Chemico-osmotic membrane behaviors of amended soil-bentonite vertical barrier
-
摘要: 研究了锌污染地下水作用下,六偏磷酸钠(SHMP)改性膨润土/砂阻隔屏障回填料的化学渗透膜效应行为和扩散特性。通过单个试样多阶段的化学渗透试验,以去离子水和不同浓度的硝酸锌溶液作为试验溶液,对SHMP改性膨润土/砂回填料的化学渗透膜效率系数、有效扩散系数及阻滞因子进行了测定。结果表明,回填料的化学渗透膜效率系数随初始硝酸锌溶液浓度的增大而减小,随后下降趋势逐渐趋于稳定。改性膨润土/砂回填料对重金属锌的化学渗透膜效率系数约为未改性材料的2~3倍。随着初始硝酸锌溶液浓度的增加,SHMP改性膨润土/砂回填料的有效扩散系数增大,而阻滞因子则随之减小。Abstract: A systematic investigation is presented on chemico-osmotic membrane behaviors and diffusive properties of model sand/hexametaphosphate (SHMP)-amended bentonite cutoff-wall backfill (SHMP-SB) for the containment of zinc-impacted groundwater. A multi-stage chemico-osmotic test is conducted to determine the chemico-osmotic efficiency coefficients, effective diffusion coefficients and retardation factors of the backfill using the zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2) solution with varied concentrations. The results indicate that the measured chemico-osmotic efficiency coefficients of SHMP-SB gradually decrease and then tend to stabilize with the increasing Zn(NO3)2 concentration. A comparison with the previous studies shows that the measured chemico-osmotic efficiency coefficient of SHMP-SB is about 2-3 times that of the parent soil-bentonite backfill in the Zn(NO3)2 solutions. The effective diffusion coefficient increases with the increasing source concentration of Zn(NO3)2 solution, whereas the retardation factor of zinc decreases with the increasing Zn(NO3)2 concentration.
-
Keywords:
- SHMP /
- sand-bentonite /
- chemico-osmotic membrane behavior /
- diffusive property /
- zinc nitrate
-
0. 引言
自20世纪70年代以来,为了防止受污染地下水的迁移,由天然钠基膨润土和原位开挖土组成的土-膨润土(soil-bentonite,SB)竖向阻隔屏障在美国逐渐被广泛应用[1]。然而,中国高质量的钠基膨润土矿源极其匮乏,在SB阻隔屏障工程中应用更多的是钙基膨润土及钠化改性膨润土,但钙基膨润土膨胀性较弱,而钠化改性膨润土在富含金属阳离子地下水作用下,无法满足SB阻隔屏障的防渗要求[2]。基于上述现实需求,Yang等[3]采用六偏磷酸钠(SHMP)对钙基膨润土进行改良,改良后的回填料相对于未改良的材料拥有更低的渗透系数(低于1×10-9 m/s)。
在竖向阻隔屏障中及低水力梯度条件(低于1×10-9 m/s)下,达西流速较低,扩散是溶质的主要运移方式[4]。溶质在竖向阻隔屏障的运移通常是根据对流-扩散-机械弥散理论来分析的,但该理论并没有考虑耦合流(如化学渗透)的影响。近年来,SB回填料类似阻滞膜的化学渗透膜效应受到了越来越广泛的关注[5]。相关研究[6-8]表明SB回填料存在“半透膜效应”,但是上述研究主要基于SB回填料,关于SHMP改性SB回填料的化学渗透膜效应及扩散特性还未见报道,故有必要对其进行研究。
本文通过单个试样多阶段的化学渗透试验,定量地评价了SHMP改性SB回填料在重金属Zn作用下的化学渗透膜效应和扩散特性。研究成果对SHMP改性SB回填料阻隔Zn污染地下水的实际应用具有重要指导意义。
1. 试验材料和方法
1.1 回填料
试验所用SHMP改性SB回填料由砂土、商用膨润土及SHMP组成。其中,砂土取自南京江滩地区,经洗净风干后过1.0 mm筛;商用膨润土产自江苏镇江,为钠化改性钙基膨润土,阳离子交换量为78.1 mM/100 g(M为mol/L的简写),蒙脱石含量为66.9%,属于高液限黏土(CH);SHMP为国标工业级,购自上海星萌化工科技有限公司,相对密度约为1.85,水溶液呈酸性。
试验材料制备方法如下:首先采用直接拌合法将膨润土和SHMP混合制备SHMP改性膨润土,其中SHMP占总质量的2%。然后将制备好的SHMP改性膨润土分成两部分:一部分采用自来水制备固液比为8%的改性膨润土泥浆;另一部分与砂土干拌混合制备SHMP改性SB回填料,其中改性膨润土占总干质量的9.6%。通过向SHMP改性SB回填料中添加改性膨润土泥浆,以控制其坍落度为125 mm,同时加入适量砂土以保证回填料中各组分比例不变。制备完的SHMP改性SB回填料的含水率为32.1%。
1.2 试验溶液
本试验采用煮沸的去离子水(DIW)和硝酸锌(Zn(NO3)2)溶液作为试验溶液,其中Zn(NO3)2购自成都市科龙化工试剂厂,为分析纯(AR)级,以模拟Zn污染地下水中的典型污染物。共配置6种浓度的Zn(NO3)2溶液(0.5,1,5,10,20和50 mM),其电导率和pH值根据规范ASTM D1125[9]和ASTM E70[10]测定,详细信息如表1所示。
表 1 试验溶液Table 1. Summary of liquids used in study溶液 浓度c0/(mM) 电导率/(μS·cm-1) pH值 去离子水 0 30.7 6.91 硝酸锌溶液 0.5 83.3 6.54 1 147.6 6.46 5 490.0 6.18 10 919.0 5.97 20 2410.0 5.78 50 5470.0 5.59 1.3 试验仪器及方法
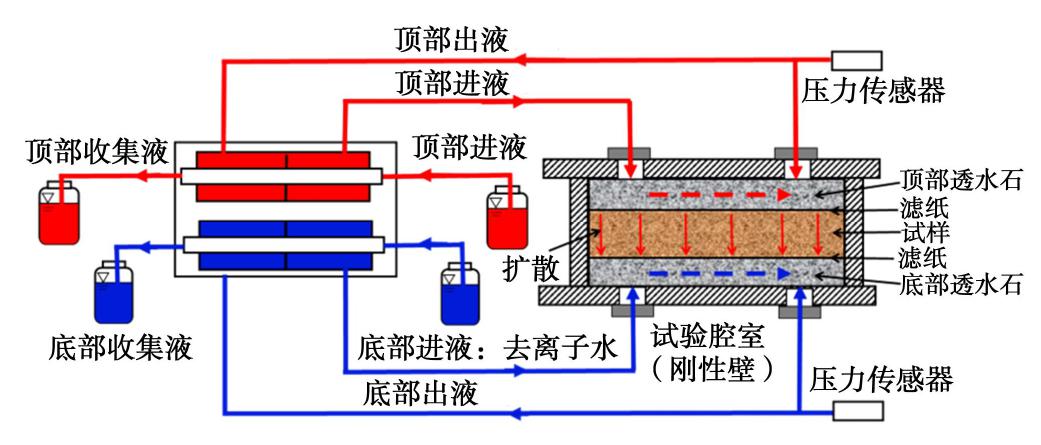
试验仪器由试液供给-收集系统、试验腔室、压差测试系统和数据采集系统四部分组成,其示意图如图1所示。其中,精密注射泵控制购自浙江嘉善瑞创电子科技有限公司,流量范围为0.016478~20.52105 mL/min;压力传感器(HM50-1-A-F1-W2)购自德国HELM公司,量程为0~100 kPa,精度为0.001 kPa;数据采集仪采用澳大利亚CAS公司生产的DataTaker DT80G Series 3型数据采集器。试验腔室由底座、试样环、顶盖以及两块透水石组成,试样环的横截面积为30 cm2,试样高度为1 cm。
化学渗透试验主要分为3个阶段:①试样冲刷阶段,在底座施加20 kPa的压力采用去离子水自下而上冲刷试样,当顶部渗出液的电导率低于初始电导率的50%后可进行下一阶段试验;②基准压差测试阶段,在试样顶部和底部分别采用去离子水进行循环抽注,抽注速度根据Malusis等[11]的研究采用0.0252 mL/min,当压差值稳定(该值即基准压差)后,可进行下一阶段试验;③化学渗透压差测试阶段,在试样顶部循环抽注Zn(NO3)2溶液,底部仍采用去离子水进行循环抽注,待压差值稳定后,顶部更换更高浓度的Zn(NO3)2溶液继续试验。试验过程中持续收集顶部及底部渗出液,并测量其电导率、pH值和浓度。
1.4 膜效率及扩散参数的计算
岩土工程材料的化学渗透膜效应通常采用化学渗透膜效率系数ω定量评价,其测试方法分为开方边界条件和封闭边界条件两类[11]。本文的试验装置采用封闭边界条件测量试样的化学渗透膜效率系数,并兼具测量扩散参数的功能。
根据试样两端的压差可以计算
ω 的数值[12]:ω=ΔPΔπ, (1) 式中,
ΔP 为试样两端实际化学渗透压差(kPa),Δπ为试样两端理论化学渗透压差(kPa),其数值可由van’t Hoff方程计算[13]:Δπ=vRT∑Ni=1ΔCi。 (2) 式中 v为电解质分离离子数,对于Zn(NO3)2,v取3;R为通用气体常数,可取 8.3145 J/(mol·K);T为绝对温度(K),室温为20 ℃则为293.15 K;ΔCi为试样两侧溶质浓度差(M);N为溶质离子种类。
封闭边界条件试验系统中,可采用稳定状态法测量溶质的有效扩散系数
D* :D*=LnC0t×dQtdt, (3) 式中,L为试样高度(m),n为试样孔隙率,
Qt 为单位面积累计溶质通量(mg/m2):Qt=1A∑Ntj−1Δmj=1A∑Ntj=1Cb,jΔVj, (4) 式中,
Δmj 为Δt时间间隔内收集的流出溶液中的溶质质量增量(g),ΔV为Δt时间间隔内收集的流出溶液中的体积增量(mL),Cb为试样低浓度一侧Δt时间间隔内收集的流出溶液中的溶质浓度(M)。阻滞因子Rd的表达式为
Rd=6D*LTL, (5) 式中,TL为
Qt -t曲线横坐标截距(d)。2. 试验结果及讨论
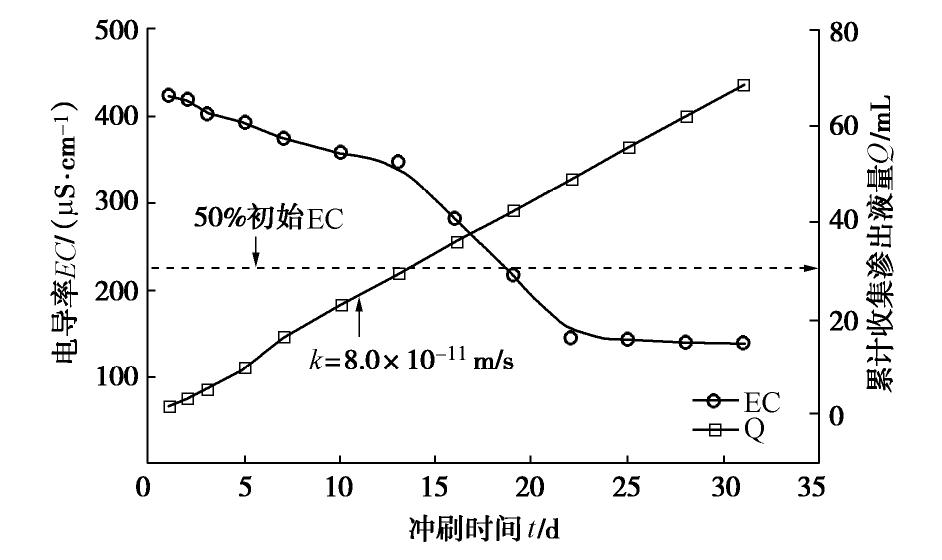
图2总结了在冲刷阶段顶部渗出液的电导率及累计渗出液量随时间变化结果。由图2可以看出,渗出液电导率随时间变化,由初始值425 μS/cm下降到稳定值140 μS/cm左右,稳定值低于初始值的50%,故满足后续试验开展的要求。累计渗出液量与时间呈线性正相关关系,根据达西定律可计算试样渗透系数为8.00×10-11 m/s,小于常用的SB防渗要求上限值1×10-9 m/s。
在压差测试阶段和化学渗透压差测试阶段中,顶部和底部收集液的pH值随时间变化关系如图3所示。在压差测试阶段(前14天),顶部和底部收集液的pH值相近,都在7.1~7.2。在化学渗透压差测试阶段,顶部收集液的pH值随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液的浓度增大而快速减小,而底部收集液pH值减小则相对较缓慢,且降幅相对较小。图4为顶部和底部收集液的电导率变化情况。在压差测试阶段,顶部和底部收集液的电导率在120~150 μS/cm,与冲刷阶段渗出液相近。在化学渗透压差测试阶段,顶部和底部收集液的电导率随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液的浓度增大而增大。但是,底部收集液的电导率较顶部收集液变化相对滞后,且增幅也相对较小。顶部和底部的pH值和电导率变化差异是由于顶部更换更高浓度的Zn(NO3)2溶液后,顶部溶液的理化性质会迅速改变,而底部溶液的电导率和pH值变化是由于缓慢的溶质扩散作用,所以会出现滞后。另外,各浓度梯度下,顶部和底部的电导率和pH值达到稳定所需的时间随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度增长而增大。图5表示顶部和底部收集液浓度随时间的变化关系。可以发现,在化学渗透压差测试阶段,收集液浓度随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度增长而增大。在各浓度梯度下,当收集液浓度稳定后,顶部收集液浓度小于初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度,而底部收集液浓度大于0 mM,这是由于在化学梯度作用下,一部分锌离子通过扩散作用进入试样内部,击穿试样后进入底部收集液[12]。
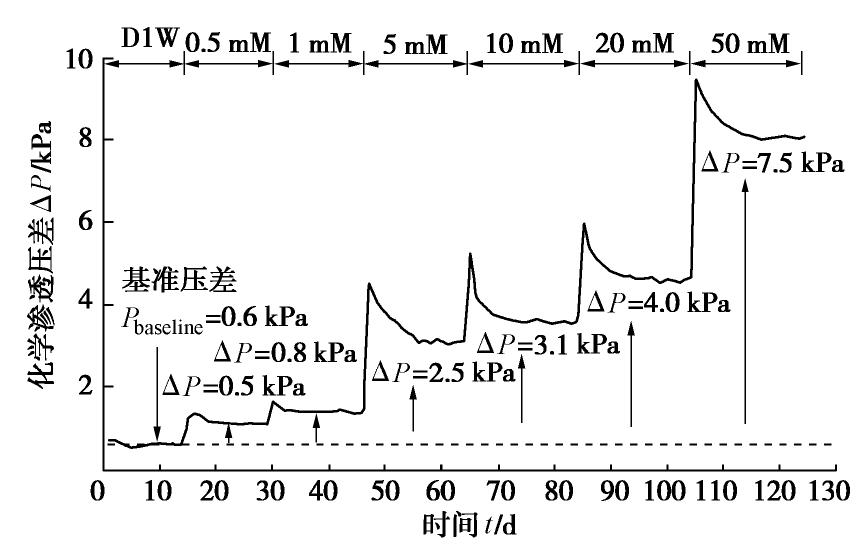
图6为试样两端压差随初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度的变化情况。在压差测试阶段,压差在短暂波动后逐渐稳定,其稳定值(0.6 kPa)即为基准压差。该阶段试样两端无化学势,产生压差的原因可能是试样两端透水石孔隙结构不同,透水石中依然还存在未去除的残留阳离子或试样顶部和底部的抽注速度存在微小差异[14]。在化学渗透压差测试阶段,试样两端压差在各浓度梯度下首先急速上升,达到峰值后快速下降,最后逐渐趋于稳定。这是由于化学渗透开始时,上一浓度梯度残留在试样顶部的溶液被更高浓度的Zn(NO3)2溶液取代,顶部压力迅速变化达到峰值;而底部浓度由于缓慢的离子扩散过程变化相对滞后,压力变化小,因此压差迅速上升。随着试验的进行,顶部溶液浓度有所降低的同时底部浓度升高,压差逐渐降低,直至扩散达到稳定后,压差亦逐步稳定。从图6中还可以发现压差稳定值随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度的增大而增大,这是由于浓度越高,试样两端的浓度差越大,化学梯度也越大,从而使试样的化学渗透现象更为显著,具体表现为试样两端的压差越大。
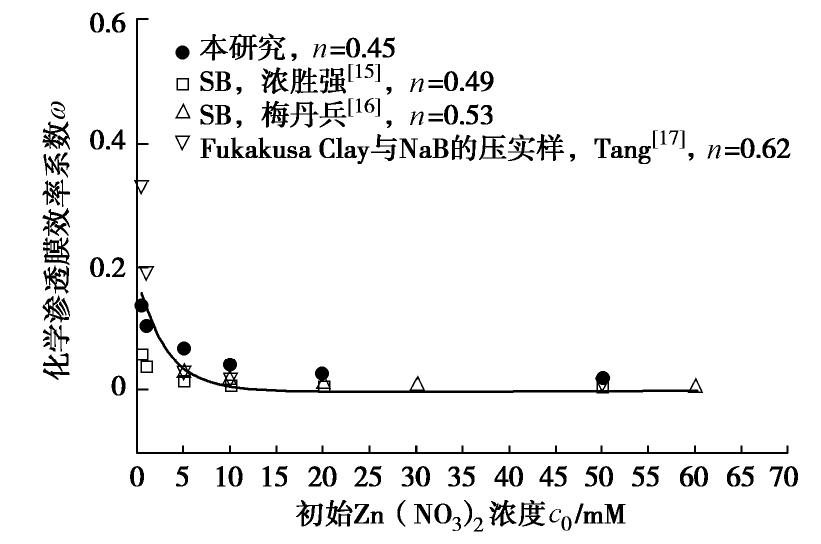
图7总结了本文及国内外部分学者对SB材料在重金属Zn作用下的化学渗透膜效率系数的研究结果。其中,沈胜强[15]采用的材料为膨润土含量10%的SB材料;梅丹兵[16]采用的材料为膨润土含量12.5%的SB材料;Tang[17]采用的是95% Fukakusa Clay与5%钠基膨润土(NaB)组成的压实样。由图7可见,随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度的增加,试样的化学渗透膜效率系数减小。在较低的初始Zn(NO3)2浓度范围内,化学渗透膜效率系数下降迅速,但超过某一临界浓度(10 mM)后,化学渗透膜效率系数下降趋势变缓并逐渐趋于稳定,这是由于膨润土的扩散双电层的厚度与入渗溶液浓度的平方根成反比,当浓度增大到一定值时,双电层压缩不再明显,因此化学渗透膜效率系数不再发生明显变化。由图7也可以发现本文所用SHMP改性回填料的化学渗透膜效率系数约为未改良回填料的2~3倍,对Zn的阻滞能力有所提高。
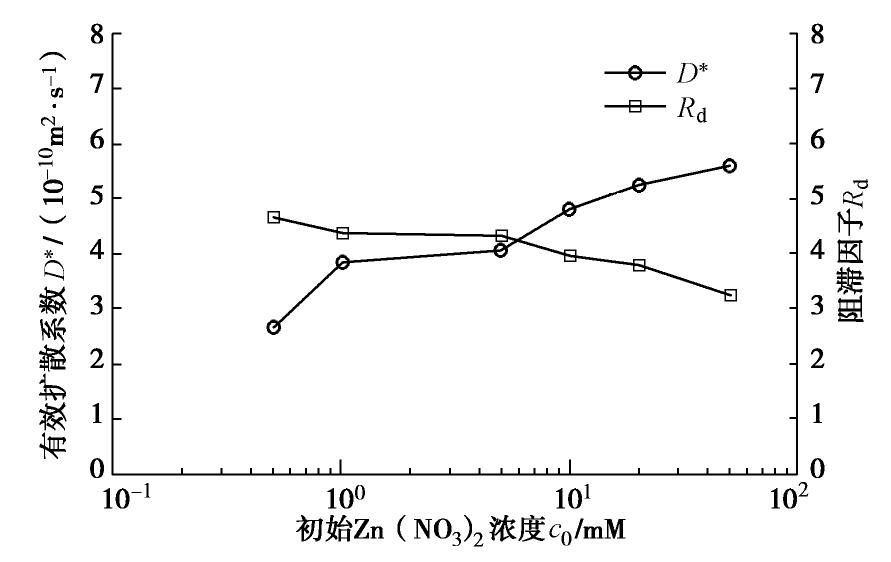
有效扩散系数D*和阻滞因子Rd随初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度变化情况如图8所示。随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度由0.5 mM增长至50 mM,有效扩散系数由2.66×10-10 m2/s增大至5.62×10-10 m2/s,而阻滞因子则随之减小,这意味着试样对Zn的阻滞能力存在极限。
3. 结论
本文通过单个试样多阶段的化学渗透试验,研究了在Zn(NO3)2溶液作用下,SHMP改性SB回填料的化学渗透膜效应及Zn的扩散特性,得到以下3点结论。
(1)随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度由0.5 mM增至50 mM,试样的化学渗透压差由0.5 kPa增至7.5 kPa。
(2)SHMP改性SB回填料存在“半透膜效应”。化学渗透膜效率系数随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度的增大而减小,但超过某一临界浓度(10 mM)后,化学渗透膜效率系数下降趋势变缓并逐渐趋于稳定。SHMP改性SB回填料对重金属Zn的化学渗透膜效率系数约为未改性回填料的2~3倍,对重金属Zn的阻滞能力有所提高。
(3)随着初始Zn(NO3)2溶液浓度的增加,SHMP改性SB回填料的有效扩散系数增大,而阻滞因子则随之减小。
-
表 1 试验溶液
Table 1 Summary of liquids used in study
溶液 浓度c0/(mM) 电导率/(μS·cm-1) pH值 去离子水 0 30.7 6.91 硝酸锌溶液 0.5 83.3 6.54 1 147.6 6.46 5 490.0 6.18 10 919.0 5.97 20 2410.0 5.78 50 5470.0 5.59 -
[1] SHARMA H D, REDDY K R. Geoenvironmental engineering: site remediation, waste containment and emerging waste management technologies[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2004.
[2] 杨玉玲, 杜延军, 范日东, 等. 膨润土系阻隔屏障材料渗透特性研究综述[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(增刊2): 210-216. YANG Yu-ling, DU Yan-jun, FAN Ri-dong, et al. Advances in permeability for bentonite-based hydraulic containment barriers[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(S2): 210-216. (in Chinese)
[3] YANG Y L, REDDY K R, DU Y J, et al. Short-term hydraulic conductivity and consolidation properties of soil-bentonite backfills exposed to ccr-impacted groundwater[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2018,144: 04018025. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001877
[4] SHACKELFORD C D. The ISSMGE Kerry Rowe Lecture: The role of diffusion in environmental geotechnics[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2014, 51(11): 1219-1242. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2013-0277
[5] SHACKELFORD C D, LEE J M. The destructive role of diffusion on clay membrane behavior[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2003, 51(2): 186-196. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2003.0510209
[6] HENNING J T, EVANS J C, SHACKELFORD C D. Membrane behavior of two backfills from field-constructed soil-bentonite cutoff walls[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2006, 132(10): 1243-1249. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:10(1243)
[7] 刘睿, 杜延军, 梅丹兵, 等. 土-膨润土系竖向阻隔工程屏障阻滞重金属污染物运移特性试验研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2018(5): 815-821. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK201805008.htm LIU Rui, DU Yan-jun, MEI Dan-bing, et al. Laboratory study of soil-bentonite vertical barrier on heavy metal migration retardation[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2018(5): 815-821. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK201805008.htm
[8] YEO S S, SHACKELFORD C D, EVANS J C. Membrane behavior of model soil-bentonite backfills[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2005, 131(4): 418-429. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:4(418)
[9] ASTM D1125-14. Standard Test Method for Electrical Conductivity and Resistivity of Water[S]. 2014.
[10] ASTM E70-07. Method for pH of Aqueous Solutions with the Glass Electrode[S]. 2015.
[11] MALUSIS M A, SHACKELFORD C D. Chemico-osmotic efficiency of a geosynthetic clay liner[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2002, 128(2): 97-106. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2002)128:2(97)
[12] GROENEVELT P H, ELRICK D E. Coupling phenomena in saturated homo-ionic montmorillonite: II theoretical[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1976, 40(6): 820-823. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1976.03615995004000060011x
[13] BARBOUR S L, FREDLUND D G. Mechanisms of osmotic flow and volume change in clay soils[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1989, 26(4): 551-562. doi: 10.1139/t89-068
[14] SHACKELFORD C D. Membrane behavior in engineered bentonite-based containment barriers: State of the art[J]. Coupled Phenomena in Environmental Geotechnics, 2013: 45-60.
[15] 沈胜强. 聚合物改良膨润土系阻隔屏障防渗控污性能研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019. SHEN Sheng-qiang. Containment Performances of Sand-Polymer Amended Bentonite Vertical Barriers Exposed to Heavy Metal Contaminants[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[16] 梅丹兵. 土-膨润土系竖向阻隔工程屏障阻滞污染物运移的模型试验研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2017. MEI Dan-bing. Model Test Study of Limiting Migration of Heavy Meal of Soil-Bentonite Vertical Cutoff Wall[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[17] TANG Q. Factors Affecting Waste Leachate Generation and Barrier Performance of Landfill Liners[D]. Kyoto: Kyoto University, 2013.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 刘宜昭,陆阳,刘松玉. 重金属作用下改性水泥系隔离墙化学相容性研究. 岩土力学. 2023(02): 497-506 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张志红,杨灏闻,郑九州. 高岭土-膨润土化学渗透膜效应试验及微观机理分析. 岩土工程学报. 2023(09): 1963-1970 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李东风,郑文杰,文少杰,胡文乐. 改性黄土材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附阻滞特性实验和内在机理探究. 环境工程. 2023(S2): 1268-1275+11 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 施建勇. 江苏省地基基础行业技术创新与应用. 江苏建筑. 2023(S1): 28-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 董洋,张文,李大伟,姚兰,初文磊,王海东,殷晓东. 柔性垂直防渗技术膨润土-黏土密封材料防渗性能研究. 环境工程技术学报. 2022(03): 824-833 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李双杰,伍浩良,傅贤雷,蒋宁俊,万佳磊,李江山,杜延军. 氧化镁碱激发矿粉-膨润土-土竖向屏障材料阻隔铅污染物的化学渗透膜效应. 岩土工程学报. 2022(06): 1078-1086 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: