Shear characteristics and stress-dilation relation of medium sand under normal to high pressures
-
摘要: 为研究高围压范围内砂土相对密实度和围压对土体强度和变形特性的影响,对3种不同相对密实度砂土试样在常至高围压下进行常规三轴固结排水剪切试验,获得偏应力–轴向应变–体应变关系曲线,同时进行颗粒破碎分析。结果表明:在常至中压范围(0.8 MPa≤
σ3 ≤2 MPa),应力–应变曲线均表现出不同程度的应变软化,其剪胀性随相对密实度增加和围压的降低而增强;当进入高围压范围时(σ3 >2 MPa),应力–应变曲线逐渐向应变硬化型转变,试样体积逐渐趋于剪缩。颗粒破碎程度随着围压和密实度的增大而增大,在高围压时由于中密和密砂剪切后期出现了明显的颗粒破碎,导致剪切过程中出现了二次相变。不同密实度土体的破坏内摩擦角和对数围压表现良好的线性关系,拟合确定了破坏内摩擦角随对数围压增加的衰减率,同时基于Bolton应力–剪胀关系拟合确定了试验砂土的临界状态内摩擦角,建立了剪胀指标与初始相对密实度及平均有效应力的关系式,为高压情况下砂土地基稳定性分析等提供强度参数。Abstract: The triaxial shear tests on the sands with various relative densities under normal to high pressures are carried out to investigate the effects of density and confining pressure on sand strength and deformation characteristics. Their mechanical properties are analyzed. Among the pressures ranging from normal to medium (0.8 MPa≤σ3 ≤2 MPa), the strain-stress curves show strain softening to different extents, and the shear dilatancy increases with the increase of relative density and the decrease of confining pressure. When entering high confining pressure range (σ3 > 2 MPa), the strain-stress curves gradually turn into strain hardening type and the sample volume gradually turns into shear contraction. Prominent particle breakages will occur in the later shearing period of medium and dense sands at high confining pressure, which may lead to the secondary phase transition in the shearing process. The failure friction angles decrease with the logarithmic confining pressure linearly, and the attenuation rates of failure friction angles for different density sands are determined by linear fitting. Based on the Bolton’s stress-dilation relation, the critical state friction angle of the sand is determined, and the relationship among dilatancy index, initial relative density and average effective stress is established to provide strength parameters for stability analysis of sandy soil foundation under normal to high pressures. -
0. 引言
砂土剪切特性受土体状态(相对密实度、围压和土体结构)和颗粒组成(颗粒形状、级配、表面特征和矿物组成)共同影响[1-3]。Been等[4]进行大量三轴试验研究Kogyuk砂的力学特性,并采用状态参数描述砂土当前状态,衡量砂土剪胀性。陆勇等[5]开展了常压至高压条件下的砂土力学试验,分析砂土粒径和围压对峰值强度、残余强度的影响及等向压缩线与临界状态线的特征与关系。朱俊高等[6]通过三轴试验发现密实度对砂土应力–应变及强度特性影响较大,并且对破坏时轴向应变有显著影响。Xiao等[7]通过对掺有不同比例的棱角形和圆形玻璃微珠砂土进行排水三轴压缩试验,系统地研究了颗粒形状对砂土强度、剪胀性和应力–剪胀关系的影响。
粒状土体峰值剪切强度由两部分组成:与颗粒间摩擦、颗粒重排列和颗粒破碎有关的临界状态分量及发生剪切所需的剪胀分量。Rowe[8]通过试验证明了粒状土体的剪胀由粒间接触应力分布控制,通过假设土体破坏时达到最小能量比推导了平面应变条件下的应力-剪胀关系。Bolton[9]通过大量的三轴试验和平面应变试验结果,给出了峰值内摩擦角
ϕp 和剪胀角ψp的关系。对于平面应变试验,ϕp =0.8ψp+ϕcv ;对于三轴试验ϕp =0.5ψp+ϕcv [10],ϕcv 为临界状态内摩擦角。一些学者[11-14]在Bolton的基础上,将ϕp 和ϕcv 表达成ϕp =aψp+ϕcv 的形式,a由相应的试验数据拟合确定。Chakraborty等[11]通过分析低围压下的平面应变试验和三轴试验数据得到参数a≈0.6;Esposito等[12]通过低围压下的三轴试验得到更新世砂的参数a=0.72;Vaid等[13]通过对Erksak砂进行50~2500 kPa下不同应力路径的三轴试验,得到参数a=0.33;Guo等[14]通过100~500 kPa下的三轴试验得到Ottawa砂的参数a= 0.63。目前,关于砂土剪切特性的研究多为常压条件,但随着高土石坝等大型项目的兴建和深部地下工程的开发,地基土体常处于高应力状态,此时砂土的强度和变形特性与常压不同,但对高应力状态下砂土的特性研究有限。因此,本文针对中粒石英砂进行常压至高压范围内三轴试验,分析相对密实度、围压和颗粒破碎对砂土剪切变形及强度的影响,并利用Bolton公式,基于试验结果建立了常压至高压下的应力–剪胀关系,可为实际工程分析中高应力下强度参数的确定提供参考。
1. 试验系统、材料及方案
1.1 试验系统
本试验使用英国GDS高压三轴试验装置。该试验系统由GDSLAB数据采集软件、通道数据采集板、压力/体积控制器、500 kN GDSVIS加载系统和三轴压力室组成。试样尺寸为 Ø50 mm
× 100 mm。围压、反压压力控制器量程均为0~16 MPa,轴压压力控制器量程为0~32 MPa。偏应力q、轴压σ1 、围压σ3 、孔压u和轴向应变ε1 均由传感器及数据转换装置自动采集和输出。1.2 砂样制备及试验方案
试验砂土为灌砂法专用标准砂(石英中砂),相对密度Gs=2.63,试验砂土粒径在0.1~1 mm之间,0.25~0.5 mm范围的粒径占总质量89.5%,中值粒径d50=0.35 mm,不均匀系数Cu=1.57,曲率系数Cc=0.96。根据土工试验方法标准[15],采用漏斗法和振锤法分别测定最小和最大干密度,
ρmin= 1.55 g/cm3,ρmax= 1.745 g/cm3 。利用干砂制备相对密实度Dr=30%,50%和70%的3种试样,其中Dr = (emax-e)/(emax-emin),对应的初始孔隙比e0分别为0.64,0.602,0.564。制样过程如下:①首先在三轴压力室底座上装套橡皮膜,用橡皮筋箍紧橡皮膜使其固定于底座,同时,为防止高压条件下压力室内的硅油通过橡皮膜端部进入试样,在橡皮筋外侧安装铁箍。②拼装成样桶,抽气保证成样桶与橡皮膜贴紧。③将事先烘干并称量过的砂样分五次缓慢的通过30 cm长的漏斗倒入成样桶内,且始终保持漏斗底端距离砂面2 cm;每次装样后使用击实锤进行击实至指定高度。④对试样抽50 kPa负压,持续15 min后待试样成型缓慢卸掉成样桶。对于围压
σ3 =8.0 MPa的高压情况,为避免砂样棱角刺穿橡皮膜,参考文献[16],制备砂样时装套了两层厚度分别为0.8和0.5 mm的橡皮膜。为使砂样接近完全饱和状态,对试样进行了2 h通气饱和、12 h水头饱和,并以50 kPa为一级逐级施加反压至500 kPa进行反压饱和,对于固结排水剪切试验(CD),反压值大小对排水剪切强度基本无影响[17-18]。所有试样经过上述饱和后,测得的孔隙水压力系数B值均能达到0.98及以上。为了研究围压和相对密实度对砂土的应力–应变关系、土体变形特性及强度特性的影响,分别对松砂(Dr= 30%)、中密砂(Dr=50%)和密砂(Dr=70%)进行200,400,800,1200,2000,3000,4000,6000,8000 kPa共9个围压条件下的CD试验,共计27组常规三轴剪切试验。通常认为常压压力在0~0.8 MPa之间,中压为0.8~2.0 MPa,超过2.0 MPa则为高压[5]。其中试验的剪切速率定为0.05 mm/min,换算成轴向应变为0.05%/min。2. 试验结果
2.1 固结后孔隙比
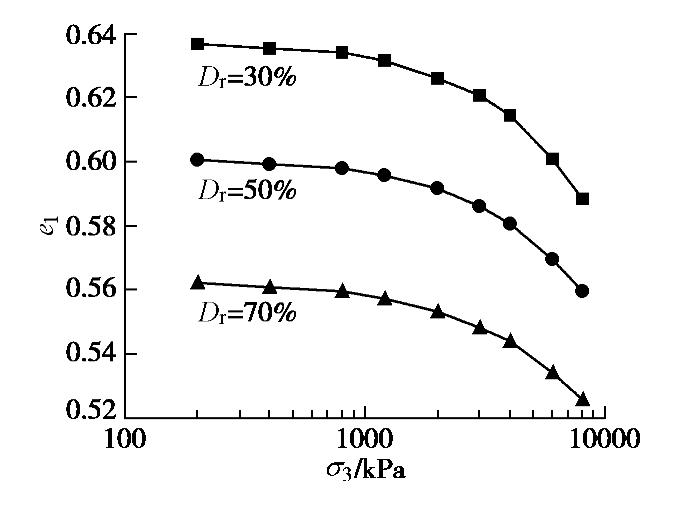
图1为3种相对密实度砂土在不同围压σ3下固结完成后的孔隙比e1,同时将e1列于表1。由图可见,随着围压
σ3 增加,孔隙比e1逐渐减小;当σ3 ≤0.8 MPa时,即处于常压范围时,松砂、中密和密砂的孔隙比e1的变化并不明显,当进入中压范围σ3 >0.8 MPa后,孔隙比e1减小开始变得明显,并且孔隙比e1的变化量随着砂土密实度的增加而减小。表 1 不同相对密实度砂土固结后孔隙比和峰值应力比Table 1. Void ratios after consolidation and peak stress ratios of sands with various relative densities围压/kPa 松砂 中密砂 密砂 e1 qf/p′f e1 qf/p′f e1 qf/p′f 200 0.637 1.44 0.601 1.63 0.562 1.67 400 0.636 1.33 0.600 1.50 0.561 1.55 800 0.634 1.31 0.598 1.43 0.560 1.46 1200 0.632 1.29 0.596 1.34 0.557 1.44 2000 0.626 1.16 0.592 1.31 0.553 1.40 3000 0.621 — 0.586 1.22 0.548 1.27 4000 0.615 — 0.581 1.19 0.544 1.22 6000 0.601 — 0.570 — 0.534 — 8000 0.589 — 0.560 — 0.526 — 2.2 应力–应变关系
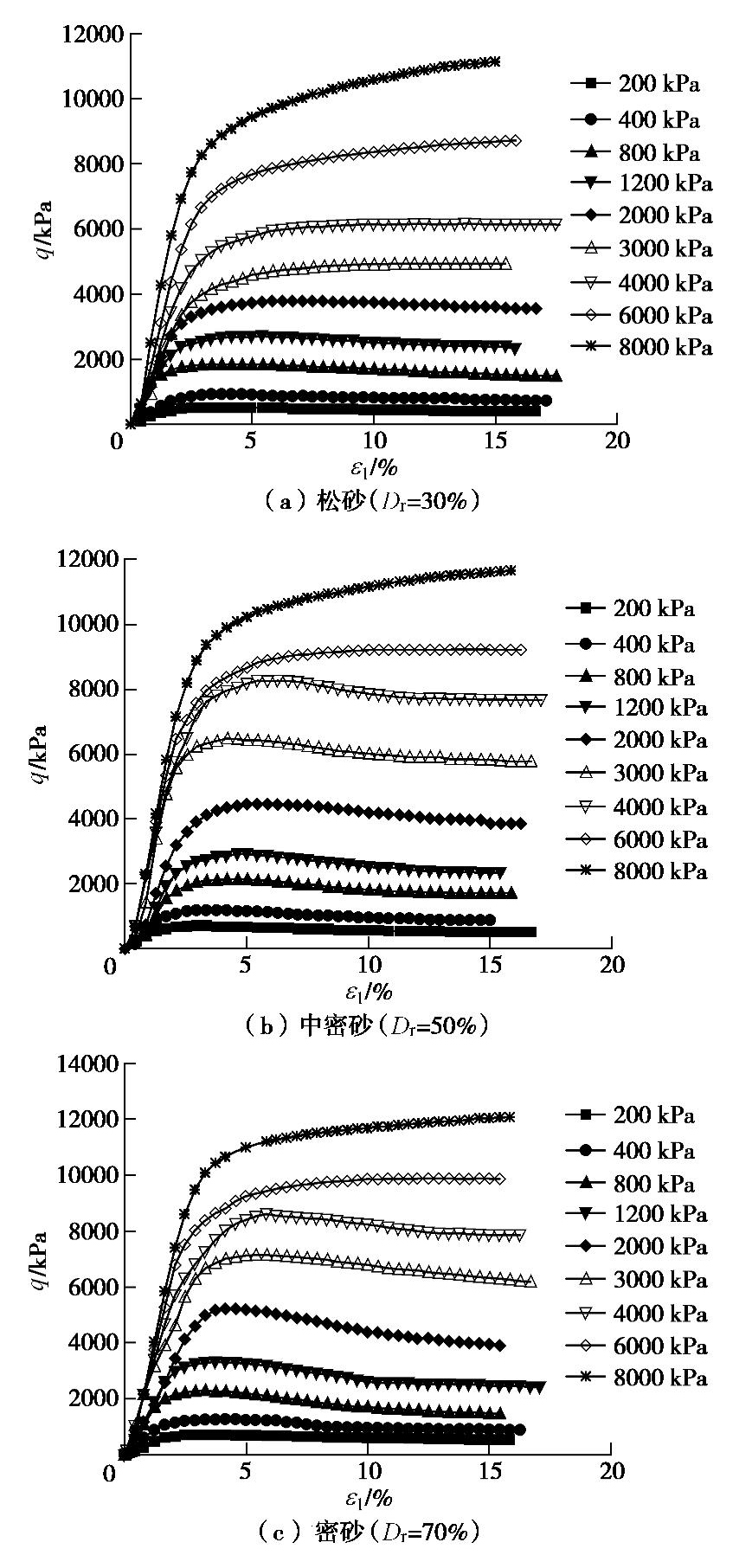
图2给出3种不同相对密实度砂土试样在施加不同围压时得到的偏应力q和轴向应变
ε1 的关系曲线。由图可见,随着围压σ3 增加,偏应力q逐渐增加;当σ3 ≤2 MPa时,即处于常、中压范围时,松砂、中密和密砂的q–ε1 曲线均表现出不同程度的应变软化,即q–ε1 关系曲线上出现了明显的峰值点,峰值过后偏应力q随轴向应变ε1 的继续增加而缓慢减小;当进入高压范围σ3 >2 MPa后,存在界限围压值,超过该界限围压值后,q–ε1 曲线由应变软化特征变为应变硬化特征,且该界限围压值受相对密实度的影响。对于本试验砂土,松砂的界限围压值处于2.0~3.0 MPa之间,中密砂和密砂的界限围压值处于4.0~6.0 MPa之间。并且在加载的最大应变范围内,q–ε1 曲线基本都没有达到平稳状态。表1列出了应变软化型砂土的峰值应力比
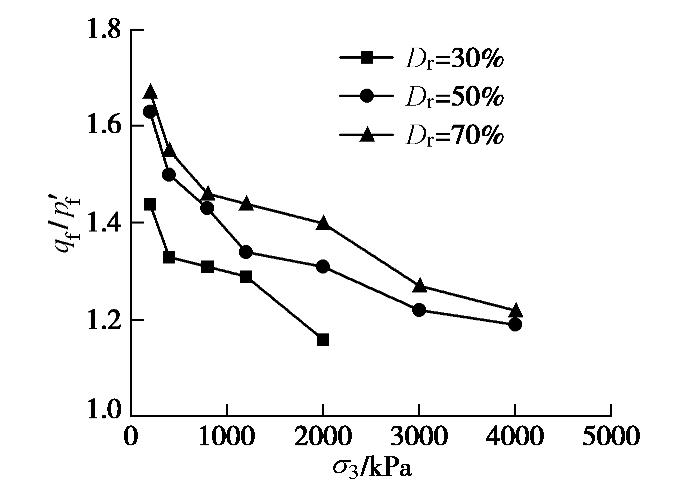
qf/ p′f ,p′f 为峰值有效平均主应力,同时绘制了不同密实度时qf/p′f -σ3 的关系曲线,如图3所示。由图3可知,砂样的峰值应力比受围压影响较为显著,随着围压σ3 增大qf/p′f 呈非线性减小,在常压范围(σ3 ≤0.8 MPa)内,qf/p′f 衰减速率较快,进入中压后(σ3 > 0.8 MPa),qf/p′f 减小速率放缓。2.3 体变–轴向应变关系
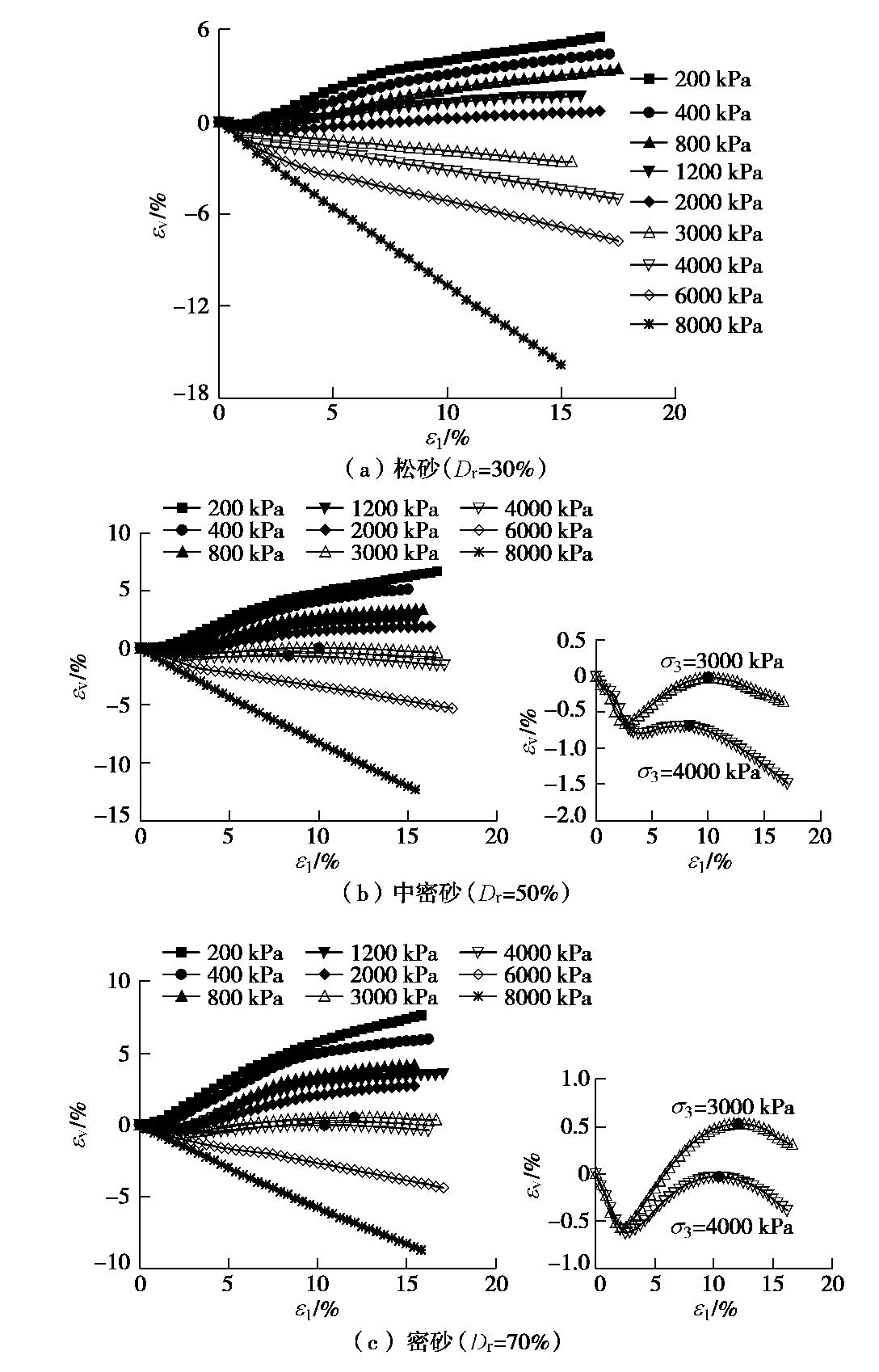
图4给出了3种相对密实度砂土试样的体应变
εv –轴向应变ε1 的关系曲线,其中体缩为负,体胀为正。可以看出,在常中压范围内(σ3 ≤2 MPa),剪切过程中3种密实度砂土试样的体应变变化规律相似,在剪切初期出现轻微的体积收缩,但随着轴向应变ε1 的增加,砂样体积开始膨胀,其剪胀性随着相对密实度增加和围压的降低而增强;松砂在σ3 ≥3.0 MPa时,剪切过程中试样体积始终收缩;中密和密砂在σ3 =3 MPa和4 MPa时,剪切过程中均出现了二次相变,即试样体积先收缩,然后膨胀,随着轴向应变继续增加,体积又开始收缩。中密砂在上述两围压时二次相变点对应的轴向应变分别为9.8%和8.3%;密砂的二次相变点对应的轴向应变分别为12.07%和10.4%,出现二次相变现象可能与颗粒破碎有关,在后面进行分析。在σ3 =6 MPa和8 MPa时,剪切过程中中密及密砂试样始终处于剪缩状态。3. 结果分析
3.1 颗粒破碎分析
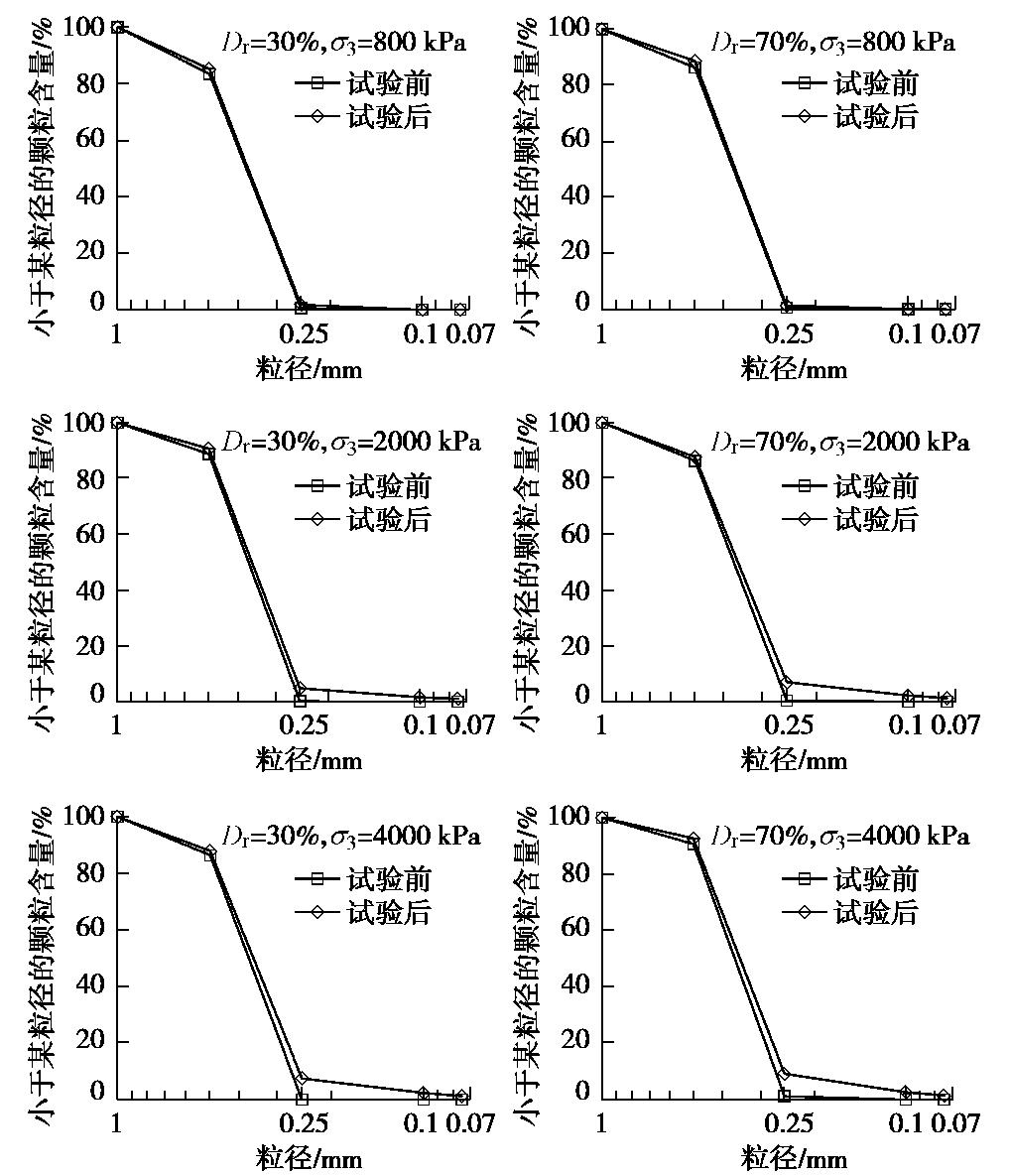
砂土在剪切过程中可能发生颗粒破碎,而颗粒破碎与初始相对密实度和围压有关。为探讨剪切试样是否发生颗粒破碎及颗粒破碎可能对抗剪强度的影响,对比了不同围压下试验前后砂样的颗粒级配曲线,图5仅绘出松砂(Dr=30%)和密砂(Dr=70%)在0.8,2及4 MPa 3种围压下试验前后的颗粒级配曲线。
由图5可以发现,常压范围内(
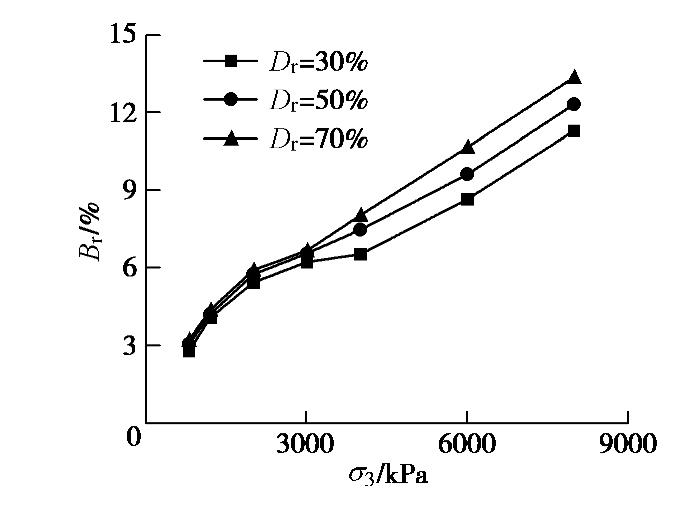
σ3 ≤0.8 MPa)砂土剪切完成后基本无颗粒破碎或存在少量破碎,中及高围压下(σ3 >0.8 MPa)剪切完成后(ε1 =15%~20%)颗粒破碎明显,并且颗粒破碎程度随着围压的增大而增大。不同围压和密实度下0.5~1 mm粒径的颗粒有11.3%~33.7%破碎;试验前粒径小于0.25 mm的颗粒含量小于0.8%,试验后,由于颗粒破碎,这部分粒径的含量明显增加,对于σ3 =8 MPa的密砂剪切后,含量增至12%,甚至出现少量的小于0.075 mm的粒径。为了定量描述颗粒破碎情况,采用Hardin[19]提出的相对破碎概念,即Br = Bt/Bp,Bt为破碎前颗粒级配曲线与破碎后颗粒级配曲线之间的面积;Bp为试验前颗粒级配曲线与粒径线0.074 mm之间的面积。图6给出密实度不同的试样在不同围压下剪切完成后的相对破碎。由图可见,相同围压下剪切,砂土越密颗粒破碎量越多;在
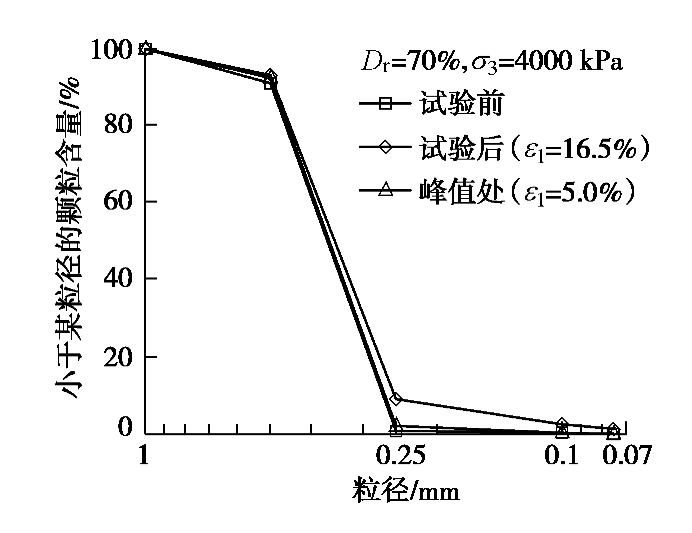
σ3 =0.8~2 MPa时,3种密实度砂土的相对颗粒破碎Br均增长较快;之后随着σ3 增加,Br增速放缓,当σ3 继续增加到某一更高围压时,颗粒破碎又出现较快的增长,对于松砂,该围压值为4 MPa,对于中密和密砂,该围压值为3 MPa。由于中密和密砂在σ3 ≥3 MPa时剪切后期出现了明显的颗粒破碎,颗粒破碎会使试样体积收缩,因此,中密和密砂在σ3 =3 MPa和4 MPa时轴向应变–体应变曲线出现了二次相变,即从体缩转向体胀,又转为体缩。为调查峰值强度时颗粒破碎情况,选择Dr=70%,
σ3 =4 MPa的试样在峰值强度处中止试验,对比峰值强度处、剪切试验前及试验后的颗粒级配曲线,如图7所示。由图可见,在峰值强度时,颗粒破碎量非常微小,由此可推断,对于表现为应变软化型的本文其它试样,在峰值强度时的砂样与初始试样的级配基本相同。3.2 围压及初始密实度对抗剪强度的影响
采用式(1)计算砂土破坏内摩擦角
ϕf ,其中(σ′1/σ′3)f 为破坏时主应力比,对于应变软化型,(σ′1/σ′3)f 为应力–应变曲线峰值点,ϕf 即为峰值内摩擦角ϕp ;对于应变硬化型,取ε1 =15%对应的应力比。sinϕf=(σ′1/σ′3)f−1σ′1/σ′3)f+1。 (1) 对于三轴试验,峰值剪胀角定义如下[16]:
sinψp=(dεv/dε1)max2−(dεv/dε1)max, (2) 式中,
dε1 为轴向应变增量,dεv 为体应变增量。峰值剪胀角为εv -ε1 曲线斜率最大处对应的值。由式(1),(2)计算得的砂土破坏内摩擦角和峰值剪胀角列于表2。
表 2 不同相对密实度砂土破坏内摩擦角和峰值剪胀角Table 2. Values ofϕf and ψp of sands with various relative densities围压σ3/kPa 破坏内摩擦角 ϕf /(°)峰值剪胀角ψp/(°) Dr=70% Dr=50% Dr=30% Dr=70% Dr=50% Dr=30% 200 39.95 38.84 34.21 19.07 16.96 12.11 400 37.65 36.40 33.14 17.17 15.36 11.01 800 36.13 35.13 32.33 15.33 12.25 9.91 1200 35.27 33.06 31.66 13.33 9.92 6.96 2000 34.53 32.56 28.91 9.66 8.70 4.23 3000 32.87 31.12 26.32 5.82 4.72 0 4000 31.20 30.49 25.72 4.90 3.92 0 6000 26.87 26.12 25.43 0 0 0 8000 26.08 25.60 25.19 0 0 0 由表2可知,对于围压
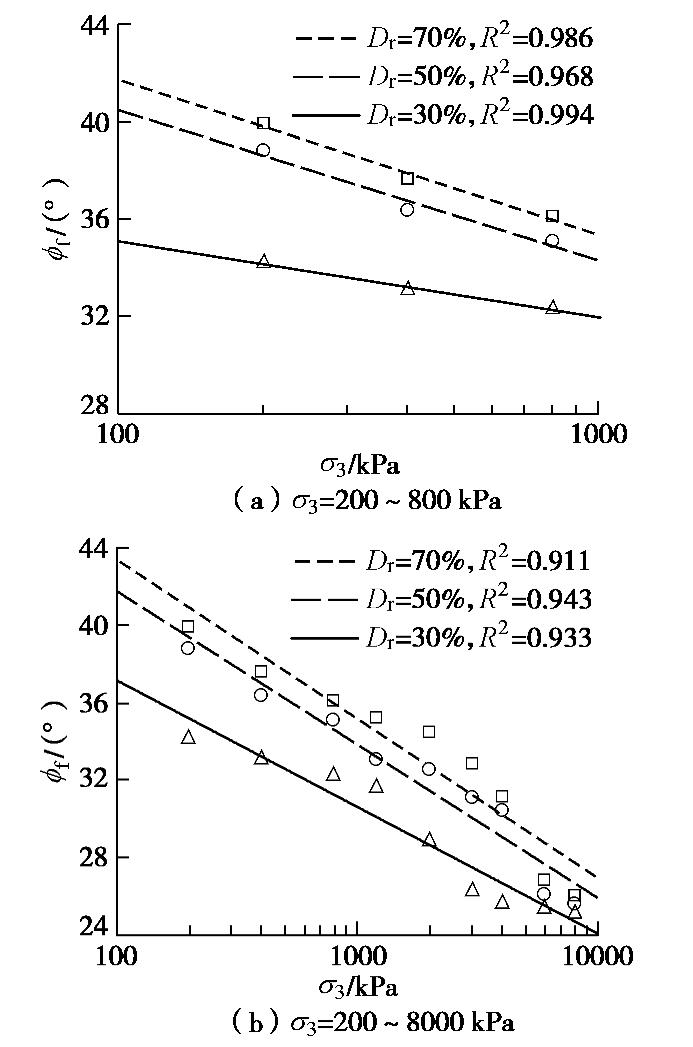
σ3 相同的试样,随着相对密实度Dr增大,砂样的破坏内摩擦角和峰值剪胀角逐渐增加;对于初始相对密实度Dr相同的砂样,随着围压σ3 的增加,砂样破坏内摩擦角和峰值剪胀角减小。图8分别绘制了常压范围(
σ3 ≤0.8 MPa)和常至高压范围(σ3 ≤8 MPa)的围压σ3 与破坏内摩擦角ϕf 的关系,横坐标为对数坐标。以线性关系进行拟合,发现对于3种密实度砂土ϕf 与lgσ3 均存在良好的线性关系,拟合度R2在0.9 以上。常压范围(
σ3 ≤0.8 MPa),3种相对密实度砂土的破坏内摩擦角ϕf 和围压σ3 关系:密砂:ϕf=54.41−6.34lgσ3 ,中密砂:ϕf=52.82−6.16lgσ3 ,松砂:ϕf=41.35−3.12lgσ3 。} (3) 常至高压范围(
σ3 ≤8 MPa)的拟合结果为密砂:ϕf=59.89−8.24lgσ3 ,中密砂:ϕf=57.61−7.91lgσ3 ,松砂:ϕf=50.23−6.55lgσ3 ,} (4) 式中,
σ3 单位为kPa。由图8可见,砂土密实度越大,随着围压增加,内摩擦角衰减越快,这与Hsu等[20]的结论一致。在常压范围内,对于松砂,围压lg
σ3 每增加1,ϕp 降低3.12°,中密及密砂降低6.16°和6.34°,这与Frydman等[9,21-22]文献的结果接近。Frydman[21]给出Caesaria风积砂(松砂)降低约3°,Dickin[22]给出Erith砂降低4°,Bolton[9]给出Sacramento河砂和Ottawa砂降低6°。从常至高压范围的拟合结果看,ϕf 随lgσ3 的减小速率较常压时增大;对于松砂,围压lgσ3 每增加1,ϕf 降低6.55°,中密及密砂降低7.91°和8.24°;这主要因为高压时ϕf 以ε1=15%确定,并且此应变时出现了明显的颗粒破碎,导致ϕf 偏低。3.3 临界状态内摩擦角及应力–剪胀关系
土体受剪切作用至体应变保持不变(零剪胀)时,土体达到临界状态,对应的内摩擦角为临界状态内摩角。三轴试验时,在剪切变形范围内,一般剪胀试样很难达到临界状态,常以剪缩反应获得临界状态[23]。实际上,由于三轴试验在大变形时,试样端部约束、膜嵌入和剪切带的形成等很难保证试样均匀变形,临界内摩擦角并不是很容易准确确定[3,14]。本三轴试验的加载范围内不同初始密实度和围压的砂样均未达到严格意义上的临界状态。临界状态内摩擦角是土体固有变量,一般认为土体临界状态内摩擦角不受初始相对密实度和围压的影响[8-9],其值唯一。
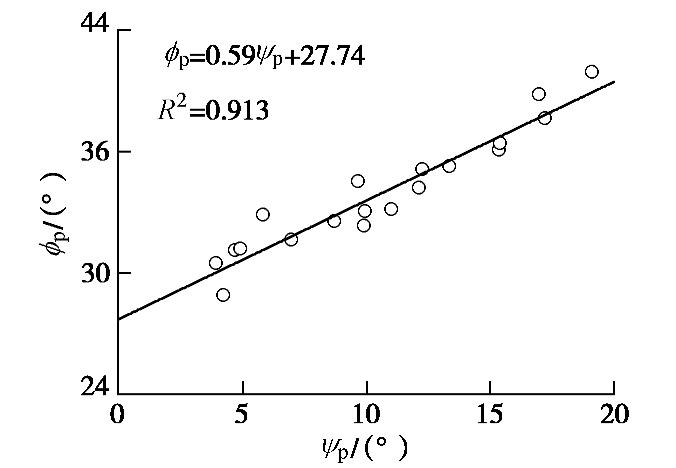
根据Bolton提出的峰值内摩擦角
ϕp 和剪胀角ψp的线性拟合关系,拟合线的纵轴截距即为临界内摩擦角ϕcv 。为获得临界内摩角,将不同初始密实度和围压的所有试验获得的ψp和ϕp 绘于图9(不包含ψp= 0°的试验数据),并用线性函数进行拟合,拟合度R2=0.913,拟合结果如下式,ϕp=0.59ψp+27.74。 (5) 拟合公式中,ψp=0°时,对应的内摩擦角为临界内摩擦角,即
ϕcv =27.74°。需要说明的是,ϕcv 由峰值强度ϕp 和ψp拟合确定,由前文调查,峰值处砂样基本未出现颗粒破碎,因此拟合确定的ϕcv 为试验初始砂样的临界内摩擦角。Bolton[9]提出剪胀指标IR的概念以反映砂土剪胀率和超出临界状态内摩角的剪切强度。IR表达式如下式:
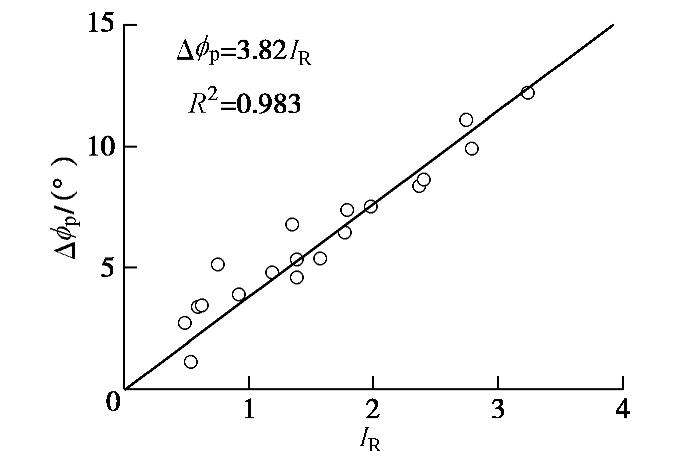
IR=−103(dεvdε1)max, (6) 其与峰值和临界状态内摩擦角差值Δ
ϕp 的关系如下式:Δϕp=ϕp−ϕcv=m IR, (7) 式中,
(dεv/dε1)max 为体应变εv与轴向应变ε1关系曲线斜率的最大值,m为无量纲参数。将各试样IR和Δ
ϕp 关系绘于图10,并用直线拟合,拟合斜率m=3.82,拟合度高达0.983,表明,对本试验砂土,剪胀指标IR每增加1,对应的峰值内摩擦角增加3.82°。土体剪胀性受相对密实度和有效约束应力水平的影响,Bolton等[9-10]将剪胀指标IR如下:
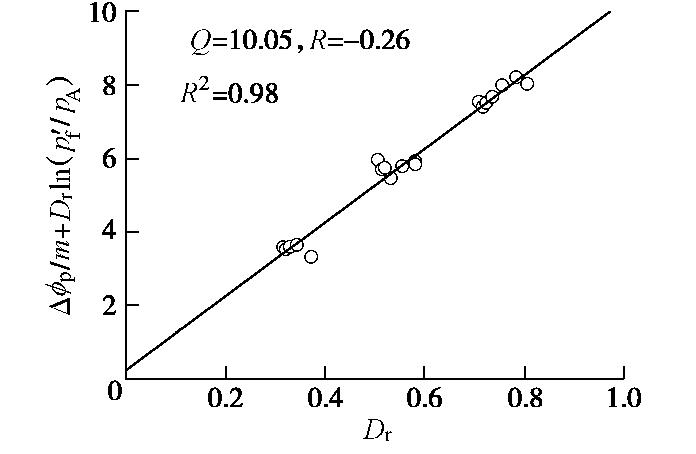
IR=Dr(Q−ln100p′fpa)−R, (8) 式中,
Q 和R为无量纲参数,pa 为标准大气压,p′f 为峰值时的平均有效应力。将式(7)代入式(8),得如下关系:
ϕp−ϕcvm+Drln100p′fpA=DrQ−R, (9) 根据式(9),绘制Dr与
Δϕp/m+Drln(100p′f/pA) 的关系,如图11所示,采用直线进行拟合,直线斜率和截距即为Q和R值。图11表明,直线拟合效果很好,拟合度为0.98,Q = 10.05,R = -0.26。故本试验砂土峰值内摩擦角与相对密实度和破坏平均有效应力的关系式为φP=3.82[Dr(10.05−ln100p′fpA)+0.26]+27.74。 (10) 对不同砂土和不同围压等级的三轴试验数据进行拟合得到Q,R值会有所不同。Chakraborty等[11]对已有低围压条件下(4~197.2 kPa)Toyoura砂三轴固结排水试验数据进行拟合分析,给出了不同围压下的Q值和R值,Q值在6.2~9.6范围内,R值在-0.23~0.8范围内;Salgado等[10]通过不同砂土的三轴试验给出常压下(100~400 kPa)不同粉粒含量Ottawa砂的Q值和R值,对于纯砂土Q = 9,R = 0.49,对于粉粒含量5%~20%的砂土,Q在7.3~11.4范围内,R值在-0.69~1.29范围内。将本文拟合结果与上面文献结果比较,本文包含常至高压试验数据拟合的Q值较常压和低压范围获得的Q值高;本文拟合的R值为负,R值的正负与临界内摩擦角有关,
ϕp 高于ϕcv 时拟合结果为负,ϕp 低于ϕcv 拟合结果为正[10],本文参与统计的试验曲线均为应变软化型(19个),ϕp 高于ϕcv ,峰值剪胀角ψp>0°,故拟合结果为负。4. 结论
本文对3种不同相对密实度砂土试样在常至高围压范围内进行了常规三轴固结排水剪切试验,研究了围压、密实度和颗粒破碎对土体强度、变形特性的影响,并建立了常压至高压下的应力–剪胀关系,获得的主要结论如下:
(1)在常至中压范围,试样的应力–应变曲线均表现出不同程度的应变软化,试样体积随轴向应变的增加开始膨胀,其剪胀性随着相对密实度增加和围压的降低而增强;当进入高围压范围(
σ3 >2 MPa)时,应力–应变曲线逐渐向应变硬化型转变,试样体积逐渐趋于剪缩,砂土越密实,开始表现为应变硬化型所需的围压越高。(2)在常压范围下(
σ3 ≤0.8 MPa)剪切完成后砂样基本无颗粒破碎或存在少量破碎,中及高围压下(σ3 >0.8 MPa)剪切完成后出现明显的颗粒破碎,并且颗粒破碎程度随着围压和密实度的增大而增大。在σ3 =3 MPa和4 MPa时,由于中密和密砂剪切后期出现了明显的颗粒破碎,导致剪切过程中出现了二次相变。(3)砂土密实度越大,随着围压增加,破坏内摩擦角ϕf衰减越快。常压范围时(
σ3 ≤0.8 MPa),对于松砂,围压lgσ3 每增加1,ϕf 降低3.12°,中密及密砂降低6.16°和6.34°;常至高压范围(0.2 MPa≤σ3 ≤8 MPa),松砂ϕf的衰减速率达到6.55,中密及密砂ϕf 衰减速率达到8°左右。(4)在常至高压范围内,基于Bolton应力–剪胀关系拟合确定了试验砂土的临界状态内摩擦角,建立了剪胀指标与初始相对密实度及平均有效应力的关系式,并确定了相关参数。本文试验结果可为常至高压情况下砂土地基稳定性分析等提供强度参数。
-
表 1 不同相对密实度砂土固结后孔隙比和峰值应力比
Table 1 Void ratios after consolidation and peak stress ratios of sands with various relative densities
围压/kPa 松砂 中密砂 密砂 e1 qf/p′f e1 qf/p′f e1 qf/p′f 200 0.637 1.44 0.601 1.63 0.562 1.67 400 0.636 1.33 0.600 1.50 0.561 1.55 800 0.634 1.31 0.598 1.43 0.560 1.46 1200 0.632 1.29 0.596 1.34 0.557 1.44 2000 0.626 1.16 0.592 1.31 0.553 1.40 3000 0.621 — 0.586 1.22 0.548 1.27 4000 0.615 — 0.581 1.19 0.544 1.22 6000 0.601 — 0.570 — 0.534 — 8000 0.589 — 0.560 — 0.526 — 表 2 不同相对密实度砂土破坏内摩擦角和峰值剪胀角
Table 2 Values of
ϕf and ψp of sands with various relative densities围压σ3/kPa 破坏内摩擦角 ϕf /(°)峰值剪胀角ψp/(°) Dr=70% Dr=50% Dr=30% Dr=70% Dr=50% Dr=30% 200 39.95 38.84 34.21 19.07 16.96 12.11 400 37.65 36.40 33.14 17.17 15.36 11.01 800 36.13 35.13 32.33 15.33 12.25 9.91 1200 35.27 33.06 31.66 13.33 9.92 6.96 2000 34.53 32.56 28.91 9.66 8.70 4.23 3000 32.87 31.12 26.32 5.82 4.72 0 4000 31.20 30.49 25.72 4.90 3.92 0 6000 26.87 26.12 25.43 0 0 0 8000 26.08 25.60 25.19 0 0 0 -
[1] 蔡正银, 李相菘. 砂土的变形特性与临界状态[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2004, 26(5): 697-701. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2004.05.025 CAI Zheng-yin, LI Xiang-song. Deformation characteristics and critical state of sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 26(5): 697-701. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2004.05.025
[2] 黄茂松, 姚仰平, 尹振宇, 等. 土的基本特性及本构关系与强度理论[J]. 土木工程学报, 2016, 49(7): 9-35. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2016.07.002 HUANG Mao-song, YAO Yang-ping, YIN Zhen-yu, et al. An overview on elementary mechanical behaviors, constitutive modeling and failure criterion of soils[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2016, 49(7): 9-35. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2016.07.002
[3] 李广信. 高等土力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004. LI Guang-xin. Advanced Soil Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2004. (in Chinese)
[4] BEEN K, JEFFERIES M G. A state parameter for sands[J]. Géotechnique, 1985, 35(2): 99-112. doi: 10.1680/geot.1985.35.2.99
[5] 陆勇, 周国庆, 顾欢达. 常压至高压下砂土强度、变形特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(11): 2369-2376. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0273 LU Yong, ZHOU Guo-qing, GU Huan-da. Experimental study of strength and deformation characteristics of sand under different pressures[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(11): 2369-2376. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0273
[6] 朱俊高, 史江伟, 罗学浩, 等. 密度对砂土应力应变强度特性影响试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(2): 336-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201602022.htm ZHU Jun-gao, SHI Jiang-wei, LUO Xue-hao, et al. Experimental study on stress-strain-strength behavior of sand with different densities[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 38(2): 336-341. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201602022.htm
[7] XIAO Y, LONG L H, EVANS T M. Effect of particle shape on stress-dilatancy responses of medium-dense sands[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2019, 145(2): 04018105. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001994
[8] ROWE P W. The stress-dilatancy relation for static equilibrium of an assembly of particles in contact[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1962, 269: 500-527.
[9] BOLTON M D. The Strength and dilatancy of sands[J]. Géotechnique, 1986, 36(1): 65-78. doi: 10.1680/geot.1986.36.1.65
[10] SALGADO R, BANDINI P, KARIM A. Shear strength and stiffness of silty sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE, 2000, 126(5): 451-462. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2000)126:5(451)
[11] CHAKRABORTY T, SALGADO R. Dilatancy and shear strength of sand at low confining pressures[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2010, 136(3): 527-532. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000237
[12] ESPOSITO M P III, ANDRUS R D. Peak shear strength and dilatancy of a pleistocene age sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE, 2017, 143(1): 04016079. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001582
[13] VAID Y P, SASITHARAN S. The strength and dilatancy of sand[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1992, 29(3): 522-526. doi: 10.1139/t92-058
[14] GUO P J, SU X B. Shear strength, interparticle locking, and dilatancy of granular materials[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2007, 44(6): 579-591.
[15] 土工试验方法标准:GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 2019. Standard for Geotechnical Testing Method: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 2019. (in Chinese)
[16] MARTIN B E, CAZACU O. Experimental and theoretical investigation of the high-pressure, undrained response of a cohesionless sand[J]. International Journal for Numerical & Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2013, 37(14): 2321-2347.
[17] 许成顺, 耿琳, 杜修力, 等. 反压对土体强度特性的影响试验研究及其影响机理分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2016, 49(3): 105-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201603012.htm XU Cheng-shun, GENG Lin, DU Xiu-li, et al. Effect of back pressure on shear strength of sand: experimental study and mechanism analysis[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2016, 49(3): 105-111. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201603012.htm
[18] 黄博, 汪清静, 凌道盛, 等. 饱和砂土三轴试验中反压设置与抗剪强度的研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(7): 1313-1319. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201207021.htm HUANG Bo, WANG Qingjing, LING Dao-sheng, et al. Effects of back pressure on shear strength of saturated sand in triaxial tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 34(7): 1313-1319. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201207021.htm
[19] HARDIN B O. Crushing of soil particles[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 1985, 111(10): 1177-1192. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:10(1177)
[20] HSU S T, LIAO H J. Uplift behaviour of cylindrical anchors in sand[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1998, 34: 70-80.
[21] FRYDMAN S. Pullout capacity of slab anchors in sand[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1989, 26: 385-400.
[22] DICKIN E A. Uplift behavior of horizontal anchor plates in sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 1988, 114: 1300-1317.
[23] SADREKARIMI A, OLSON S M. Critical state friction angle of sands[J]. Géotechnique, 2011, 61(9): 771-783.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 介玉新. Rowe剪胀方程及一种新的推导方法. 水力发电学报. 2024(01): 109-123 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李昌厚. 原状土强度与压缩特性试验研究. 科技资讯. 2024(21): 162-165 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈榕,武智勇,郝冬雪,高宇聪. 高应力下石英砂三轴剪切颗粒破碎演化规律及影响. 岩土工程学报. 2023(08): 1713-1722 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 王博,吕果,李江. 考虑粒径对砂土宏细观剪切性质的试验研究. 岩土工程技术. 2023(05): 618-622 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 高宇新,朱鸿鹄,张春新,刘威,王静,张巍. 砂土中锚板上拔三维物质点法模拟研究. 岩土工程学报. 2022(02): 295-304 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 刘先峰,马杰,袁胜洋,陈康,潘申鑫,郑立宁,胡熠. 干密度和含水率对压实红层泥岩路基填料强度特性的影响研究. 铁道科学与工程学报. 2022(10): 2910-2918 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 陈榕,孙鹤,郝冬雪,武智勇,高宇聪. 单粒组冻结砂土三轴压缩颗粒破碎规律研究. 岩土工程学报. 2022(S1): 92-97 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 于满满,杜佼蕾. 应用于强冻胀土的光伏支架基础方案分析. 太阳能. 2021(10): 52-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(12)



 下载:
下载: