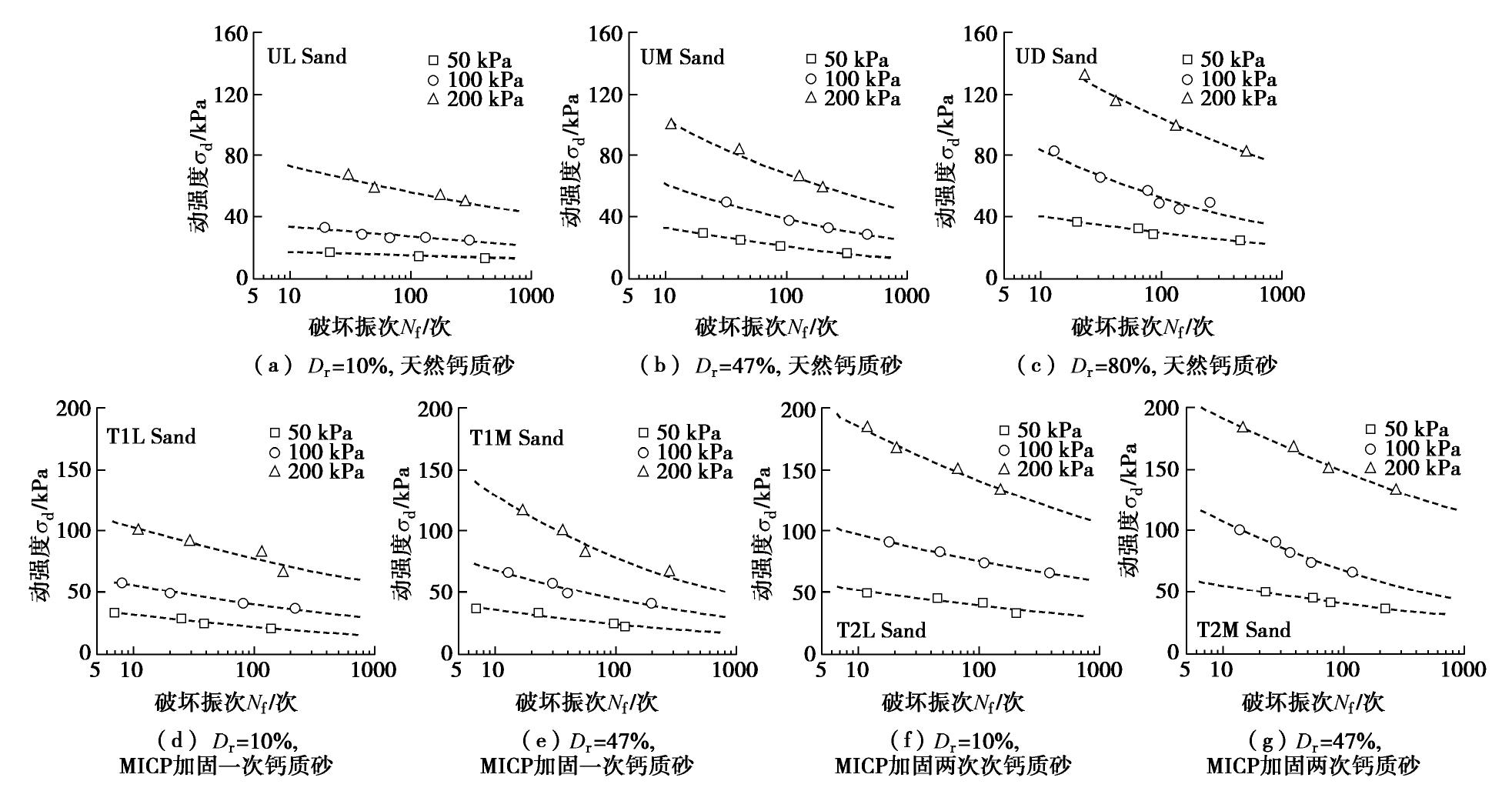
图5分别给出了不同有效围压的天然钙质砂和MICP加固钙质砂动强度曲线发展规律。图中可以看出,有效围压对不同工况下钙质砂动强度曲线均有显著影响。相同振次下,有效围压越大动强度越大,同时,试样的破坏振次随动强度的增大而减小。
![]() 图 5 不同有效围压钙质砂的动强度曲线(部分数据来自文献[24])Figure 5. Dynamic strength curve of calcareous sand with different effective confining pressures
图 5 不同有效围压钙质砂的动强度曲线(部分数据来自文献[24])Figure 5. Dynamic strength curve of calcareous sand with different effective confining pressures对于MICP加固一次的松散钙质砂,当破坏振次为50次时,200 kPa有效围压下试样的动强度较50 kPa和100 kPa有效围压下试样的动强度分别提高了244.8%和90.8%。对于MICP加固两次的中密钙质砂,当破坏振次为50次时,200 kPa有效围压下试样的动强度较50 kPa和100 kPa有效围压下试样的动强度分别提高了255.8%和105.5%。试验结果表明,有效围压对不同MICP加固程度和相对密实度下的钙质砂均有显著影响,且影响规律基本一致。
3.2 动强度经验公式优化
根据动强度经验公式进行曲线拟合,可分别求得不同MICP加固程度、相对密实度和有效围压下各组试样动强度曲线的经验参数a,b以及R2值。
由试验拟合结果可知,动强度参数指标a,b的大小同时受到MICP加固程度、相对密实度和有效围压等试验变量的影响。其中,b值的变化范围很小,大多数均集中在0.1~0.2,未在该范围内的数据的偏差值也很小;相对于b值,a值的变化范围相对较大,其值在20~250。因此,为简化动强度曲线经验公式,可将b值设为常数,利用最小二乘法的计算原则求解出各动强度曲线的经验参数a值,使其满足对所有工况下求得的动强度拟合值与实际值的差值的平方和最小。
优化后动强度经验参数修正a,b值如表2所示。由表2可知,经过优化计算后,动强度经验参数b可取0.147。此时各工况下经验公式的R2值均比较理想。进一步观察参数a的变化规律可知,优化后动强度参数指标a在30~300之间变化,同时a值的大小随着MICP加固程度、相对密实度和有效围压的增加表现出不同程度的增加,其中,MICP胶结程度和有效围压的变化对a值的影响十分显著,而相对密实度的变化对a值的影响相对较小。
表 2 优化后动强度经验参数拟合值Table 2. Optimized values of empirical parameters of dynamic strength编号 =50 kPa =100 kPa =200 kPa a b R2 a b R2 a b R2 UL 29.333 0.147 -0.096 52.950 0.147 0.635 110.938 0.147 0.921 UM 41.891 0.147 0.917 75.745 0.147 0.926 137.332 0.147 0.951 UD 59.339 0.147 0.935 107.768 0.147 0.828 206.933 0.147 0.991 T1L 44.216 0.147 0.974 79.855 0.147 0.988 150.462 0.147 0.912 T1M 49.531 0.147 0.968 92.529 0.147 0.957 162.335 0.147 0.918 T2L 77.013 0.147 0.921 149.301 0.147 0.949 270.798 0.147 0.986 T2M 81.125 0.147 0.987 141.559 0.147 0.906 286.934 0.147 0.894 3.3 统一动强度准则
根据动强度优化经验公式可知,MICP加固钙质砂的动强度大小同时受多个因素的影响,这使得动强度曲线的发展特性变得复杂。本节开展了MICP加固钙质砂统一动强度准则研究,通过建立一个可以综合考虑MICP胶结程度、相对密实度以及有效围压等变量的统一动强度准则,实现对MICP加固钙质砂动强度特性的量化计算,丰富MICP加固钙质砂动强度特性相关理论。
(1)建立统一动强度准则
前文关于MICP加固钙质砂动强度经验公式优化研究已经提到,动强度与破坏振次之间可以用幂函数
表示。由于参数b值变化范围较小,故可将b值简化为常数0.147;参数a可认为是与试验变量MICP加固程度、相对密实度以及有效围压相关的函数,故a可以用下式的函数形式表示: 。 (1) 式中
为有效围压,单位为kPa; 为相对密实度,无量纲; 为MICP加固次数,无量纲。 式(1)中各变量的具体函数表达形式可根据各影响因素对动强度曲线的影响特点来确定。通过对动强度经验公式拟合进行分析可知:首先,参数a值随相对密实度和加固程度的增长表现出不同程度的非线性增长,因此
与 之间存在乘积或者幂、指函数关系;其次,有效围压与参数a近似呈正比增长关系,因此可认为 与 和 之间可能存在乘积关系。综合以上关系,本文选择利用下列函数进行试算: , (2) 式中,a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6和a7为拟合系数。
利用式(2)对所有试验数据进行拟合,得到关于MICP加固钙质砂的动强度统一模型:
。 (3) 式中
为动应力值,单位为kPa; 为有效围压,单位为kPa; 为平衡量纲参考应力,单位为kPa; 为钙质砂相对密实度,无量纲; 为MICP加固次数,无量纲; 为破坏振次,无量纲。 MICP加固钙质砂统一动强度准则是基于试验数据回归分析得到,由于数据基数较小,故公式存在一定局限性,其适用条件为:①循环三轴试验为等压固结不排水剪切试验,波形为正弦波,频率为1 Hz;②试验有效围压为50~200 kPa,砂土相对密实度范围为10%~80%;③MICP加固程度为本文所用反应液的量进行0~2次加固;④试样的破坏标准为发生液化破坏。
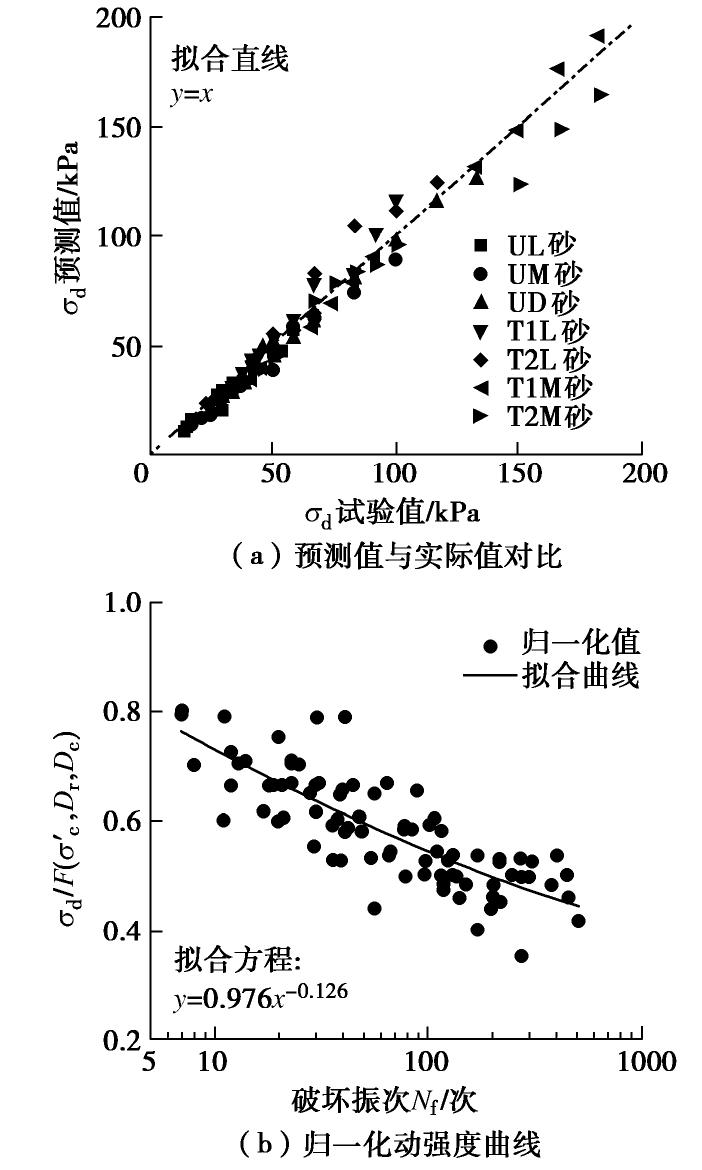
(2)统一动强度准则验证
为进一步验证MICP加固钙质砂统一动强度准则的合理性与适用性。本节利用式(3)分别计算各MICP加固钙质砂试样的预测值,然后将所得预测值与试验值进行对比分析。图6(a)给出了不同工况下MICP加固钙质砂动强度的试验结果与拟合结果的对比关系。由图可知,计算得到的预测值与试验值拟合整体效果良好,数据偏差基本在10%以内,仅个别数据偏差较大。因此,可认为提出的统一动强度准则适用于本文试验条件下的MICP加固钙质砂试样。同时,需要说明的是,造成个别数据偏差过大的原因可能在于:①MICP加固不均匀引起的试样动强度的偏差;②动三轴试样制样及循环荷载试验造成的试验数据偏差;③统一动强度准则是基于试验数据回归分析得到,由于原始数据体量较少且公式考虑影响因素不全,造成某个样本的预测值不够准确。基于这些原因,未来还需要开展更多试验和理论研究进一步完善MICP加固钙质砂的统一动强度准则。
(3)动强度曲线归一化分析
在得到MICP加固钙质砂的动强度统一模型公式后,将动强度曲线进行归一化处理。具体的,首先将式(3)进行变形得到
, (4) 令
。 (5) 随后,以
为纵坐标、 为横坐标作图,可得到一个以 , 和 为因子的关于MICP加固钙质砂的归一化动强度曲线,将本次试验所有数据按此方法进行归一化处理并作图可得到MICP加固钙质砂的动强度归一化曲线,如图6(b)所示。从图中可以看出,归一化后的动强度试验数据具有较好的规律性,这里可用拟合方程y=0.967x-0.123来表示归一化的MICP加固钙质砂动强度曲线。 通过对MICP加固钙质砂统一动强度准则进行验证和归一化动强度曲线的分析,论证了在本文试验条件下MICP加固钙质砂统一动强度准则的适用性和合理性。
4. 结论
本文通过温控MICP加固技术和室内循环三轴试验开展了微生物温控加固钙质砂动强度特性的试验和理论研究,得到的主要结论如下:
(1)分析了MICP加固程度和有效围压对MICP加固钙质砂动强度曲线的影响,研究发现MICP加固钙质砂的动强度随着MICP加固程度的增大而增大,第二次MICP加固对钙质砂动强度的提升较第一次更显著;有效围压越大,MICP加固钙质砂动强度越大;不同MICP加固程度和相对密实度下钙质砂动强度随围压的变化规律基本一致。
(2)分析了相对密实度对MICP加固钙质砂动强度曲线的影响,研究发现相对密实度对MICP加固钙质砂的动强度有一定影响。相对密实度越大,试样的动强度越大;随着MICP加固程度的提高,相对密实度对钙质砂的动强度影响逐渐减弱。试验结果表明松散钙质砂的MICP加固效率高于中密砂的MICP加固效率,同时MICP加固程度越高,该差异越明显。
(3)利用最小二乘法开展了MICP加固钙质砂动强度经验公式优化研究,得到了优化后经验参数b为0.147。建立了经验参数a与有效围压、相对密实度和MICP加固程度的函数关系,提出了MICP加固钙质砂的统一动强度准则,最后验证了该准则的合理性。
-
图 3 不同MICP加固程度钙质砂的动强度曲线(部分数据来自文献[24])
Figure 3. Dynamic strength curve of MICP-treated calcareous sand with different biocementations
图 4 不同相对密实度钙质砂的动强度曲线(部分数据来自文献[24])
Figure 4. Dynamic strength curve of calcareous sand with different relative densities
图 5 不同有效围压钙质砂的动强度曲线(部分数据来自文献[24])
Figure 5. Dynamic strength curve of calcareous sand with different effective confining pressures
表 1 MICP加固钙质砂循环三轴试验工况(部分数据来自文献[24, 26])
Table 1 Cyclic triaxial test conditions of MICP-treated calcareous sand
试样编号 相对密实度/% 有效围压/kPa 反压/kPa B值 频率/Hz 固结比 循环应力比 UL1-12 10 50
100
200300 ≥0.95 1.0 1.0 0.125~0.167 UM1-12 47 0.146~0.292 UD1-13 80 0.208~0.375 T1L1-12 10 0.167~0.333 T1M1-12 47 0.167~0.375 T2L1-12 10 0.333~0.500 T2M1-13 47 0.292~0.500 表 2 优化后动强度经验参数拟合值
Table 2 Optimized values of empirical parameters of dynamic strength
编号 σ′c =50 kPaσ′c =100 kPaσ′c =200 kPaa b R2 a b R2 a b R2 UL 29.333 0.147 -0.096 52.950 0.147 0.635 110.938 0.147 0.921 UM 41.891 0.147 0.917 75.745 0.147 0.926 137.332 0.147 0.951 UD 59.339 0.147 0.935 107.768 0.147 0.828 206.933 0.147 0.991 T1L 44.216 0.147 0.974 79.855 0.147 0.988 150.462 0.147 0.912 T1M 49.531 0.147 0.968 92.529 0.147 0.957 162.335 0.147 0.918 T2L 77.013 0.147 0.921 149.301 0.147 0.949 270.798 0.147 0.986 T2M 81.125 0.147 0.987 141.559 0.147 0.906 286.934 0.147 0.894 -
[1] SALEHZADEH H, PROCTER D C, MERRIFIELD C M. Medium dense non-cemented carbonate sand under reversed cyclic loading[J]. International Journal of Civil Engineering, 2006, 2006, 4(1): 54-63.
[2] SINGH S C, CARTON H, TAPPONNIER P, et al. Seismic evidence for broken oceanic crust in the 2004 Sumatra earthquake epicentral region[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(11): 777-781. doi: 10.1038/ngeo336
[3] WANG X Z, JIAO Y Y, WANG R, et al. Engineering characteristics of the calcareous sand in Nansha Islands, South China Sea[J]. Engineering Geology, 2011, 12(1/2/3/4), 40-47.
[4] HYODO M, HYDE A F L, ARAMAKI N. Liquefaction of crushable soils[J]. Géotechnique, 1998, 48(4): 527-543. doi: 10.1680/geot.1998.48.4.527
[5] SHARMA S S, ISMAIL M A. Monotonic and cyclicbehavior of two calcareous soils of different origins[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2006, 132(12): 1581-1591. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:12(1581)
[6] XIAO Y, LIU H, XIAO P, et al. Fractal crushing of carbonate sands under impact loading[J]. Géotechnique Letters, 2016, 6(3): 199-204. doi: 10.1680/jgele.16.00056
[7] XIAO Y, WANG L, JIANG X, et al. Acoustic emission and force drop in grain crushing of carbonate sands[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2019, 145(9): 04019057. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002141
[8] QADIMI A, COOP M R. The undrained cyclic behaviour of a carbonate sand[J]. Géotechnique, 2007, 57(9): 739-750. doi: 10.1680/geot.2007.57.9.739
[9] PORCINO D, CARIDI G, GHIONNA V N. Undrained monotonic and cyclic simple shear behaviour of carbonate sand[J]. Géotechnique, 2008, 58(8): 635-644. doi: 10.1680/geot.2007.00036
[10] 单华刚, 汪稔. 钙质砂中的桩基工程研究进展述评[J]. 岩土力学, 2000, 21(3): 299-304. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2000.03.027 SHAN Hua-gang, WANG Ren. Development of study on pile in calcareous sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2000, 21(3): 299-304. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2000.03.027
[11] STUEDLEIN A W, GIANELLA T N, CANIVAN G. Densification of granular soils using conventional and drained timber displacement piles[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2016, 142(12): 04016075. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001554
[12] XIAO Y, HE X, EVANS TM, et al. Unconfined compressive and splitting tensile strength of basalt fiber-reinforced biocemented sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2019, 145(9): 04019048. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002108
[13] MA G, HE X, JIANG X, et al. Strength and permeability of bentonite-assisted biocemented coarse sand[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, in press.
[14] XIAO Y, STUEDLEIN A, PAN Z, et al. Toe bearing capacity of precast concrete piles through biogrouting improvement[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2020, 146(12): 06020026. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002404
[15] XIAO Y, CHEN H, STUEDLEIN ARMIN W, et al. Restraint of particle breakage by biotreatment method[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2020, 146(11): 04020123. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002384
[16] XIAO Y, STUEDLEIN A W, RAN J, et al. Effect of particle shape on strength and stiffness of biocemented glass beads[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2019, 145(11): 06019016. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002165
[17] 刘汉龙, 马国梁, 赵常, 等. 微生物加固钙质砂的宏微观力学机理[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文), 2020, 42(4): 205-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN202004024.htm LIU Hang-long, MA Guo-liang, ZHAO Chang et al. Macro-and micro-mechanical regime of biotreated calcareous sand[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 205-206. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN202004024.htm
[18] 刘汉龙, 肖鹏, 肖杨, 等. 微生物岩土技术及其应用研究新进展[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文), 2019, 41(1): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN201901001.htm LIU Hang-long, XIAO Peng, XIAO Yang, et al. State-of-the-art review of biogeotechnology and its engineering applications[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2019, 41(1): 1-14. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN201901001.htm
[19] LIU H L, DENG A, CHU J. Effect of different mixing ratios of polystyrene pre-puff beads and cement on the mechanical behaviour of lightweight fill[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2006, 24(6): 331-338. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2006.05.002
[20] CONSOLI N C, FOPPA D, FESTUGATO L, et al. Key parameters for strength control of artificially cemented soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2007, 133(2): 197-205. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:2(197)
[21] 方祥位, 申春妮, 楚剑, 等. 微生物沉积碳酸钙固化珊瑚砂的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(10): 2773-2779. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.10.005 FANG Xiang-wei, SHEN Chun-ni, CHU Jian, et al. An experimental study of coral sand enhanced through microbially-induced precipitation of calcium carbonate[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(10): 2773-2779. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.10.005
[22] LIU L, LIU H, STUEDLEIN A W, et al. Strength, Stiffness, and microstructure characteristics of biocemented calcareous sand[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2019, 56(10): 1502-1513. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2018-0007
[23] XIAO P, LIU H, XIAO Y, et al. Liquefaction resistance of bio-cemented calcareous sand[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2018, 107: 9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.01.008
[24] XIAO P, LIU H, STUEDLEIN A W, et al. Effect of relative density and bio-cementation on the cyclic response of calcareous sand[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2019, 56(12): 1849-1862. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2018-0573
[25] 土工试验规程:SL237—1999[S]. 1999. Specification of Soil Test: SL237—1999[S]. 1999. (in Chinese)
[26] 刘汉龙, 张宇, 郭伟, 等. 微生物加固钙质砂动孔压模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(4): 790-801. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202104012.htm LIU Hang-long, ZHANG Yu, GUO Wei, et al. Predictions of dynamic pore water pressure for MICP-treated calcareous sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(4): 790-801. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202104012.htm
[27] WANG Y, LIU H, ZHANG Z, et al. Study on low-strength biocemented sands using a temperature-controlled MICP (Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation) method[C]//5th GeoChina International Conference, 2019, Hangzhou.
[28] SZE H Y, YANG J. Failure modes of sand in undrained cyclic loading: impact of sample preparation[J]. Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2014, 140(1): 152-169. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000971
[29] PORCINO D, MARCIANÒ V, GRANATA R. Undrained cyclic response of a silicate-grouted sand for liquefaction mitigation purposes[J]. Geomechanics and Geoengineering, 2011, 6(3): 155-170. doi: 10.1080/17486025.2011.560287
[30] PORCINO D, MARCIANÒ V, GRANATA R. Cyclic liquefaction behaviour of a moderately cemented grouted sand under repeated loading[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2015, 79: 36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.08.006
-
期刊类型引用(27)
1. 卫仁杰,彭劼,许鹏旭,李亮亮. 铝离子絮凝剂对微生物加固砂土效果的影响试验研究. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文). 2025(01): 71-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王双娇,李志清,田怡帆,李燕明,周应新,李丹丹. 微生物岩土工程技术的过去、现在与未来. 工程地质学报. 2024(01): 236-264 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 亓永帅,高玉峰,何稼,周云东,严柏杨. 可溶性大豆多糖对大豆脲酶诱导碳酸钙沉积固化风积沙效果的影响研究. 岩土工程学报. 2024(04): 823-832 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 张俊然,杨峥,姜彤. 黄原胶改良粉土的动强度特性及其微观分析. 应用基础与工程科学学报. 2024(03): 900-909 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李俊,何想,张瑾璇,赵常,肖杨,刘汉龙. 微生物加固研究可视化试验系统的开发与应用. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文). 2024(03): 73-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 郑刚,张军辉,章定文,吴江斌,周海祚. 地基处理技术现状与发展. 土木工程学报. 2024(07): 51-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. Yingxin Zhou,Zhiqing Li,Peng Zhang,Qi Wang,Weilin Pan,Shuangjiao Wang,Xiongyao Xie. Research status, hot spots, difficulties and future development direction of microbial geoengineering. Journal of Road Engineering. 2024(02): 234-255 .  必应学术
必应学术
8. 刘汉龙,赵常,肖杨. 微生物矿化反应原理、沉积与破坏机制及理论:研究进展与挑战. 岩土工程学报. 2024(07): 1347-1358 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 谢毅鑫,郑文杰,薛中飞,王琳. 微生物诱导碳酸盐沉淀修复铜污染黄土的试验研究. 岩土力学. 2024(S1): 443-450 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 单毅,平阳泽,袁杰,崔杰,童华炜,李亚东. 基于颗粒尺寸与级配的微生物固化钙质砂最大动剪切模量试验研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(10): 2455-2465 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 丁发兴,吴霞,张学民,陈雷,葛敬冉,肖杨,宫凤强,陈靖,李梓焜,刘增飞,崔昊,张训杰,吕飞. 材料强度理论研究进展述评. 铁道科学与工程学报. 2024(11): 4555-4587 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 陈浩. 纳米SiO_2-MICP协同固化淤泥效能评价与驱动机制. 长江科学院院报. 2024(12): 117-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 胡健,肖杨,肖鹏,王林,丁选明,仉文岗,刘汉龙. 基于机器学习预测微生物加固钙质砂统一动强度. 中国公路学报. 2023(02): 80-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 李能,吴杨,周福霖,谭平. 岛礁吹填珊瑚砂不排水单调和循环剪切特性试验. 中国公路学报. 2023(08): 152-161 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 张婧,杨四方,张宏,曹函,陆爱灵,唐卫平,廖梦飞. 碳中和背景下MICP技术深化与应用. 现代化工. 2023(11): 75-79+84 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 张建伟,赵聪聪,尹悦,石磊,边汉亮,韩智光. 紫外诱变产脲酶菌株加固粉土的试验研究. 岩土工程学报. 2023(12): 2500-2509 .  本站查看
本站查看
17. 卫仁杰,彭劼,陈泳,许鹏旭,李亮亮. MICP结合南海岛礁资源加固珊瑚砂的方法及效果研究. 防灾减灾工程学报. 2023(06): 1255-1265 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 史金权,肖杨,刘汉龙,Wim Haegeman. 钙质砂小应变初始剪切模量试验研究. 岩土工程学报. 2022(02): 324-333 .  本站查看
本站查看
19. 孟敏强,肖杨,孙增春,张志超,蒋翔,刘汉龙,何想,吴焕然,史金权. 粗粒料及粒间微生物胶结的破碎-强度-能量耗散研究进展. 中国科学:技术科学. 2022(07): 999-1021 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 李艺隆,国振,徐强,李雨杰. 海水环境下MICP胶结钙质砂干湿循环试验研究. 浙江大学学报(工学版). 2022(09): 1740-1749 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 王瑞,泮晓华,唐朝生,吕超,王殿龙,董志浩,施斌. MICP联合纤维加筋改性钙质砂的动力特性研究. 岩土力学. 2022(10): 2643-2654 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 王伟,李犇,罗佳乐,胡俊,姜屏,李娜. 动荷载作用历史对水泥固化钙质砂三轴力学特性影响. 自然灾害学报. 2022(05): 158-167 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 郝闪,刘松涛,李思瑶,华阳. 脲解型微生物诱导矿化沉积的研究进展. 中国建材科技. 2022(05): 73-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 刘汉龙,张宇,郭伟,肖鹏,黄明,楚剑,肖杨. 微生物加固钙质砂动孔压模型研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2021(04): 790-801 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 李广,葛超,杨泽平,梁海安,张敏思,胡光阳,曾浩,黄杰. 环境岩土工程研究进展. 江西建材. 2021(05): 3-5+7 .  百度学术
百度学术
26. 赵常,张瑾璇,张宇,何想,马国梁,刘汉龙,肖杨. 微生物加固土多尺度研究进展. 北京工业大学学报. 2021(07): 792-801 .  百度学术
百度学术
27. 曾召田,付慧丽,吕海波,梁珍,于海浩. 水泥胶结钙质砂热传导特性及微观机制. 岩土工程学报. 2021(12): 2330-2338 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(10)



 下载:
下载: